Generality
Hyperacusis is a particular medical condition characterized by an extreme aversion and hypersensitivity to sounds which - for most people - are completely normal.

Doctors have long studied the possible causes of hyperacusis, but these, at the moment, still remain a mystery.
Patients' reactions to annoying sounds are different: there are those who feel a sense of growing anxiety, those who need to cover their ears, those who enter a state of panic, etc.
For now, there is no specific treatment for hyperacusis. The therapies that doctors use are the so-called sound therapy, suitable for the treatment of tinnitus, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
What is hyperacusis?
Hyperacusis is the medical term that indicates an extreme aversion and hypersensitivity to sounds which, as a rule, do not cause any discomfort to people.
There are varying degrees of hyperacusis. In fact, some patients are more sensitive than others and feel discomfort for sounds that, in the seconds, do not create any particular disturbance.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Hyperacusis can affect people of any age.
According to some recent statistical research, relating to the United Kingdom, it would affect between 7 and 23% of the adult population and between 12 and 27% of children.
Causes
Doctors have not yet established with certainty what the precise causes of hyperacusis are.
Up to now, in fact, they have only formulated a few theories, based on some experimental observations and nothing more.
HYPERACUSIA AND HEARING LOSS
A first theory associates hyperacusis with hearing loss.
According to supporters of this hypothesis, the brains of people with poor hearing amplify the sound signals entering the ear, compensating for the reduction of hearing abilities on the one hand, and causing discomfort to the affected subject on the other.
The criticisms of this theory mainly center around the fact that not all individuals with suboptimal hearing develop hyperacusis.
HYPERACUSIA AND PARTICULAR MORBID CONDITIONS
According to a second important theory, hyperacusis is a kind of symptom resulting from some medical conditions, including:
- Migraine. It is one of the most common primitive forms of headache. The primitive term referring to a medical condition means that the disorder does not depend on other diseases, but represents a problem in its own right.
A migraine attack The pain in the head, produced by migraine, has some particular characteristics: it is one-sided, throbbing and intense, and has a tendency to get worse.
- Lyme disease. Caused by the bacterium Borrelia Burgdorferi, is an infectious disease whose agent of transmission is the tick. From a symptomatic point of view, it usually affects the skin and quite frequently also the internal organs, joints and nervous system.
- Bell's palsy. It is a facial paralysis, which arises as a result of a dysfunction of the VII facial nerve. Its appearance involves muscle weakness or paralysis on one side of the face.
- Addison's disease. It is a rare morbid condition that arises due to a dysfunction of the adrenal (or adrenal) glands. Located just above the kidneys, healthy adrenal glands produce three types of hormones in their cortical portion: androgens, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids.
- Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmune diseases are characterized by an exaggerated and improper response of the immune system (the natural barrier that defends the organism from threats from the outside world, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc.).
For unclear reasons, in individuals with an autoimmune disease, the elements that make up the immune system (mostly cells and glycoproteins) attack perfectly healthy tissues and organs, causing even very serious damage. - The presence of tinnitus. Tinnitus are very annoying ringing in the ears, perceived in the absence of external sound sources. They can be continuous or intermittent and can arise as a result of certain events or circumstances (exposure to loud noises, hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.).
- Ménière's disease. It is a disease of the inner ear which, due to an alteration of the nervous signal between the ear and the brain, causes dizziness, nausea and hearing loss. Unfortunately, the symptoms tend to worsen over time and, at the present time, do not there is still a specific cure.
HYPERACUSIA AND STRONG EMOTIONS
According to a third theory, people may develop an "aversion to certain sounds when these have negatively characterized a" past life experience.
In other words, in these situations, the "hyperacusis derives from" associating a previous story with unpleasant contours to the sounds that have distinguished it.
According to the supporters of this theory, this would explain those cases of hyperacusis associated with the so-called post-traumatic stress disorder.
HYPERACUSIA AND DAMAGE TO THE STRUCTURES OF THE EAR
According to a fourth theory, a form of hyperacusis could arise after:
- A blow to the head or the so-called whiplash
- Ear surgery
- Persistent ear infections
- Prolonged exposure to loud noises
Symptoms
By symptoms and signs of hyperacusis, doctors mean the patient's reactions to sounds perceived as annoying.
Among these reactions, the most common are:
- Sense of growing anxiety
- Cry
- Panic
- Bad mood
- Need to cover your ears
- Need to leave the room
For the most severe cases of hyperacusis, the sounds towards which there is aversion and hypersensitivity turn out to be painful. In these situations, patients describe the sensation as "a nail sticking in the head" or as "sandpaper passed over the head". brain".
THE MOST DISRUPTING NOISE FOR CHILDREN
According to doctors' observations, in children with hyperacusis the sounds that can cause discomfort are:
- The barking of dogs
- Loud and loud laughter
- The screams
- The high-pitched whistles
- The sound of thunder
- The sound of fireworks and firecrackers exploding
- The noise of high-powered trucks, cars and motorcycles
- The ringing of the school bell or the loud buzz of voices that may occur in classrooms
- The sound of balloons bursting
- Ambulance sirens
- Distorted tonal tones of some musical instruments (for example, electric guitars)
- The ringing of the telephones
- The noise of lawn mowers, drills and floor cleaners
COMPLICATIONS

In addition, people with "hyperacusis to sounds that they usually hear in the workplace, may not sustain this situation for long and abandon their work. This can have repercussions, sometimes even very serious, on their finances.
Complications in children
Children with an "aversion to sounds that they usually hear at school, may lack the necessary concentration in the classroom, jeopardizing their academic progress and performance.
Diagnosis
Doctors find it difficult to distinguish a slight acoustic intolerance from an aversion with hypersensitivity to certain sounds. The reason is very simple: they have to rely exclusively on what the patient reports and on the degree of objectivity of the latter.
To achieve an accurate and correct diagnosis, some audiometric tests are fundamental, which are used to assess the degree of acoustic hypersensitivity.
WHAT DO AUDIOMETRIC TESTS CONSIST OF?
During the audiometric tests, the doctor makes the patient listen to sounds of increasing intensity, asking the patient to signal when the perceived noise becomes unbearable.
The audiometric assessments usually performed include: "tonal audiometry, the strapedial reflex test and the LDL test (where LDL stands for" Loudness Discomfort Level ", ie" acoustic intensity of the discomfort level ").
WHO IS THE DIAGNOSIS FOR?
Generally, for a correct diagnosis of hyperacusis, it is good to rely on an otolaryngologist or an audiometry specialist.
Treatment
Doctors have not yet been able to develop a specific therapy against hyperacusis; however, in the course of their experimental tests, they realized that the so-called sound therapy, adopted for the treatment of tinnitus, is able to reduce a certain degree of acoustic aversion and hypersensitivity is also satisfactory.
Furthermore, it is recently discovered that some particular cases of hyperacusis benefit from the so-called cognitive-behavioral therapy.
SOUND THERAPY: THE BASIC CONCEPTS
In the presence of hyperacusis, the aim of sound therapy is the acoustic desensitization of the patient. In medicine, the term desensitization refers to that "set of processes aimed at the decrease (or, at best, the resolution) of a state of abnormal sensitivity towards certain substances. In practical terms, these processes consist in administering to the patient doses progressively increasing of the offending substance (i.e. that towards which the patient himself is highly sensitive).
Clearly, in the case of an acoustic desensitization, the "substances" to be "administered in increasing doses" are annoying noises.
Please note: the desensitization technique is particularly indicated in case of allergies. In these situations, the term substance is appropriate, because it refers to the allergen to which the treated patient is hypersensitive.
SOUND THERAPY MODES AND TIMES
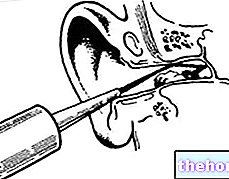
Sound therapy involves the application of a sound dispenser to the patient's ear.
This particular instrument can emit noises of adjustable intensity, which allows the desensitization treatment to be carried out with precision.
Exposure to annoying noises must occur daily: in the initial phase, the daily treatment hours range from 6 to 8; in the more advanced phase they can become even less than 6, provided however that the therapy proves effective.
Initially, the intensity of the noises emitted by the instrument is at levels that do not cause any discomfort to the patient. Moreover, if this were not the case, the treatment would be completely useless.
Acoustic desensitization for the treatment of hyperacusis lasts several months: in general, most patients must use the sound dispenser for 12-18 months.
SOME ADVICES
According to some research, they appear to have benefits:
- Relaxation and stress control techniques. According to many doctors, stress makes hyperacusis worse.
- Listen to relaxing music. It helps to reduce the stress of everyday life.
- Avoid using ear plugs. Ear plugs alter the perception of sounds and this could adversely affect sound therapy.
COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL THERAPY
The purpose of cognitive-behavioral therapy is to make the patient aware of the disease he suffers from in every aspect (symptoms, complications, etc.), in such a way that he can somehow master it. Typically, this particular treatment is reserved for mental illnesses; however, doctors have noted that it is also effective against hyperacusis characterized by strong crises of growing anxiety.