Generality
Misophonia is the term that indicates a form of acoustic intolerance, on the part of a person, towards specific noises emitted by third parties.

To the perception of sounds or noises towards which he is intolerant, the subject with misophonia can react in various ways: by feeling annoyance or discomfort, showing gestures of anger or irritability, becoming agitated, developing aggression, etc.
At the present time, there is no specific therapy against misophonia.
In fact, the treatments that doctors use are sound therapy - which is specifically indicated for the treatment of tinnitus - and cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy.
What is misophonia?
Misophonia is intolerance to specific sounds emitted by third parties (be it people or things).
Cause of negative emotional and physical reactions, misophonia is an alleged acoustic disorder, the subject of controversy among experts and not yet included in a specific pathological category.
Differences with hyperacusis
Misophonia is different from hyperacusis, which is the hypersensitivity to sounds which, as a rule, do not cause any discomfort to the human ear.
Hyperacusis is a recognized medical condition.
ORIGIN OF THE NAME
Misophonia is a word of Greek origin, the result of the union between:
- The term "misos" (μῖσος), which means "hate", and
- The term "fonos" (φόνος), which means "sound" or "voice".
So, literally, misophonia means "hatred of sound".
EPIDEMIOLOGY
According to some statistical surveys, at least 60% of people with tinnitus (or tinnitus) suffer from misophonia.
At the general population level, misophonia appears to affect around 20% of people.
Misophonia can affect people of any age, although it is good to underline that, for reasons that are still unclear, the subjects most at risk are prepubertal women.
Causes
There is still little clarity on the possible causes of misophonia.
Doctors and experts on the subject are inclined to believe that the disorder is, in some way, connected to a malfunction of the central auditory system (or apparatus) present at the level of the brain; while they exclude that at the origin there are specific problems of the ear (for example, at the level of the vestibular apparatus) or anatomical-structural alterations of the brain.
Symptoms and Complications
Symptoms of misophonia are behavioral responses to specific sounds and / or noises. Therefore, these sounds or noises can be considered as the so-called "trigger" of reactions and gestures of "intolerance."
The most common behavioral responses of misophonia consist of:
- Discomfort or discomfort
- Episodes of panic, sometimes even uncontrolled
- Episodes of anger
- Agitation
- Aggression and irritability
- Tendency to move away from the source of the sound towards which there is intolerance
- Anxiety attacks, with physical symptoms of fight-flight reactions (muscle tension, sweating, rapid heartbeat, etc.)
- Disgust
As for the so-called "triggers" of misophonia, the most common triggering sounds are:
- Oral sounds, such as eating, sipping a drink, kissing, sucking through a straw, swallowing food, nail biting, spitting, licking, flossing, chewing, scraping teeth on cutlery, brushing teeth, munching on crunchy foods , grind your teeth, crack your jaw etc.
- Voices with a nasal, buzzing, muffled or hissing tone, out-of-tune chants and vocal sounds emitted during the interjections "ah!", "Eh!", "Oh!" etc.
- The nasal sounds, that is, emitted by the nose. This category includes noises produced on the occasion of: deep breaths, snorting, snoring, breathing difficulties, congested breathing and hiccups.
Always remaining in this area, the nasal sound of yawning, sneezing and the act of "sniffing" deserve a special mention. - The sounds of animals. They can be objects of intolerance: the barking of dogs, the chirping of birds, the croaking of frogs, the lapping and whining of cats and dogs, etc.
- The sounds emitted with the movements of the body, such as: the cracking of the joints (ex: neck, hands, legs, etc.), the noise emitted by the nails hitting a table or the noise produced by certain types of footwear (ex: heels)
- The sounds made by young children, when they cry, stammer, scream etc.
- Ambient sounds, such as: cell phone ringtones, clocks ticking, dishes rattling, the noise of chainsaws, rustling or tearing of paper, the noise of lawnmowers, slamming of doors and windows , vehicle horns, too loud radio or TV volume, background noise emitted by refrigerators, computer keyboard noise, certain objects rubbing on certain surfaces, squeezing plastic bottles, etc.
COMPLICATIONS OF MISOPHONIA
In extreme cases, misophonia can affect the social sphere, with the affected person avoiding certain places, the workplace, school, family environment, etc., in order not to hear the annoying sound, which causes symptoms of intolerance. .
From this, the complications that can derive are mainly two: tendency to isolation and difficulty in establishing and / or maintaining interpersonal relationships.
ASSOCIATED CONDITIONS
For reasons still unknown, many people who manifest the symptoms of misophonia suffer from: the so-called obsessive compulsive disorder, the so-called obsessive compulsive personality disorder, various forms of depression, bipolar disorder, Tourette's syndrome, anxiety disorders or disorders food.
Diagnosis
For a correct diagnosis of misophonia, the following are essential: the "physical examination, a questionnaire relating to the so-called" triggers "of intolerance reactions and, finally, the tests that allow to exclude all those recognized medical conditions, responsible for similar symptoms ( differential diagnosis).
It is during the diagnostic phase that whoever visits the patient realizes if the latter also suffers from tinnitus.
What is tinnitus, also known by the plural term of tinnitus?
The term tinnitus defines an annoying ringing in the ears, in the absence of external sound sources.
On some occasions, tinnitus is a temporary and totally reversible phenomenon; in other situations, however, it constitutes an almost recurrent, almost disabling disorder, which can also have negative repercussions on normal daily activities.
WHO TAKES CARE OF THE DIAGNOSIS?
Various specialists have the necessary skills in identifying misophonia, including: doctors with expertise in audiology, psychiatrists, speech therapists and psychologists.
SOME DETAILS ABOUT THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
The conditions under observation during the differential diagnosis include: hearing loss linked to aging, hyperacusis and disorders that cause acoustic hallucinations.
Treatment
Also complicit in the uncertainties surrounding the problem, doctors and audiology experts have not yet developed a specific therapy against misophonia. However, in the course of their numerous experimental tests on patients, they were able to note, curiously, that the so-called sound therapy, adopted for the treatment of tinnitus, is useful to improve the level of tolerance of certain sounds and reduce the degree of intolerance.
Furthermore, it is quite recently discovered that some particular cases of misophonia also benefit from cognitive-behavioral therapy, which is a very common technique of psychotherapy.
SOUND THERAPY: THE BASIC CONCEPTS
The purpose of sound therapy, also known as TRT (Tinnitus Retraining Therapy) is the acoustic desensitization of the patient. In medicine, the term desensitization refers to that "set of processes aimed at the decrease (or, at best, the resolution) of a state of abnormal aversion / sensitivity towards certain substances.
In practical terms, these processes consist in administering to the patient progressively increasing doses of the offending substance (ie the one towards which the patient is highly sensitive), in such a way as to trigger an adaptation process.
Clearly, in the case of acoustic desensitization for the treatment of misophonia, the "substances" to be "administered in increasing doses", in order to reduce intolerance and accustom the ear to hearing them, are annoying and unbearable noises and sounds.
Please note: the desensitization technique is particularly indicated in case of allergies. In these situations, the term substance is appropriate, because it refers to the allergen to which the treated patient is hypersensitive.
MODES AND TIMES OF SOUND THERAPY
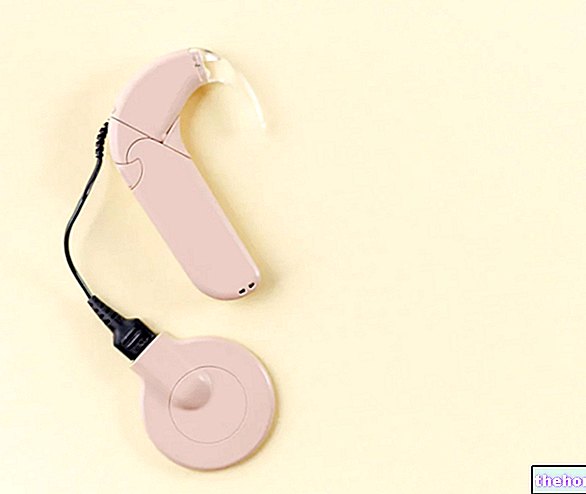
Sound therapy involves the application of a sound dispenser to the patient's ear.
This particular instrument can emit noises of adjustable intensity; the possibility of adjusting the sounds allows the desensitization treatment to be carried out with precision.
Exposure to annoying noises must occur daily: in the initial phase, the daily treatment hours range from 6 to 8; in the more advanced phase they can become even less than 6, provided however that the therapy proves effective.
Initially, the intensity of the noises emitted by the instrument is at levels that do not cause any discomfort to the patient. Moreover, if this were not the case, the treatment would be completely useless.
COGNITIVE-BEHAVIORAL THERAPY
The purpose of cognitive-behavioral therapy is to educate the patient about the disorder he is suffering from, so that he can somehow master it.
Typically, this particular treatment is reserved for mental illnesses (as mentioned, it is a psychotherapy technique); however, doctors have noted that it is also effective against various hearing disorders - including misophonia and hyperacusis - characterized by increasing panic attacks and anxiety disorders.
ARE THERE ANY DRUGS EFFECTIVE AGAINST MISOPHONIA?
Several doctors have tested different classes of drugs on people with misophonia, with the intent to understand if there was one or more drug substances capable of having any therapeutic effect.
These trials did not produce the desired results. Therefore, from a pharmacological point of view, misophonia is not curable.
Medicines tested for the treatment of misophonia include: anxiolytics, antidepressants and dietary supplements based on vitamins, minerals or fish oil.
Prognosis
According to reliable statistical studies, with the appropriate treatments, 80% of people with misophonia recover from the disorder, without relapses.
Thus, in general, the prognosis for misophonia tends to be more than positive.
To get good results, it is important to act promptly and before the condition becomes complicated.
Prevention
At the present time, doctors are unaware of whether there is a way to prevent misophonia. They certainly agree that prompt treatment of misophonia avoids the resulting complications.