Although it is certain that celiac people are more prone to suffer from thyroid diseases, it is difficult to provide precise percentages, given the discord between the various epidemiological data that prevent the exact relationships between the two diseases to be established.
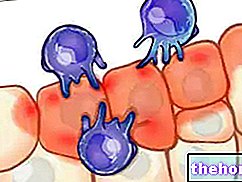
and subclinical hyperthyroidism related to autoimmune thyroid diseases that escape some studies due to serological findings within the normal limits.Although in these celiac patients the TSH and thyroxine (T4) values are within the normal range, it is often possible to highlight a positivity to the dosage of anti-thyrooglobulin and anti-thyroxine antibodies, which testify to an increased risk of developing pictures of hypo- or hyperthyroidism associated with thyroid diseases. autoimmune.
It should also be stressed that the association between celiac disease and autoimmune thyroid disease is not consequential; this means that autoimmune diseases of the thyroid can be diagnosed both before and after the detection of celiac disease.
Considering the link, albeit unstable, between the two diseases, the opposite is also valid, ie the increased risk of celiac disease in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis compared to the general population.
Therefore, in these subjects there will be a higher percentage of positive test for Ab-anti-tTG (anti-transglutaminase antibodies) and EMA (anti-endomysium antibodies).
For the same reason, a gluten-free diet appears to be able to positively influence the course of these thyroid diseases, but there are exceptions highlighted by numerous studies that express a contrary opinion on the matter.
Therefore, it is not yet clear whether and to what extent autoimmune thyroiditis in celiac patients depends on the duration and intensity of gluten exposure, and vice versa.
In the case of hypothyroidism associated with celiac disease, for example, it has been seen how a gluten-free diet allows in many cases to reduce the dosage of replacement therapy with L-thyroxine; this effect could however be mostly due to the better intestinal absorption of the drug, deriving from the restoration of the normal structure and functionality of the enteric mucosa.
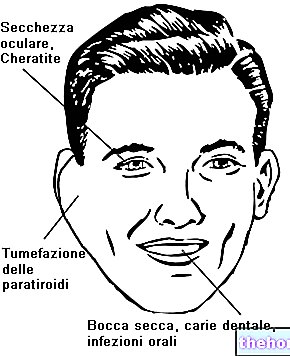
and TSH to investigate thyroid function.These investigations are particularly important for celiacs in whom the presence of antithyroid autoantibodies has already been detected.
;