What is Diabetes
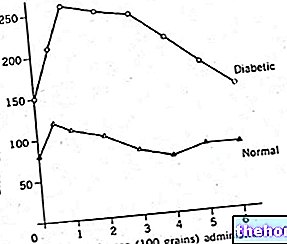
Diabetes is one of the most common endocrine diseases in industrialized countries: it is a pathology characterized by hyperglycemia, therefore by the "increase in sugars in the blood; it is caused by a reduced insulin secretion by the pancreas, which is often associated with" increased resistance of peripheral tissues to the action of insulin itself.

Symptoms
The characteristic signs of the disease and the diabetic symptoms can be summarized as follows:
- Hyperglycemia;
- Polyuria: need to urinate more times than normal;
- Polyphagia: excessive hunger, therefore desire to eat in an exaggerated way;
- Polydipsia: need to drink higher than normal;
- Glycosuria: presence of sugar in the urine.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is a multifactorial disease and can be divided according to the etiology into 5 different types:
- TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS: in this type of diabetes we have a destruction of the beta cells of the pancreas, which are those that produce insulin. This destruction can be on an autoimmune basis, in which case the antibodies recognize the insulin-secreting pancreatic cells as non-self, or on an idiopathic basis, that is, not related to a "certain etiology, however excluding the autoimmune one. This diabetic picture, being insulin-dependent. , and having an onset at a young age, it is more severe than the other forms.
- TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: Diabetes is characterized by hyperglycaemia due to "impaired insulin secretion by the pancreas and / or the development of insulin resistance (normal insulin production with deficiency of specific receptors for this hormone). Type 2 diabetes is prevalent in adulthood, it can be favored by an "unregulated diet and a sedentary lifestyle; it is often associated with a picture of obesity.
- MODY (Maturity Onset of the Diabetes of the young): Mody is due to a series of genetic alterations in the pancreas, which determine a deficit in the function of beta cells; it is serious but represents a fairly rare pathology.
- SECONDARY DIABETES MELLITUS: Diabetes, in addition to having an immune, dietary and genetic basis, can be a consequence of certain pathologies that affect the endocrine system, or the intake of drugs that act at the metabolic level. Some examples: diseases of the exocrine pancreas; endocrinopathies (Cushing's syndrome, pheochromocytoma and hyperthyroidism); use of drugs such as glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, beta-blockers and thiazides; some types of infections (cytomegalovirus); genetic pathologies (Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Huntington's chorea);
- PREGNANT DIABETES: with an "incidence of 2-5% of pregnancies, some pregnant women develop diabetes mellitus, which - although it represents a transient and easily treatable condition - if underestimated, can compromise the health of the fetus and newborn (excessive weight at birth can be one of the consequences).
Complications
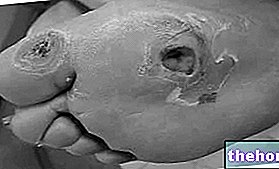
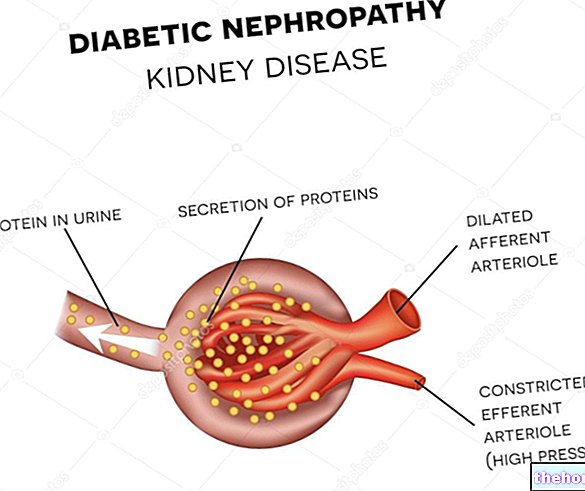
Diabetes represents a real health problem, since in the long term it can lead to very serious complications, especially at the level of the circulatory system, but not only: atherosclerosis, diabetic glomerulopathy (kidney), diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy and ulcer diabetic are just some of the associated pathologies.
Treatment
First let's talk about the natural remedies they can help in the treatment of diabetic pathology it is necessary to specify and emphasize that this is a serious disease which, as such, must be treated effectively with adequate drug therapy and a correct lifestyle.
Since diabetes is a disease linked to glucose metabolism, the first factor that must be corrected in affected subjects is nutrition: it is necessary to moderate the consumption of carbohydrates without completely eliminating them, but reducing their daily intake and avoiding the intake of sugars. simple (representing an immediate form of glucose). In addition, for people predisposed to forms of hyperglycemia there are some rules that must be absolutely respected: avoid being overweight and eat regular meals throughout the day. To avoid excessive consumption of carbohydrates, it is necessary to: increase the intake of whole grains and starchy foods rich in fiber; consume fresh vegetables and fruit (avoid dried and very sweet fruit such as grapes and figs), but also eggs, fish and white meats to ensure an adequate protein intake; eliminate or drastically reduce alcohol consumption and limit consumption of salt and salty foods.
After having corrected the diet, one must act on the level of physical exercise (when other pathologies do not prohibit it), in order to prevent the risk of cardiovascular pathologies.
Drugs for Diabetes
Traditional Pharmacological Therapy
Type 1 diabetes requires daily administration (even several times a day) of insulin, through subcutaneous injections or through the use of pumps (insulin pumps); type 2 diabetes, which is not insulin-dependent, requires treatment with drugs capable of to act on blood sugar and insulin production. The drugs mainly used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes are:
- SULFANILUREE (Glibenclamide; Glipizide; Tolbutamide; Chlorpropamide; Glimepiride): this class of drugs stimulates the release of insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas, reduces serum glucagon levels and increases the binding of insulin to target receptors. Side effects: hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal disturbances, itching, nausea, anemia.
- BIGUANIDES (Metformin; Phenformin): these drugs do not stimulate insulin secretion but increase the insulin sensitivity of target tissues. Side effects: lactic acidosis, diarrhea, metallic taste, anorexia.
- ALPHA-GLUCOSIDASE INHIBITORS (Acarbose; Miglitol): drugs that inhibit the alpha-glucosidase present on the intestinal brush border, consequently reducing the absorption of sugars. Side effects: flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal cramps.
Other articles on "Natural Remedies and Herbal Teas for Diabetes"
- Medicinal plants and diabetes
- Herbal teas and diabetes