"Gestational diabetes
Risks and Complications
As anticipated, in the presence of gestational diabetes there is no risk to the life of the child, but it is still important to better control the glycemic values to avoid complications.
Among these, the best known and most widespread is called macrosomia, which is an excessive development of the fetus compared to its gestational age, with a birth weight greater than 4-4.5 kg.
The reason for this excess weight is to be found in the large availability of glucose (sugar) linked to maternal hyperglycemia.

Poor metaboyl control of gestational diabetes can give rise to hypertensive complications and facilitate the onset of maternal diabetes in the postpartum period. Women with GDM in fact constitute a population at high risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the following years: for both these two forms of diabetes the most important risk factors are similar, such as obesity, visceral distribution of adipose tissue and family history of diabetes.
Macrosomia, like the opposite condition, seems to increase the risk of obesity and its late complications (type II diabetes, atherosclerosis, hypertension) in childhood and later age groups.
As anticipated in the introductory part, gestational diabetes does not normally involve abortion or malformations, however possible in the event that chronic hyperglycemia is already present at the moment of conception but still in the dark about the pregnant woman and the medical staff. All this contributes to underline the importance of a pre-conception visit when pregnancy is still sought.It is clear that even a diabetic woman can carry out a pregnancy with serenity and without any complications, but it is essential that conception is preceded by a preventive medical consultation and optimal control of diabetes before, during and after pregnancy. Conception and the very first weeks of gestation, in particular, must take place in a situation of perfect glycemic control.
Care and Prevention
After diagnosis, the goal of treatment is adequate glycemic control. In this regard, the recommended reference glycemic levels are as follows:
In this sense, the daily self-monitoring of blood glucose, as prescribed by the doctor, is particularly important. Usually, a correct dietary setting allows you to keep blood sugar within the limits considered "optimal" for pregnancy. When this does not happen, It is possible to achieve optimal blood sugar levels by resorting to small insulin injections, following with the utmost care what is prescribed by the doctor.
For further information: Medicines for the Treatment of Gestational Diabetes "
Importance of lifestyle
Despite this possibility of resorting to pharmacological help, dietary therapy and physical activity remain the cornerstone of treatment. This intervention strategy aims to improve the behavioral habits of the woman, who must try to maintain them even in post partum.
Postpartum monitoring
In the absence of weight control interventions, associated with proper nutrition and proper physical activity, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the span of a few years from a pregnancy marked by gestational diabetes is in fact quite concrete, estimated at 50% - after a decade - for seriously overweight women (compared to 25% of non-obese women). This possibility justifies the recommendation to undergo a test 6-8 weeks after childbirth, or in any case after breastfeeding. control glucose load.
If the results are negative, the examination will still be repeated after two or three years, with particular attention of a preventive nature when a new pregnancy is sought; the risk that gestational diabetes recurs on this occasion is around It is also advisable to periodically monitor blood pressure and blood levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol and HDL, especially in the presence of severe overweight.
Diet
As regards food hygiene rules, in the presence of gestational diabetes the general recommendations recommended for normoglycemic pregnant women are valid, with renewed attention to the reduction of sugars in favor of complex carbohydrates; the former are generally contained in sweets and sugary drinks (including many industrial fruit juices), while the latter are abundant in legumes and cereals, such as pasta, bread and rice (which must however be consumed in moderation). Further advice is available in the articles on the site dedicated to the combination of nutrition and pregnancy (see also: diet in pregnancy).
In general, the diet will be healthy and varied, adapted to the nutritional needs of the mother and child, which change - for example - in relation to the maternal weight recorded before pregnancy.
Height
Weight
Physical activity
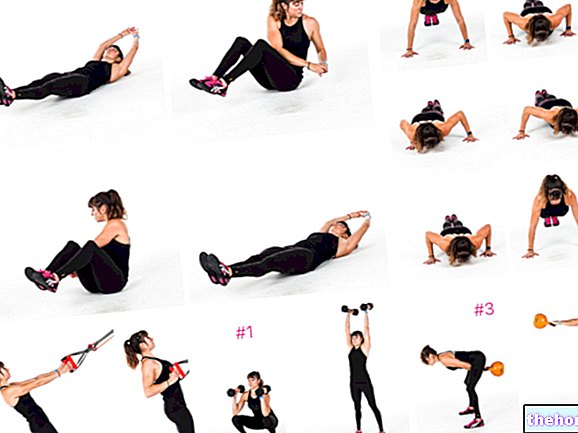
As regards the relationship between physical activity and gestational diabetes, it has been shown that in the absence of contraindications, 30-40 minutes of aerobic activity (for example walking briskly for a few km), with a daily frequency or at least three times a week, significantly improve the values postprandial and fasting glycemic levels.
Water activities are especially indicated in the third trimester of pregnancy and in the presence of circulatory problems in the lower limbs. All this, obviously, without exaggerating, preferring constancy and duration to intensity (breathlessness and breathlessness must not occur).
Other articles on "Gestational Diabetes: Risks, Cures, Prevention"
- Gestational diabetes
- Gestational Diabetes - Medicines for the Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
- Diet and Gestational Diabetes