Bruxism is a more marked phenomenon during sleep and is caused by the involuntary contraction of the muscles involved in chewing; it is considered an "anomalous activity not aimed at a purpose, otherwise called parafunction.
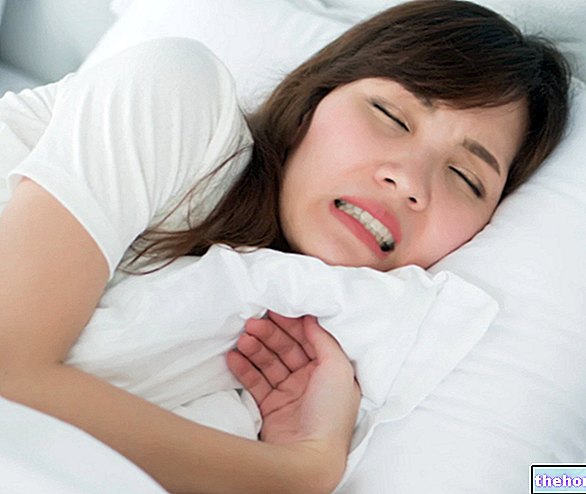
Bruxism consists of a rubbing associated with an involuntary and violent clenching of the teeth of the two arches, lower and upper. This phenomenon can sometimes be noisy and annoying, not so much for those who perform it - who often do it without realizing it - but for those close to them.
and jitters;The abuse of alcohol, drugs or smoking could also be factors involved in the onset of bruxism. Furthermore, it is believed that the development of this problem can also be favored by a certain family predisposition.
When children grind their teeth, the triggering cause could be found in the presence of inflammation of the ear (otitis) or disorders of the teeth (pain in the teeth); in such situations, bruxism could represent an attempt, unconscious and probably in vain, to reduce the painful stimuli perceived by the child. Of course, the cause of bruxism in children could also be of another nature and very often, as with adults, it can only be determined with the help of a doctor.
; in other words, the "clenched teeth" position is maintained in a static way, without carrying out a real grinding.
Furthermore, according to some specialists, even simple dental contact - without clamping or grinding - could represent an initial form of bruxism. In fact, in normal resting conditions, the two dental arches should not come into contact and the chewing muscles should be relaxed. Even the slightest contact between the teeth causes a contraction of this group of muscles and exposes the individual to a potential risk of developing "real" bruxism in the presence of predisposing conditions (for example, stress, anxiety, etc.).