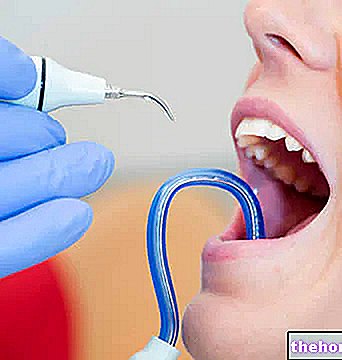
Excessively sensitive teeth cause the perception of sharp and stinging painful stimuli. Although brief, these events are perceived with considerable violence.
Hypersensitivity occurs during contact of the teeth with sweet, acidic, hot or cold foods, or during very energetic brushing (cleaning) and chewing.
The causes can be different and of a physiological or pathological type. Treatment differs according to the triggering agent.
The published material is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of Sensitive Teeth; such indications must in no way replace the opinion of the treating physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
.
- Caries;
- Dental trauma;
- Bruxism wear
- Exposure of the roots of the teeth and presence of periodontal pockets.
- The correct brushing technique requires that the movement be vertical (for both sides of the arches), never horizontal. It starts from the collar of the teeth and proceeds towards the apex, without crossing over into the opposite arch.
- Only on the chewing surfaces of premolars and molars is a horizontal movement applied.
- The optimal cleaning frequency is after each meal.
- Type of dental floss: it can be waxed or unwaxed, depending on the use (removal of tartar or plaque, close or crooked teeth, etc.). It is necessary to be very careful not to injure the gums by making them bleed.
- Type of toothbrush: the most effective is a short head, equipped with soft bristles of variable length.
- Consume low acid foods.
- Brush your teeth at least half an hour after a meal and not immediately, to avoid the action of acids contained in food.
- Use mildly aggressive toothpastes.
- Treat any gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Avoid self-induced vomiting (typical of some eating disorders, such as bulimia nervosa and anorexia nervosa).
- Prevent rubbing between the teeth induced by night grinding thanks to the use of a bite.
- Breaking down hard and stubborn foods.
- Using your teeth to cut, break or squeeze objects.
- Wrong cleaning operation.
- Consume foods that can mechanically damage them.
- Eat lots of acidic foods.
- Brush your teeth immediately after meals.
- Use very aggressive toothpastes and whitening treatments.
- Neglecting GERD regurgitation.
- Neglect the night grinding.
- Low in carbohydrates and simple sugars. Obviously, it is not advisable to follow a low-glucose diet with the sole intent of preventing tooth decay.
- With non-cariogenic sugar alcohols: some are synthetic, such as xylitol, and are used to sweeten food and chewing gum.
- Sugar-free and xylitol chewing gums can also help clean your teeth.
- Foods rich in calcium and phosphorus: these two minerals are contained in large part in milk and derivatives. They are natural constituents of hydroxyapatite, an essential material for bones and teeth.
- Foods rich in fluoride: it is necessary for the structuring of the external enamel of the teeth. They contain a good amount of it: peach products, wine, tea, fruit juices etc.
- Food and drink at room temperature.
- Non-acidic foods and drinks.
- Food and drink not at all or not very sweet and not sticky.
- Excessively rich in carbohydrates: all carbohydrates fermentable by bacteria are predisposing to the onset of caries. Even complex ones, consisting mainly of starch, play a fundamental role. In all, the glycides should represent approximately 45-60% of the total energy.
- Excessively rich in simple sugars: they are the most harmful and are found in all sweets but also in fruit. A small part is hidden in the vegetables. The total amount should be between 10-16%.
- Oily seeds in shell: hazelnuts, walnuts, pistachios, almonds, pine nuts etc.
- Fruit with seeds or seeds: they can be chewed by mistake (seeds of plums, cherries, papaya, etc.) or voluntarily (seeds of kiwis, grapes, etc.).
- Shellfish: in some recipes, such as spaghetti with seafood or seafood soups, it may happen that the shell of bivalve molluscs (mussels, clams, oysters, etc.) or gastropods (sea snails) breaks and ends up in the hollow oral.
- Meat on the bone: Biting into the bone can break the teeth. This is the case of: ribs, Florentine, pancetta and coppone with bone, chops, etc.
- Very hard foods: the most striking case is made up of crunchy almonds or dried chestnuts.
- Cold foods and drinks: ice cream, ice lollies, slushes, milkshakes, smoothies, frozen desserts, desserts and cakes from the fridge, water and other drinks etc.
- Hot food and drinks: broth, fried, roasted on the grill, hot chocolate, tea, herbal teas etc.
- Acidic foods and drinks: cola, orangeade, soda, juices, natural fruit juices, lemonade, vinaigrette and citronette-based dressings, citrus desserts (grapefruit, lemon) etc.
- Sweet foods and drinks: candy, hazelnut spread, honey, condensed milk, spoon desserts, jam, packaged fruit juices, caramel, marshmallows, meringues, etc.
dental.
- With appropriate frequency and intensity.
- In a technically correct way.
- With an intact and suitable toothbrush.