Definition
Among the highly disabling rheumatic diseases, ankylosing spondylitis plays an important role: we are talking about a systemic and autoimmune pathology, with a chronic course, which involves the spine and the musculoskeletal system. Degenerating, Ankylosing Spondylitis can lead to a real fusion of the joints.
Causes
The cause of ankylosing spondylitis lies in a "genetic abnormality (HLA-B27 gene and HLA-B7 gene). Ankylosing spondylitis is an almost exclusively male disease.
Symptoms
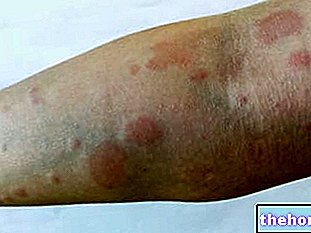
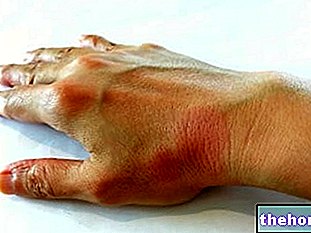
A sufferer of ankylosing spondylitis often complains of pain and stiffness in the back, especially in the morning and in moments of inactivity. As the disease progresses, back pain gradually worsens and the damage extends to multiple points of the spine, with changes in the spine and difficulty in movement.
- Complications: cardiovascular changes, anemia, low-grade fever, pulmonary fibrosis, aortic insufficiency, Crohn's disease, acute uveitis
The information on Ankylosing Spondylitis - Drugs for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Ankylosing Spondylitis - Drugs to Treat Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Medicines
Unfortunately, the initial vague and vague symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis can delay diagnosis; the disease, discovered in the advanced stage, is not reversible, consequently there is no drug capable of reversing the disease.
In general, the goal of treatment is to reduce pain and, when possible, to correct any damage and deformity affecting the spine and joints.
For pain control, the most commonly used drugs in therapy are anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and some corticosteroids, to be taken orally or intravenously.
The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against ankylosing spondylitis, and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the most suitable active ingredient and dosage for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment:
- Ibuprofen (eg Noan, Vatran, Pedea) Indicatively, for the control of pain associated with ankylosing spondylitis, it is recommended to take 400-800 mg of active, every 6-8 hours, as needed. It is also possible to take the drug intravenously (400-800 mg / 30 minutes every 6 hours, as needed). Indicated to treat the painful symptoms that accompany the mild forms of ankylosing spondylitis.
- Diclofenac (eg Fastum, Dicloreum): for the control of mild pain associated with ankylosing spondylitis (early stage), it is recommended to take 25 mg of active, 4 times a day. Follow the instructions given by the doctor.
- Celecoxib (eg Onsenal): selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase II. For the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, it is recommended to take the drug orally, at a dosage of 200 mg, in a single intake or in two divided doses. If, after a 6-week treatment, the patient does not find any benefit, the dose can be increased up to 400 mg per day Alternatively, change therapy.
- Prednisone (eg. Deltacortene, Lodotra): corticosteroid drug used in therapy to reduce inflammation, even in the context of ankylosing spondylitis. Prolonged treatment with steroids can cause serious side effects, such as diabetes, osteoporosis and cataract. Indicatively, the dosage includes to take 5-60 mg of the drug, divided into 1-4 doses per day.
- Paracetamol (eg. Acetamol, Tachipirina): to alleviate the pain associated with mild ankylosing spondylitis, paracetamol exerts a moderate therapeutic action. Remember that the drug is not an anti-inflammatory. Take the drug orally in the form of tablets, syrup, effervescent sachets or suppositories; it is recommended to take paracetamol at a dosage of 325-650 mg every 4-6 hours for 6-8 consecutive days, to lower the fever, which is often associated with ankylosing spondylitis. It is also possible to take the drug intravenously: 1 gram every 6 hours or 650 mg every 4 hours for adults and adolescents who weigh more than 50 kilos: if the patient weighs less than 50 kilos, administer 15mg / kg every 6 hours or 12 , 5 mg / kg every 4 hours. Consult your doctor.
- Sulfasalazine (eg. Salazopyrin): anti-inflammatory-immunomodulatory drug indicated to treat the symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis involving peripheral joints. As an indication, take 500 mg of the drug in the first week of treatment; the dose must be increased gradually: in the second week it is possible to take 500 mg of active substance twice a day, while in the third week of treatment it is recommended to take 500 mg orally in the morning, followed by 1000 mg in the evening. The maintenance dose, on the other hand, involves taking 1000 mg of the drug orally, twice a day. If the patient does not report benefit after 3 weeks of therapy, it is possible to increase the dose of the drug up to a maximum of 3 grams per day. Consult your doctor.
- Methotrexate (eg Reumaflex, Methotrexate HSP, Securact): the drug is an antagonist of folic acid synthesis, capable of heavily influencing the body's immune response. It is indicated to alleviate the symptoms accompanying ankylosing spondylitis, especially in the case of involvement of the peripheral joints. In general, take 7.5 mg of the drug once a week. Alternatively, take three doses of 2.5 mg orally, every 12 hours, once a week. Do not exceed 20 mg per week.
- Adalimumab (eg. Humira): injectable biological drug. It is recommended to take 40 mg of the drug, subcutaneously, every other week. In combination with this drug, NSAIDs, corticosteroids or methotrexate can also be prescribed. Consult your doctor.
- Etanecerpt (eg Enbrel): the drug is an inhibitor of tissue necrosis factor, a chemical messenger present in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. The active principle is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 25 mg, 2 times a week; alternatively, it is possible to take a dose of the drug equal to 50 mg, once a week. Children with this disorder can take the drug based on their body weight. Consult your doctor.
- Infliximab (eg Remicade): this is also a biologic drug widely used in therapy for the control of pain associated with ankylosing spondylitis. The indicative dosage is to take 5 mg / kg of the drug at the second and sixth week of treatment (starting to count from the first infusion). Thereafter, continue with this administration every 6-8 weeks. If the patient with ankylosing spondylitis does not report any therapeutic effect after the sixth week, it is recommended to stop treatment and change therapy, consult your doctor.
- Golimumab (eg Simponi): Probably, new generation drugs such as golimumab are far more effective than first generation ones. It is an anti-inflammatory drug used in therapy both for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for ankylosing spondylitis. The drug is administered monthly subcutaneously, at a dose of 50 mg. It is recommended to inject the drug always on the same day of the day. The patient who weighs over 100 kilos can take a double dose (100 mg).
In the light of recent studies, it seems that a diet rich in omega 3 can decrease inflammation (or in any case avoid its degeneration), as well as reduce pain and postural stiffness. It should be remembered, however, that omega 3 supplementation, in a healthy and balanced diet, it cannot replace, but only enrich, the drug treatment for ankylosing spondylitis.