Edited by Dr. Massimo Bonazzelli
Synonyms
The Slow Forward Seated Barbell Exercise is also known as the Seated Military Press, Seated Front Military Press, Seated Shoulder Press, Seated Barbell Over-the-Neck Press
Type of Exercise
Slow forward with a seated barbell is a basic exercise
Variants
- Slow forward with standing barbell
- Slow behind with standing barbell
- Slow behind with sitting barbell
- Push press in front
- Push press behind
Slow forward with seated barbell: Execution
The starting position sees the athlete sitting on a bench inclined at about 75 °, with his back in his position of strength, legs apart and feet firmly resting on the ground behind the knees to favor the maintenance of the three natural curves of the back and to support the weight more effectively. The elbows are flexed, the wrists straight and the shoulders are adducted and extra-rotated so that the elbow, wrist and barbell are exactly on the vertical plane from a side view. The barbell rests on the upper part of the sternum or on the collarbones as well as on the hands that grab it at a variable distance, but always greater than that between the shoulders. The execution consists in pushing the barbell upwards on the vertical plane on which it was lying before starting, thus trying to trace a straight line segment. During the push, the shoulders flex in the sagittal plane and abduct in the longitudinal plane, while the elbows extend and the shoulder blades i They begin to rotate upwards when the elbows are at shoulder height or slightly higher. The execution ends with the complete extension of the elbows. During the whole execution of the exercise it is advisable to place part of the weight on the feet. This is the basic exercise of distension above the nape and correct execution requires good mobility of the shoulder.
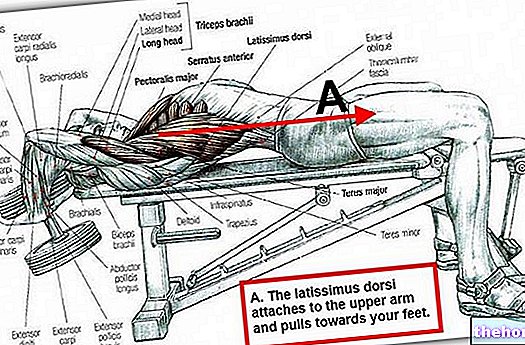
Muscles involved in slow forward sitting barbell exercise
Group 0
- Anterior deltoid
- Upper bundles of the pectoralis major
- Coracobrachialis
- Brachial biceps
Shoulder flexion
Group 1
- Lateral deltoid
- Supraspinatus
Shoulder abduction
Group 2
- Brachial triceps
- Anconeus
Elbow extension
Group 3
- Inferior bundles of the large thoracic dentate
- Lower bundles of the trapezius
- Intermediate beams of the trapezius
Upper scapular rotation
Function of the stabilizing muscles: Stability of the shoulder, shoulder blade, elbow, grip, torso, hip, knee, ankle and foot