Premise
Thyroid symptoms is an improper way to define the symptoms and signs of conditions affecting the thyroid gland.

Before proceeding with the list of the various symptoms, it is useful to briefly review what these diseases are and what they are characterized by:
- Hyperthyroidism. It is the direct consequence of an overactive thyroid producing excess thyroid hormones, even when they are not really needed.
In other words, hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces more thyroid hormones than the body needs. - Hypothyroidism. It is the exact opposite of hyperthyroidism. Therefore, it is the direct consequence of an underactive thyroid that does not produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the needs of the body.
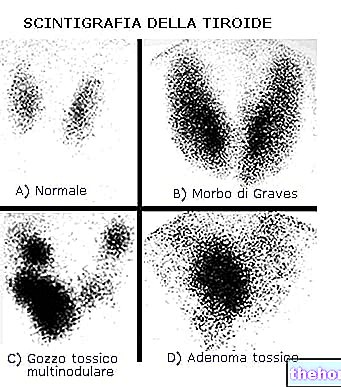
- The goiter. It is the generalized pathological enlargement of the thyroid. Its onset can be associated with various problems, including the aforementioned hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
- Thyroiditis. It is inflammation of the thyroid. Often it has an autoimmune origin.
- Nodules of the thyroid gland. They are anomalous protuberances of the thyroid gland, generally well delimited and circumscribed, having more often a benign than malignant nature.
- Thyroid cancer. It is the malignant tumor of the thyroid gland and represents a major cause of thyroidectomy, which is thyroid removal surgery.
Maybe the readers don't know that ...
According to a "survey by the World Health Organization", around the world, people with a pathology or a thyroid dysfunction would be about one billion.
Symptoms Hyperthyroidism
To learn more, read: Hyperthyroidism Symptoms "
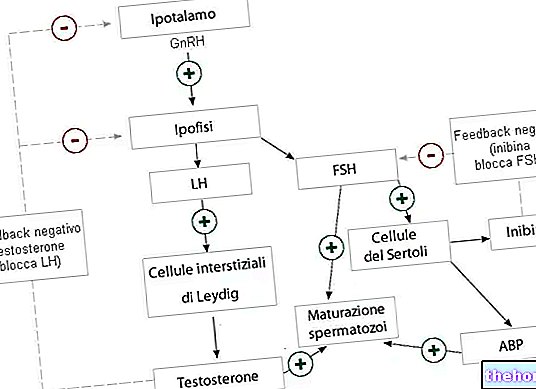
The presence of an excess of thyroid hormones in the circulation - an index of hyperthyroidism - induces various changes:
- increases cardiac activity and oxygen consumption (the second derives from the first),
- favors the raising of the basal body temperature,
- increases the catabolic activity of the metabolism
- alters the balance of the nervous system.
In the individual concerned, these changes are responsible for:
- Drop in body weight, in spite of an increase in appetite and food introduced;
- Excessive sweating, warm and velvety skin, and intolerance to high temperatures;
- Increased heart rate, arrhythmias, palpitations, hypertension and hypertrophy of the left ventricle;
- Anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, mental fatigue and insomnia;
- Shortness of breath, asthenia (muscle weakness), increased breathing rate and hand tremors
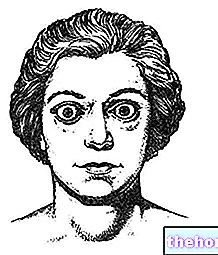
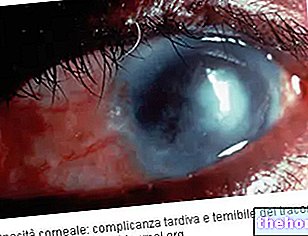
- Graves 'ophthalmopathy (see also Graves' disease or Basedow's disease); this involves bulging eyes, swollen and red eyes, eye pain, sensitivity to light, double vision and reduced eye motility;
- Brittle, fine and thin hair;
- Decreased fertility and sexual desire
- Abnormalities of the menstrual cycle (reduced or absent flows), in women, and gynecomastia, in men;
- Accelerated intestinal transit, accompanied by diarrhea;
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
- Behavioral disorders and learning difficulties in children.