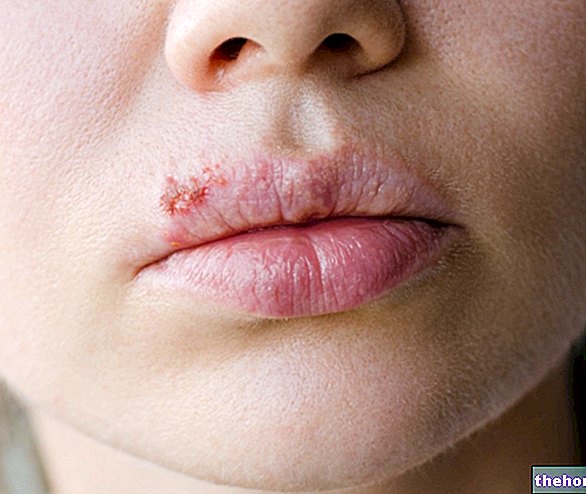
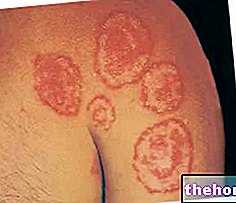
Herpes Simplex (HSV)
Transplacental and perinatal
The fetus can be infected transplacental in the course of the mother's genital herpes (caused by "Herpes Simplex type 2), with a high incidence of abortions, but the most important infection occurs at the time of birth, due to the passage through the genitals. infected.

Chickenpox Zooster
Transplacental and perinatal
Congenital chickenpox can occur if the mother has contracted the infection within the 20th week of gestation (1-2% risk) or just before delivery. In the first case there can be various malformations, such as underdevelopment of the lower limbs, skin scars, atrophy of the optic nerve with blindness, cataracts. In the second case, the newborn presents a typical rash with blisters and a severe infection with death in 25% of cases.
Screening is carried out through ultrasound, which is able to see some of the alterations caused by chickenpox, and through the dosage of IgG and IgM specific for Varicella Zoster. If the mother is positive, a passive immunization with immunoglobulins will be performed. specific to mitigate the severity of the disease and the risk of congenital varicella syndrome. These are effective only when administered within 96 hours of exposure. Even the administration of the same immunoglobulins to newborns seems to reduce the severity of the infection. There is a vaccine, not mandatory, but recommended within the first years of life or in people at risk who have not yet had the disease (health professionals and women who wish to a pregnancy).
Parvovirus B19
Transplacental
This virus causes the so-called "Fifth Disease" (or Megaloeritema) in children. Infection contracted by the pregnant woman carries a risk of fetal infection of about 30%. No malformative effects are described, but severe anemia with fetal death. An early indicator of fetal injury is an increase in the maternal blood of a substance. called protein alpha-fetoprotein. If this is positive, it is essential to search for the DNA of the virus with PCR from the sampling of the umbilical cord. Screening is carried out with ultrasound and with the search for specific IgM and IgG and, if these are positive, repeated ultrasound scans are recommended in order to promptly highlight the possible onset of serious fetal alterations.
HIV
Transplacental, perinatal, postatal
Pediatric AIDS represents, in industrialized countries, 3% of all reported cases and in Africa as much as 20%. It is not possible to predict whether the child of an infected mother will also be infected because, although the totality of those born to HIV-positive mother present at birth specific antibodies against the virus, only about 20% will develop the disease. Currently, it is possible to detect the presence of the virus by means of the HIV test and the search for its genome (of RNA) with PCR. The administration of antiviral drugs in pregnancy and early in the newborn reduces the probability of AIDS infection by 70%, which in the newborn that manifests it has a rapid and malignant evolution.
Other viruses
Congenital malformations following measles contracted by the mother during the first trimester are very rare, but a certain incidence of miscarriages and premature births has been reported in the case of infection after the second trimester. The virus of Epsten-Barr (which causes mononucleosis) and influenza viruses are implicated in rare cases of fetal malformations in mothers infected in the first trimester. Maternal virus infection Coxsackie A and B it can cause fetal heart, brain and adrenal gland lesions if contracted in the first trimester. The maternal-fetal transmission of "hepatitis B it frequently occurs in the newborn at the time of labor or during breastfeeding and it is necessary to give the child, within 48 hours of birth, the administration of specific immunoglobulins against the virus followed immediately by vaccination. This seems to reduce the rate of transmission to 1. %. The mother suffering from hepatitis C it can infect the child, but overall this is infrequent.
More articles on "Infections in Pregnancy: Herpes, Chickenpox, Papilloma, HIV"
- Infections in pregnancy
- Infections in pregnancy: syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia
- Infections in pregnancy: toxoplasmosis and malaria