Generality
Pleural mesothelioma is a rare malignant tumor that originates from the mesothelium making up the pleura.
The pleura is the serous membrane that surrounds and protects the lungs and that lines the cavity in which the lungs reside.
The main cause of pleural mesothelioma in humans is exposure to asbestos or asbestos.

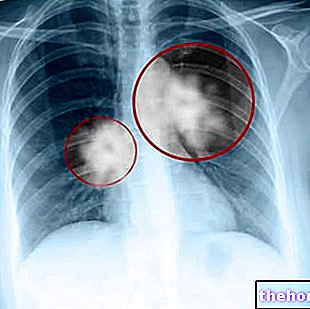
CT scan of a patient with pleural mesothelioma. Note the tumor mass indicated by the yellow arrows compressing the right lung. From wikipedia.org
Typical symptoms are: chest pain, cough, dyspnoea, hemoptysis, pleural effusion, fatigue and fever.
For a precise diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma, the fundamental examination, which removes all doubts, is the biopsy.
Possible treatments include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
The prognosis is generally negative.
What is Mesothelioma?
A mesothelioma is any malignant tumor (or cancer) that originates from a cell in the mesothelium.
The mesothelium is the layer of squamous cells that lines several internal organs - including the lungs, heart, some abdominal organs, testicles in men and uterus in women - and the cavities within which these organs reside.
The layer of squamous cells of the various mesotheles present in the human body gives life to serous-type membranes.
What is pleural mesothelioma?
Pleural mesothelioma is the malignant tumor that originates from the pleura, ie the mesothelium that lines the lungs (visceral pleura) and the cavities within which the lungs reside (parietal pleura).
A few more details on the pleura
The pleura serves, first of all, to protect the lungs.
Secondly, it produces a lubricating fluid that favors its flow on the surface of the lungs, so as to allow the latter greater freedom of expansion.
Between the visceral pleura (resting on the lungs) and the parietal pleura (on the cavities around the lungs), there is a virtual space known as the pleural space or pleural cavity.
MAIN FEATURES
Pleural mesothelioma has good infiltrating capabilities (ie it is capable of spreading to neighboring tissues) and can contaminate the pericardium with its tumor cells.
In addition, it also has a good metastatic capacity, ie it is able to spread some of its tumor cells in organs and tissues distant from the site of origin.
The cancer cells involved in the aforementioned diffusion process - also known as metastasis - are called metastases.
OTHER TYPES OF MESOTHELIOMA
In addition to pleural mesothelioma, there are:
- Pericardial mesothelioma: it is mesothelioma that originates from the pericardium, that is the mesothelium of the heart and the sac that contains the heart
- Peritoneal mesothelioma: it is the mesothelioma that originates from the peritoneum, that is the mesothelium within which some abdominal organs reside.
- Testicular mesothelioma (or mesothelioma of the vaginal tunic of the testicle): it is the mesothelioma that originates from the mesothelium of the testicles; mesothelium of the testes which is also known as the vaginal tunic of the testicle.
- Perimeter mesothelioma (or mesothelioma of the uterine serous tunic): it is the mesothelioma that originates from the mesothelium of the uterus, also known as uterine serous tunic.
Causes
For humans, the main cause of pleural mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos or asbestos.
Asbestos is a set of minerals (inosilicates and phyllosilicates), arranged in elongated bodies (the so-called "asbestos fibers") and capable of being easily dispersed in the air.
Precisely by virtue of its easy dispersion in the air, asbestos is an inhalable product, which penetrates the human organism through the respiratory system.
The effects of an "exposure to" asbestos at the level of the pleura appear after many years: a pleural mesothelioma can arise after 20, or even 50 years (N.B: this also applies to other types of mesothelioma).
Asbestos and mesothelioma in general
Asbestos is the main culprit in any type of mesothelioma.
According to an interesting Anglo-Saxon statistic for the United Kingdom, 9 out of 10 men with mesothelioma and about 8 out of 10 women with mesothelioma are people who have had contact with asbestos in their life.
RISK FACTORS RELATED TO "ASBESTOS
While once it was widely used in industrial plants for its resistance to fire, acids, microorganisms and wear, today asbestos is no longer in use and many countries around the world have even banned its marketing, precisely because its harmful effects on human health. This greatly reduced the risk of exposure to asbestos and, clearly, also the risk of developing pleural mesothelioma and other related disorders (other mesotheliomas, asbestosis, etc.).

Asbestos
At the present time, the people still dangerously exposed to asbestos are: those who live in the vicinity of old mining quarries for asbestos, those who live near old buildings with parts in asbestos and those who live near rich natural places of those mineral components forming the asbestos.
It is important to underline this concept: the earlier it begins and the greater the "exposure to asbestos" over the course of life, the higher the risk of developing pleural mesothelioma.
Places of greatest exposure to asbestos, before its abolition:
- The cement-based tools that produced Eternit (Eternit was the trade name of "asbestos).
- The textile industries that produced sheets, overalls and gloves based on asbestos and derivatives.
- Shipyards and railways.
- Building installations.
- Industries for friction materials, such as brakes and clutches.
- Quarries for the extraction of the minerals that make up asbestos.
OTHER CAUSES OR RISK FACTORS ONLY
According to some scientific studies, they could favor the appearance of pleural mesothelioma:
- Coming into contact with the SV40 virus, after a previous exposure to asbestos. Research on the subject is still scarce and requires further investigation.
- Exposure to radiation from radiotherapy.
- Exposure to thorium dioxide.
- Exposure to a mineral known as erionite, found in Turkey.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Pleural mesothelioma accounts for nearly 75% of human mesotheliomas and holds the record as the most common mesothelioma.
Most pleural mesothelioma patients are over 50 (70-year-old patients are by far the most numerous). This characteristic incidence in the middle-advanced age population is explained by the very slow effects that contact with asbestos has on humans.
Mesothelioma Epidemiology
Mesothelioma is a very rare malignant tumor. For example, in the UK, it affects 2,600 people every year; in Italy, just over 2,000 individuals per year.
In the past, mesothelioma patients were mainly men (N.B: the male / female ratio was 5 to 1, in favor of males); today, the situation is slightly different and the number of sick men, compared to women, has decreased.
In all likelihood, the greater incidence in the male population, demonstrated in the past, was linked to the fact that asbestos workers - when this substance was still widely used - were mostly men.
Symptoms and Complications
Typical symptoms and signs of a pleural mesothelioma are:
- Pain in the chest and sometimes in the lower back
- Shortness of breath (dyspnoea)
- Persistent cough and / or hoarseness
- Pleural effusion
- Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Fever above 38 ° C, with sweating, especially at night
- Muscle fatigue and weakness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Unexplained weight loss
For further information: Pleural Mesothelioma Symptoms
SPECIAL FEATURES OF THE INITIAL STAGES
Usually, at the beginning, pleural mesothelioma is asymptomatic, that is, devoid of obvious symptoms and signs.
This particularity makes early diagnosis difficult.
COMPLICATIONS OF THE PLEURIC MESOTHELIOMA
In severe cases, pleural mesothelioma can cause the appearance of several tumors in the chest, collapse of one or both lungs (pneumothorax) and pulmonary embolism.
Also, at an advanced stage, it can spread metastases to various organs of the body.
Diagnosis
The diagnostic process for the detection of pleural mesothelioma begins with an accurate physical examination and a careful medical history (clinical history). He then continues with some imaging tests, including chest x-ray, CT scan, nuclear magnetic resonance, and PET. Finally, it ends with a biopsy, the most indicative examination and the one that confirms any suspicion born during the previous evaluations.
IMPORTANCE OF THE HISTORY
As stated, pleural mesothelioma almost exclusively affects people exposed to asbestos.
This characteristic makes the medical history a fundamental point of the diagnostic process, as an individual who has never had contact with asbestos in life, even if he has suspected symptoms, most likely suffers from a disorder other than pleural mesothelioma.
Medical conditions that cause symptoms and signs similar to those of pleural mesothelioma include lung cancer, pulmonary fibrosis and infections of the lungs.
IMAGE DIAGNOSTICS
The diagnostic imaging tests allow the doctor to identify the exact location of the tumor mass or masses and to see if they have invaded other organs or tissues or have had particular effects (pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism, etc.).
BIOPSY
The biopsy consists in the collection of a sample of cells from the tumor mass and in the laboratory analysis of this sample.
Through the analysis of cancer cells, the doctor is able to understand the type of cell that gave rise to the malignant tumor: if it appears that the process of formation of the tumor mass began at the level of a cell of the mesothelium of the pleura, then the aforementioned tumor mass is a pleural mesothelioma.
In addition, biopsy is useful because it detects two important characteristics of a malignant tumor: staging and grade.
In the case of pleural mesothelioma, collection of the cell sample for biopsy can be done through thoracoscopy or thoracotomy procedures.
What are the staging and grade of a malignant tumor?
The staging of a malignant tumor includes all the information, collected during the biopsy, concerning the size of the tumor mass, its infiltrating power and its metastasizing capacity.
The degree of a malignant tumor, on the other hand, includes all those data, which emerged during the biopsy, concerning the extent of transformation of the malignant tumor cells, compared to their healthy counterparts.
Treatment
The choice of which treatment to adopt in the case of pleural mesothelioma depends on several factors, including: the stage and grade of the malignant tumor (presence of metastases, progression of the disease, etc.), the general state of health of the patient (patients are generally elderly) and the affected body regions.
Currently, the treatment options for pleural mesothelioma are: surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
SURGERY
The goal of surgery is the removal (or resection) of the tumor mass constituting pleural mesothelioma.
In general, all mesotheliomas - therefore also pleural mesothelioma - lend themselves little to surgical removal.
To further complicate the operation, then, can be the site of "uncomfortable onset of the tumor mass: if the latter, in fact, originates in an" area that is difficult to reach with surgical instruments, removal is very complex.
RADIOTHERAPY
In the case of pleural mesothelioma, radiotherapy can represent an "alternative to" surgery - if this is not possible - or a form of adjuvant treatment, to be performed after surgical removal of the tumor mass (adjuvant radiotherapy).
When radiotherapy is of adjuvant value, it destroys cancer cells that the surgeon has not been able to remove.
CHEMOTHERAPY
Chemotherapy in the case of pleural mesothelioma consists in the administration of one or more anticancer drugs, systemically or intrapleurally (i.e. directly into the thoracic cavity)
Depending on the characteristics of the tumor present, the treating physician can decide whether to opt for pre-surgical chemotherapy (also called neoadjuvant chemotherapy) or for post-surgical chemotherapy (also known as adjuvant chemotherapy).
The goal of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is to reduce the tumor mass, so as to make subsequent surgical removal easier.
The goal of adjuvant chemotherapy, on the other hand, is to eliminate tumor cells that the surgeon was unable to remove through resection.
POSSIBLE CARE OF THE FUTURE
Recently, doctors and researchers are experimenting with the effects of some particular medicines, belonging to the category of monoclonal antibodies and also known as biological drugs.
Among the biological drugs that appear to have therapeutic effects against pleural mesothelioma, tremelimumab deserves a particular mention.
Prognosis
Pleural mesothelioma almost always has a negative prognosis, as its diagnosis occurs, very often, too late, when the situation is already strongly compromised.
Although there are patients who survive up to 3 years, in the case of pleural mesothelioma the average survival rate is about 12 months.