Diagnostic hysteroscopy requires special preparation, which also includes a series of tests aimed at establishing a woman's suitability for the procedure in question.
Lasting 10-15 minutes, diagnostic hysteroscopy involves inserting the hysteroscope into the uterine cavity through the vaginal opening, which acts as an exploratory probe.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is a safe and therefore low-risk procedure.
Those who undergo diagnostic hysteroscopy can return to their daily activities as early as the day following the procedure.
If the diagnostic hysteroscopy were to detect anomalies, the gynecologist who performed it immediately informs the patient, also explaining the possible remedy or treatment for what has been found with the procedure in question.
Brief review of what "is" Hysteroscopy
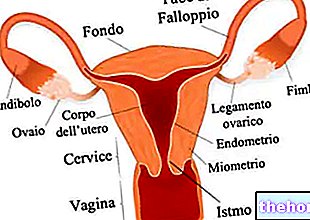
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic gynecological procedure, which allows to evaluate from the inside the state of health of the uterus - in particular of the uterine cavity, cervical canal and endometrium - and, in case of need, to intervene surgically , in order to cure some medical condition.
Hysteroscopy is based on the use of an instrument known as a hysteroscope; the latter is a long tube, similar to a drinking straw, which, thanks to the equipment of a camera and a system for connecting to a monitor, acts as an exploratory probe of the uterus and cervix, after its insertion into the uterine cavity , through the vaginal opening.
Hysteroscopy is a procedure usually performed on an outpatient or outpatient basis Day surgery; therefore, except in special cases, it never provides for the patient to be hospitalized.
Hysteroscopy is a subject for gynecologists, ie doctors with a specialization in gynecology.
o uterine polyps;

- Understanding the reasons for an "infertility;
- Evaluate the general health of the endometrium during menopause;
- Evaluate the phenomenon of endometrial hyperplasia;
- Go back to the causes of an "irregularity in the menstrual cycle;
- To trace the causes of an abnormal loss of blood from the uterus;
- Research the causes of menstruation in women who have passed the menopause;
- Plan in detail a surgical intervention at the level of the uterus;
- Understanding the reasons that lead a woman to have recurrent miscarriages;
- Check for abnormal presence of endometrial tissue in the myometrium (adenomyosis);
- Verify the presence of a "congenital anomaly affecting the uterus" (eg bicornuate uterus, didelph uterus, septal uterus, uterine agenesis, etc.);
- Take a sample of the endometrium to be subsequently subjected to appropriate laboratory analysis (biopsy). This practice allows to ascertain the presence of an endometrial carcinoma (a malignant tumor of the endometrium) and to establish its stage of advancement.
Important note
The above tests are also provided in the case of possible operative hysteroscopy.
On the day of the procedure: how to behave?
Remember that: at this stage of preparation, there is "suitability" for the diagnostic hysteroscopy procedure.
On the day of the diagnostic hysteroscopy, the patient must wear comfortable and practical clothes, because then she will have to take them off in favor of a hospital gown specially prepared for her by the medical staff.
What to do if anesthesia is planned?
Under certain circumstances, diagnostic hysteroscopy may require local anesthesia.
Local anesthesia for diagnostic hysteroscopy does not require special preparations.
Did you know that ...
Unlike what happens in the case of diagnostic hysteroscopy, the anesthesia for operative hysteroscopy is of a general type.
Frequently Asked Questions: for menstruating women, when is it best to perform Diagnostic Hysteroscopy?
For menstruating women, the most suitable time to perform a diagnostic hysteroscopy (but also an operative one) is in the first 7 days following menstruation. In fact, performing the procedure in this period of the menstrual cycle allows gynecologists a better vision. and more detailed of the uterus and its internal cavities.
, liquid or thin surgical instruments.The distension (or dilation) of the uterus is essential not only to facilitate the conduction of the hysteroscope inside the uterus, but also to allow a better analysis of the internal anatomy of the organ and to make the whole less painful. procedure.
In this phase of the procedure, it is important to carefully monitor the intrauterine pressure by the entire medical staff, which must remain at a value between 60 and 70 mmHg. Maintaining these blood pressure values, in fact, avoids the over-distension of the walls constituting the uterine cavity.
SECOND PART
When the hysteroscope is finally in the uterus and the uterus is sufficiently dilated, the gynecologist starts the visual exploration of the uterine cavity, endometrium and cervical canal. Remember that what the hysteroscope takes, through its camera and with the help of the light source, is visible by all the medical staff on a special external monitor.
If diagnostic hysteroscopy is needed for a biopsy, it is at this point in the procedure that endometrial sample collection operations are performed.

PART THREE
Once the gynecologist has finished the exploration, he proceeds to gently extract the hysteroscope; the operation of extracting the hysteroscope is important and is also part of the diagnostic hysteroscopy: in fact, it serves to assess the integrity of the uterine isthmus, that is the point of passage between the internal cavity of the uterus and the cervical canal .
Where is anesthesia placed, when it is foreseen?
In the above description of the various procedural steps that characterize diagnostic hysteroscopy, local anesthesia is placed after the patient has been accommodated, but before the insertion of the speculum and the hysteroscope.
Once administered, the anesthetics work within minutes.
When anesthesia is foreseen, another professional figure is added to the medical staff composed of the gynecologist and his nurses: the anesthetist. The anesthetist is a doctor specialized in anesthesia and resuscitation practices.
Instrumentation for Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
The instrumentation for diagnostic hysteroscopy includes: hysteroscope, speculum (vaginal valves), forceps, dilators, cannulas, insufflator, video camera system, sterile gauze, fiber optic cable, CO2 conductor cable, etc.
The preparation of this instrumentation - however obviously properly sterilized - takes place while the patient is wearing the gown provided for the procedure.
Did you know that ...
There are two types of hysteroscope: the hysteroscope for diagnostic hysteroscopy procedures, whose diameter is between 4 and 5 millimeters, and the hysteroscope for operative hysteroscopy procedures, whose diameter is 7-8 millimeters.
How do patients feel during a "Diagnostic Hysteroscopy?"
Without the practice of anesthesia, the patient undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy may experience slight discomfort / pain during the introduction of the hysteroscope into the vagina and cervical canal. This sensation, however, is temporary, as, as readers will remember , the gynecologist follows the introduction of the hysteroscope by dilation of the uterine cervix and uterus.
What is the Duration of Diagnostic Hysteroscopy?
As a rule, a diagnostic hysteroscopy procedure lasts 10-15 minutes.
Did you know that ...
Operative hysteroscopy has a longer duration than diagnostic hysteroscopy; in fact, it can last between 30 and 60 minutes.
When is the return home expected after a "Diagnostic Hysteroscopy?"
After a diagnostic hysteroscopy, the patient can go home immediately, even if she has received local anesthesia.
, until the end of the latter. This is a precautionary measure to prevent infections. vaginal. The result of lesions caused by the passage of the hysteroscope along the uterine cervix and the cervical canal, this adverse effect can last from a few days to even a little over a week;
- Abdominal pain and cramps. Often, the painful sensation can be controlled with a pain reliever, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen (an NSAID);
- Sense of tiredness and / or malaise;
- Reflex pain in the shoulder, resulting from the use of gas rich in carbon dioxide.
Complications
By complications of a diagnostic or operative procedure, doctors mean problems of a certain clinical relevance, which can occur during or after the aforementioned procedure.
Potential complications of diagnostic hysteroscopy procedures include:
- Uterine perforation;
- Bladder perforation;
- The development of a "pelvic infection (eg: metritis).
Curiosity: how common are the complications of a "diagnostic hysteroscopy?"
According to a study by Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynecology, only 8 out of every 1,000 patients undergoing diagnostic hysteroscopy would be subject to uterine perforation and only 3 out of 10,000 patients would undergo utero-bladder perforation and a "pelvic infection.
How to recognize any complications?
Symptoms that characterize the possible complications of a "diagnostic hysteroscopy include:
- Intense and protracted abdominal pain that does not subside with the most common analgesics;
- Fever above 38 ° C;
- Heavy and recurrent vaginal bleeding.
Furthermore, doctors advise against performing diagnostic hysteroscopy in case of: nulliparity, intact hymen and cervical stenosis.