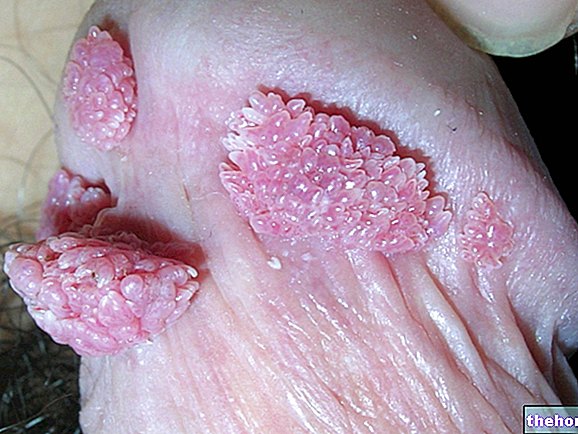
Genital herpes is a contagious disease caused by a virus.
The herpes virus group is quite large; those that affect the genitals are called herpes simplex and are differentiated into type 1 and type 2. Type 1 most often affects the mouth, eyes and nose, while type 2 electively affects the genital area.

Initially, itchy symptoms, heat, swelling and superficial tension on an intimate level arise. This sensation rapidly evolves into tingling and burning, heralding the local onset of small serous blisters. After being resorbed or ruptured, these lesions evolve into superficial crusts that bleed easily.
The published material is intended to allow quick access to advice, suggestions and general remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of Genital Herpes; these indications must in no way replace the opinion of the treating physician. or other healthcare specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
What to do
Genital herpes infection is chronic and cannot be cured permanently.
Therefore, once the infection has taken place, the treatment of acute conditions has an exclusively preventive role and largely involves the support of the immune system:
- Moderate periods of strong psychological stress (work, family, other commitments, etc.).
- Prevent the contagion of other systemic or localized infections, for example: flu, candidiasis, bacterial proliferation, etc.
- Proper and balanced nutrition.
- Promote the specific intake of vitamins (vitamin C and vitamin D) and mineral salts (magnesium, iron, zinc and selenium) which support immunity.
- Promote the global intake of antioxidant molecules (in addition to the aforementioned vitamin C, also vitamin A, vitamin E, polyphenols, etc.). These elements hinder the formation of free radicals and improve the general oxidative condition.
- Increase the intake of essential omega 3 fatty acids (anti-inflammatory function and stimulating the production of antibodies).
- Integrate the diet with probiotic foods (increase the intestinal bacterial flora, involved in the trophism of the immune system).
- Increase, if possible, the intake of lysine amino acid (although the reasons are not known).
- Engage in sports with a reasonable frequency and intensity. At moderate levels, motor activity improves the body's defenses and efficiency.
- Take medications only after consultation or prescription.
- Use intimate cleansers with a slightly acidic pH and underwear made of natural fabrics.
- When herpes overlaps with parallel infectious diseases, localized medical applications of acid solution (lactic acid) may help.
What NOT to do
Other behaviors are capable of promoting acuity and should be avoided. Between these:
- Excess with hardly sustainable work, family and social commitments. Even if the challenging period seems limited, it may be enough to trigger the infection.
- Getting sick regularly, both at a general or systemic level (for example flu), and localized (bacterial, fungal infections, etc.).
- Neglecting the trophism of the immune system:
- Diet lacking in vitamins and mineral salts involved in the correct functioning of natural defenses (see previous paragraph).
- Diet lacking in antioxidants.
- Diet that includes allergenic foods (in predisposed subjects, especially shellfish, dried fruit, egg and milk proteins, etc.) or those responsible for food intolerance (eg gluten for celiacs).
- Diet lacking in prebiotics and probiotics.
- Take arginine-based food supplements; it seems that it favors the acute.
- Follow sports protocols with excessive frequency, volume and intensity, without respecting recovery times and not listening to your body.
- Making illogical use of drugs (abuse), especially antibiotics (which negatively affect the intestinal flora).
- Use underwear made with synthetic fabrics, irritating or containing annoying pigments; economic clothing of dubious origin (foreign) is particularly responsible for adverse reactions.
What to eat
Diet cannot cure herpes but affects the frequency and severity of relapses. It is advisable to encourage the intake of some foods rather than others. Particularly:
- For vitamin C or ascorbic acid: peppers, citrus fruits, parsley, kiwi, lettuce etc. They must all be fresh.
- For vitamin D: fish, fish oil and egg yolk.
- For zinc: liver, meat, milk and derivatives, some bivalve molluscs.
- For selenium: meat, fish products, egg yolk, milk and derivatives, fortified foods (potatoes, etc.).
- For magnesium: oil seeds, cocoa, bran, vegetables and fruits.
- For iron: mainly meat, fishery products and egg yolk.
- For polyphenolic antioxidants: especially fresh fruit and vegetables, but also red wine, seeds, aromatic herbs, tea, roots, medicinal herbs, etc.
- For lysine: meat, cheese, some fishery products and legumes (especially soy).
- For probiotics: all fermented foods such as yogurt, tofu, tempeh, buttermilk etc.
- For omega 3: oily fish, some oil seeds and related oils, algae.
What NOT to Eat
Incorrect eating behaviors such as:
- Single-issue diets.
- Vegan diet.
- Diet free of vegetables and greens.
- Diets based solely on:
- Cooked foods.
- Preserved foods.
- Food supplements of arginine (which as we have already said has a negative effect).
Natural Cures and Remedies
There are products that “could” improve the trophism of the immune system or act positively on the infection.
These include:
- Echinacea and other immunostimulating plants.
- Royal jelly
- Propolis (also for topical use).
Pharmacological treatment
In the fight against genital herpes, drugs are not decisive and are not a remedy.
The molecules used in the ointments and tablets have the purpose of: improving symptoms, forcing the regression of viral proliferation and simplifying healing.
Some are:
- Zinc and / or heparin cream: decrease the duration and discomfort of the rash.
- Aciclovir (or similar): reduces the replicative capacity of viruses.
- Interferon: powerful antiviral action.
- Immunostimulants: mainly natural or synthetic thymic hormones.
- Antihistamines: against itching.
Prevention
The prevention of genital herpes is of two types:
- Prevention against contagion: these are purely hygienic measures. Herpes simplex spreads very easily with sexual activity; less frequently if the disease is latent. The use of public toilets, swimming pools, towels and linen of others are considered less significant risk factors but not to be neglected.
- Prevention against acute illnesses after contagion: all the precautions mentioned in the previous paragraphs apply.
Medical treatments
There are no definitive treatments for herpes simplex.
Any therapy is purely palliative or intended to improve symptoms.
In addition to the prevention of contagion, the prevention of manifestations and the possible use of drugs, there are no other medical treatments against genital herpes.