In women it is commonly found - albeit in very small concentrations - in the vaginal microflora, together with the characteristic lactobacilli, which in normal conditions hinder their excessive proliferation.
In the human body, small colonies of Ureaplasma urealyticum can also be found in the pharynx and rectum.
Ureaplasma can be transmitted both through vaginal, anal or oral sexual intercourse and through the maternal-fetal route (during pregnancy or at the time of delivery).
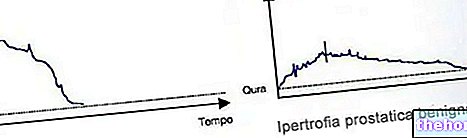
; squeezing the shaft penetrates up to the glans, we also notice the release of a whitish and stringy secretion, which sometimes comes out spontaneously. From the urethra, the infection can easily spread to the structures connected to it, such as the prostate and testicles, causing prostatitis and epididymitis respectively; if not properly treated, it can seriously compromise male fertility.
In women, an "uncontrolled growth of ureoplasma is involved in the development of bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease and urethral syndrome; also in this case, if not adequately treated, the infection can compromise fertility. However, these are pathologies that generally have a "polymicrobial etiology and are therefore caused by several microorganisms, which probably have a synergistic effect between them; in addition to ureoplasma, Chlamydia trachomatis, Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis can therefore come into play. and others. Also in this case the symptoms are those attributable to the classic sexually transmitted genital infections and include vaginal burning and pain during and after intercourse.
Infection transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriages, premature births and various problems with the fetus (increased incidence of pneumonia and neonatal meningitis).
In immunocompromised patients, the infection can extend to the upper urinary tract (kidney) and bone (arthritis).
; tetracyclines are traditionally used, however - due to the increasingly frequent presence of resistant ureoplasma - other drugs, such as azithromycin or doxycycline, can also be used. The choice of the most suitable therapy will be made by the doctor on the basis of the diagnostic results , including the antibiogram. Sexual rest is important until healing has been ascertained; therapy should also be extended to sexual partners both in the presence and absence of specific symptoms.
For further information: Drugs to Treat Ureaplasma Infections in general - goes through some basic hygiene rules and daily behavior. The use of substances with a non-acidic pH or anti-lactobacillary activity, for example, facilitates the infectious process. Irrigation, sanitizing sprays, soaps and perfumed talcs should be avoided. Irrigations, in fact, alter the natural saprophytic flora present. in the vagina; perfumed talcs and sprays can instead produce irritation of the vaginal mucosa.
You should also avoid wearing synthetic underwear as well as jeans and pants that are too tight, such as to retain moisture and heat, creating favorable conditions for the development of harmful microorganisms, including Ureaplasma urealyticum. When they finally dry and clean the private parts, they should always perform a movement from forward to backward and not vice versa. This is to avoid the easy and risky transport of bacteria from the rectum to the vagina and thus prevent infections.