Generality
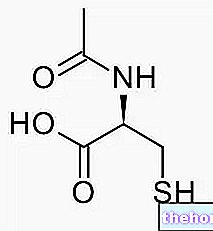
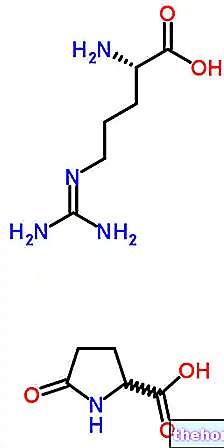
Typically, glutamine peptide is a mixture of two dipeptides:
- L-alanyl L-glutamine: derived from the union of glutamine with the amino acid alanine
- and L-glycyl-L-glutamine: derived from the union of glutamine with the amino acid glycine.

It would be the best pharmacokinetic properties to justify the use of the glutamine peptide as a nutritional supplement, replacing the classic L-glutamine.
In addition to sports, glutamine peptide is now also used in the treatment and management of sarcopenic and cachectic states or in cases of structural damage to the intestinal mucosa.
Indications
Why is glutamine peptide used? What is it for?
The use of glutamine peptide in the integrative setting has been inherited from total parenteral nutrition.
Therefore, most of the biological functions of these dipeptides are to be traced back to the evidence derived from clinical use.
More precisely, the glutamine peptide would present:
- An "immunomodulatory activity: it supports the body's immune defenses;
- An "anti-catabolic activity: prevents muscle catabolism, such as that induced by a particularly intense and prolonged" sporting activity, or by rather restrictive diets;
- An "antioxidant activity;
- A "protective activity against the enteric mucosa.
All the aforementioned functions, maintained even after oral intake, would derive from the biological role of glutamine. In fact, this amino acid represents a fundamental nutritional resource for cells in active replication, such as enterocytes and cells of the immune system.
It should also be remembered the antioxidant role of glutamine, as a direct precursor of glutathione.
Properties and Effectiveness
What benefits has glutamine peptide shown during the studies?
Most of the studies relating to the biological efficacy of glutamine peptide derive from the clinical use of the same molecule, through total parenteral nutrition.
In this "field of use", the literature seems to agree in defining the potential advantages of the glutamine peptide, especially in the case of severe burns and major traumas.
In such conditions, the glutamine peptide would exert a very important anti-catabolic role, avoiding clinically risky conditions such as cachexia and sarcopenia, and facilitating wound healing.
At the same time, the glutamine peptide could support the immune system, reducing the risk of opportunistic infections, with a poor prognosis, in hospitalized patients.
Less relevant, and somewhat contradictory, would be the evidence relating to the usefulness of the glutamine peptide in sports.
Dosage and method of use
How to use glutamine peptide
Effective dosages of glutamine peptide obviously vary according to purpose.
In sports, the suggested dosages of glutamine peptide range between 1,500 and 4,500 mg per day, divided into at least two intakes.
The recommended doses of glutamine peptide tend to increase significantly in the clinical setting, particularly in the treatment of severe trauma and major burns.
Side effects
At the recommended doses, the use of glutamine peptide was generally safe and well tolerated.
In rare cases of overdosing, the use of glutamine peptide would have resulted in the onset of constipation and abdominal bloating.
Contraindications
When should glutamine peptide not be used?
The use of glutamine peptide is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the active ingredient.
Pharmacological interactions
What drugs or foods can modify the effect of the glutamine peptide?
The pharmacological interactions of the glutamine peptide fully replicate those of the amino acid L-Glutamine.
Therefore, the intake of glutamine peptide would seem to balance the side effects on the intestinal mucosa induced by drugs such as methotrexate and indomethacin.
Precautions for use
What do you need to know before taking glutamine peptide?
The use of glutamine peptide is generally contraindicated, without appropriate medical supervision, during pregnancy and in the subsequent breastfeeding period.
The use of glutamine peptide should be done with particular caution and under close medical supervision in patients with impaired renal function.