The hepatitis virus is most commonly transmitted through contact with blood or other body fluids (semen, vaginal fluid), as well as from mother to child during childbirth.
Compared to other viral hepatitis, form B is potentially more serious, as it can become chronic and have a malignant course, up to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
The danger of hepatitis B, for several years now, has led the health organizations of many countries, including Italy, to start prevention strategies through vaccination.
belonging to the genus Orthohepadnavirus, family Hepadnaviridae. It is one of the most infectious viral agents in the world: it is transmitted fairly easily from one person to another, through exposure to infected blood or body fluids, such as sperm, vaginal fluids and precoital secretions. Transmission can also occur from the infected mother to the newborn during childbirth (very frequent mode of contagion in the pre-vaccination era). In Italy, however, the chances of contracting the hepatitis B virus have decreased since compulsory vaccination for newborns was introduced in 1991.

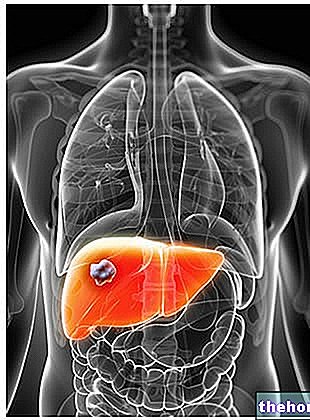
The hepatitis B virus (also called HBV from Human Hepatitis B Virus) has as its main target the hepatocytes, ie the liver cells, where it settles and begins to proliferate. The result of this viral proliferation is inflammation of the liver, with cell damage. The disease can manifest itself with pains, fever and jaundice, that is, with the yellow discoloration of the skin, but often the symptoms are vague or even absent.
In most cases, hepatitis B spontaneously evolves towards recovery, but the virus responsible for the disease may not be completely eliminated by the immune system. If the pathogen persists for a long time, it can slowly damage the infected person's liver and cause very serious consequences.