Definition
We speak of "fecal incontinence" to indicate a partial or total loss of control of the anal sphincter, with subsequent involuntary release of:
- Liquid stools
- Solid stools
- Intestinal gas

Symptoms
Often, when we talk about faecal incontinence, we tend to overlook that even the involuntary emissions of intestinal gas are a characteristic symptom.
In addition to flatulence, fecal incontinence is distinguished by the release of modest - sometimes large - quantities of fecal material, the consistency of which varies according to the cause that favored it.
Many adults, over the course of their lives, declare that they have had a single episode of fecal incontinence, often in the context of diarrhea: in such circumstances, "incontinence should not" be interpreted as a dangerous symptom, nor as a warning light. serious pathologies. One or two episodes of fecal incontinence must not arouse unnecessary alarmism, even if the doctor's opinion is always and in any case recommended.
Different speech when fecal incontinence recurs over and over again within a few days. In similar circumstances, the symptoms accused by the patient can vary according to the factor that arises at the origin:
- Loss of control of the emission of fecal material
- Flatulence
- Completely unnoticed urge to defecate
- Stimulus to defecate felt but inability to control the anal sphincter
- Impossibility of postponing the urge to defecate
- Diarrhea / constipation / fecaloma
- Abdominal swelling
- Soiling of underwear (phenomenon known as "fecal soiling')
Attention!
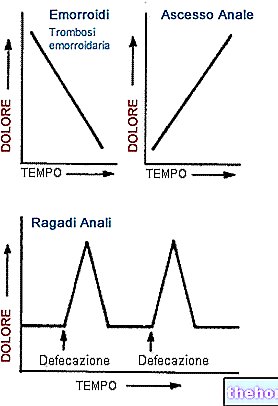
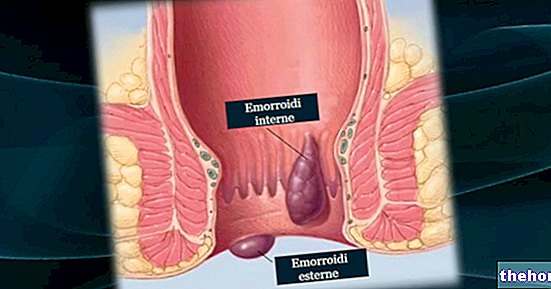
It is good to distinguish fecal incontinence proper from pseudo-incontinence. Some symptoms, in fact, could initially suggest a similar condition, when instead it is something else. The presence of mucous and / or yellowish anal secretions and the perception of anal humidity could in fact be a lit indicator of different anal diseases (eg infections, rectal prolapse, anal fistula, hemorrhoids, etc.) or, more simply, synonymous with poor personal intimate hygiene.
Complications
For most patients with faecal incontinence, the heaviest complication associated with this disorder lies in psychological discomfort and a heavy feeling of embarrassment. Not being able to control it, faecal incontinence risks manifesting all its symptoms in the middle. of a conversation or in business hours. The stress and anxiety connected to this disorder are the psychological complications that inevitably derive from the awareness of not being able to fully control one's bowel function in terms of evacuation. It should not be forgotten, then, that many patients affected by fecal incontinence tend to isolate themselves , avoiding contact with people as much as possible.
In addition to psychological disorders, fecal incontinence can give rise to physical problems, such as in particular:
- Maceration of the skin surrounding the anal area
- Anal skin whitening (due to moisture in the area)
- Bedsores
- Increased risk of urinary tract infections
- Anal and / or genital itching
- Anal ulcers (infrequent)
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of "fecal incontinence begins with a" thorough medical history: here, the doctor will ask the patient specific questions regarding the frequency of evacuation, eating habits, the presence of any pathologies, the use of drugs and symptoms .
The anamnesis is important to frame the patient and put a first diagnostic hypothesis on the cause of fecal incontinence. In fact, only by going back to the cause will it be possible to cure the root disorder.
However, the "medical history" must be supported by a physical examination (digital rectal test) and possibly by a series of more in-depth diagnostic analyzes:
- Digital rectal examination, essential for analyzing any sphincter defects and rectal prolapse. The doctor introduces a finger (protected by a glove and lubricated) into the patient's anal sphincter to assess the strength of the muscles in the area and any abnormalities in the rectal site.
- Balloon expulsion test: the doctor introduces a special balloon filled with water into the patient's rectum, who is asked to expel it. Here, the doctor evaluates the time needed by the patient to expel the balloon: a time greater than one minute can be interpreted as a defecation anomaly / disorder.
- Anorectal manometry: useful test to evaluate the pressure exerted by the anal sphincters at rest and during contraction.
- Proctography or cine defecography: This test uses X-rays to estimate the amount of fecal material that the rectum can contain, while evaluating how the stool is expelled. To perform the test, a special contrast fluid is introduced into the rectum and bladder to opacify the organs of the pelvic floor: in this way, through a video recording, it is possible to observe the bowel movements of the subject during the expulsion of feces, thus allowing a global analysis of the intestinal expulsive dynamics.
- Proctosigmoidoscopy: an examination that involves the insertion of an endoscope into the anal canal, the sigma and the rectum to visualize the intestine and possibly detect pathological signs (such as inflammation) or scar tissue.
- Electromyographic tests, useful for ascertaining or denying possible alterations in the nervous system.
- Anorectal ultrasound: examination indicated to evaluate the structural patency of the anal sphincters.
The diagnostic tests described above can therefore clarify the cause of fecal incontinence and the severity of the condition.
More articles on "Faecal incontinence: symptoms, complications and diagnosis"
- Faecal incontinence
- Faecal incontinence: treatment, interventions and diet