Generality
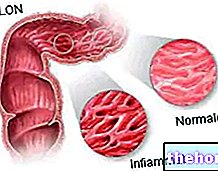
Duodenitis consists of an inflammatory condition that affects the initial part of the small intestine, called the duodenum.

In some cases, however, duodenitis can be the consequence of other pathologies affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
In the event that duodenitis is caused by other underlying pathologies, it is referred to as secondary duodenitis. If, on the other hand, the "duodenal inflammation is an" isolated "phenomenon and not dependent on other diseases in progress, we speak of primary duodenitis.
Causes
As mentioned, the triggering causes of duodenitis can be of different origins and nature. However, generally, duodenitis is a disorder related to an increase in stomach acid secretion (hyperchlorhydria). This increase, in turn, can be caused by various factors, among which we find the infections sustained by Helicobacter pylori, which can lead to the onset of gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Furthermore, duodenitis can occur in association with gastritis, so in these cases we prefer to talk about gastroduodenitis.
At the same time, inflammation of the duodenum can also be caused by taking certain types of drugs, such as, for example, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). In addition to this, factors such as stress and an incorrect diet can also favor the onset of this pathology.
Finally, chronic duodenitis can be associated with pathologies and intolerances, such as Crohn's disease, some forms of intestinal parasites (such as, for example, giardiasis) and celiac disease.
Symptoms
For further information: Duodenitis Symptoms "
The main symptoms that can occur in patients with duodenitis are:
- Pain in the upper abdomen;
- Abdominal swelling
- Nausea;
- He retched;
- Difficulty in digestion;
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Feeling of generalized malaise;
- Anorexia;
- Decrease in body weight.
In addition, in some cases, the typical symptoms of duodenitis can also be accompanied by the appearance of heartburn.
In the most serious cases, however, duodenal inflammation can favor the onset of lesions in the intestinal mucosa, with consequent haemorrhage.
Diagnosis
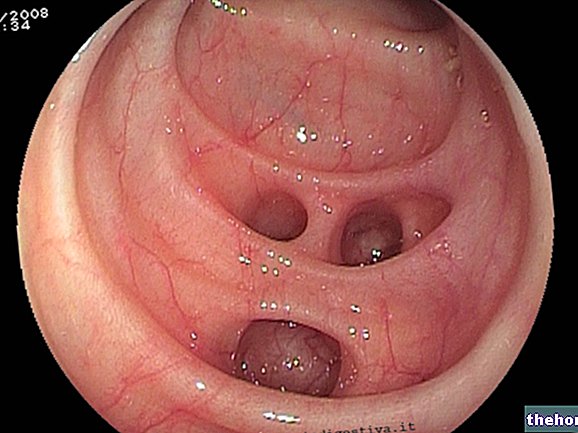
The diagnosis of duodenitis - in addition to the analysis of the symptoms afflicting the patient - can also be carried out by performing a gastroduodenal endoscopy with biopsy by a specialized doctor.
In this way, in fact, it is possible both to directly analyze the intestinal mucosa and to determine the presence or absence of a concomitant gastritis and / or peptic ulcer.
Treatment
The treatment of duodenitis varies according to the cause that caused it.
- In the event that the inflammation is caused by an excessive acid secretion from the stomach, one can proceed with the administration of antacid drugs (such as, for example, calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide) .
- If duodenitis is associated with gastritis and / or peptic ulcer, then the doctor may decide to intervene with the administration of gastroprotective drugs, such as proton pump inhibitors or H2 antihistamines (for more detailed information, please refer to the reading of the "dedicated article" Drugs for the treatment of gastritis and for the treatment of "peptic ulcer").
- In the event that the hyperchlorhydria that generated duodenitis was caused by bacterial infections sustained by Helicobacter pylori, the doctor will provide for the institution of a pharmacological therapy aimed at eradicating this pathogen. Generally, the eradication therapy of theHelicobacter pylori involves the administration of antibiotic drugs (such as amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole and / or tetracycline) in combination with gastroprotective drugs. In any case, for more information, we recommend reading the dedicated article already present on this site: "Triple therapy for the" eradication of Helicobacter pylori ".
- Finally, in the case of chronic duodenitis associated with diseases such as Crohn's disease, giardiasis or celiac disease, the doctor will establish the most suitable therapy (pharmacological or not) for the treatment of the primary causes underlying the onset of "duodenal inflammation:
- Crohn's Disease Cure Medicines
- Medicines for the Treatment of Giardiasis
Diet
In patients suffering from duodenitis, as well as in those who are at risk of developing it, the diet plays a fundamental role. In fact, in some cases, an incorrect diet is precisely the triggering factor for this "duodenal inflammation.
In this regard, patients with duodenitis should not consume foods that irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa, such as alcohol, coffee, spicy foods and carbonated drinks and should, instead, eat easily digestible foods, such as lean meat and fish, cereals and vegetables. Further advice is contained in the article: Diet for gastritis.
Finally, it would be good for patients suffering from duodenitis to also abstain from the habit of smoking.