Generality
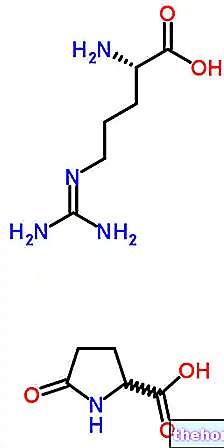
L-citrulline, or more simply citrulline, is a ubiquitous alpha-amino acid, present both in the human organism and in many plant species from which it is extracted.

However, the human organism is also an excellent source of citrulline, especially the intestine - which synthesizes over 90% of the organic citrulline content - and the liver, whose synthesis is achieved through the urea cycle. .
Precisely due to the appreciable endogenous biosynthesis, citrulline is classified among the conditionally essential amino acids.
In fact, there are particular conditions in which the need for citrulline rises to such levels that the body is no longer able to meet these needs. These are conditions such as short bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel diseases, malabsorption syndromes, cycle disorders. "urea and liver disease, all circumstances for which the dietary intake of citrulline becomes essential.
While not participating in protein synthesis processes, citrulline plays a key role in the organic economy, for:
- The antioxidant activity;
- Cardio- and vaso-protective activity;
- The detoxifying activity;
- The precursor activity of arginine.
These properties will influence the clinical use of citrulline.
Indications
Why is citrulline used? What is it for?
For several years now, citrulline has been actively used in both clinical and sports fields.
In addition to the antioxidant activity, others, of different nature, have been added, which have facilitated the spread of citrulline supplements.
To testify the enormous interest of the scientific community towards this amino acid derivative, there is the growing number of studies on orinitine, published by the most prestigious international universities.
At the moment, with due doubts and with many fields still to be clarified, citrulline would seem useful in:
- Treat and prevent hypertension;
- Improve the metabolic picture in the course of metabolic syndrome;
- Reduce cardiovascular risk;
- Improve protein metabolism in particular conditions, such as sarcopenia, autoimmune diseases and inflammatory bowel diseases;
- Treat some urea cycle disorders;
- Delay the complications of degenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis.
To the aforementioned activities, others would be added, still much discussed and not entirely supported by noteworthy scientific evidence, such as:
- The performance improvement activity;
- The beneficial action in the course of erectile dysfunction.
Properties and Effectiveness
What benefit has citrulline shown during the studies?
Given the huge amount of scientific work currently published, it is not easy to summarize all the biological potential of citrulline, supported by strong evidence.
In general, however, it is possible to clearly describe some of the main activities of this molecule.
Citrulline and antioxidant activity
Initially observed on plants, in particular on watermelon (fruit with a high content of citrulline), the antioxidant action probably represents the first biological activity studied for this amino acid.
The intake of citrulline, but actually also of watermelon and watermelon seeds, would seem, both in experimental models and in clinical trials, to protect the organism from the harmful action of the reactive oxygen species.
Through complex molecular mechanisms, many of which are not fully characterized, citrulline could act as a direct scavenger against oxygen free radicals, protecting macromolecules, such as DNA and membrane lipids, from any structural and functional damage.
The antioxidant activity seems to be co-responsible for the cardioprotective action of this molecule.
Citrulline and hypertension
Nitric oxide is known as one of the most important vasodilating agents, therefore having a natural antihypertensive activity.
Many studies have shown how the production of nitric oxide can be supported by the adequate presence of Arginine.
However, integration with Arginine, due to the numerous metabolic processes that this amino acid undergoes following its intake, does not seem to determine an appreciable increase in the concentrations of this molecule.
According to very recent studies, the use of citrulline could exert an antihypertensive action, acting precisely on this path.
Following the ingestion of citrulline, both in experimental models and in some clinical trials, an increase in plasma arginine concentrations and an "increased activity of the endothelial enzyme responsible for nitric oxide synthesis were observed.
All this would result in a vasodilation induced by citrulline, potentially valuable in case of hypertension.
Citrulline and erectile dysfunction
Along the lines of what has just been described for hypertension, the use of citrulline, precisely through the induction of nitric oxide, could also play an important role in the management of conditions such as erectile dysfunction.
Although there is no unanimity regarding the clinical efficacy of citrulline, in some clinical trials, still very small in number, the daily use of citrulline would have resulted in an improvement in the clinical picture in patients with mild erectile dysfunction.
For further information: Citrulline and Erectile Dysfunction.
Citrulline and protein synthesis
Some studies, mostly of an experimental nature, have shown the anabolic activity of citrulline.
In spite of what is widely advertised, the anabolic and anticatabolic activity of citrulline would have been observed only in some particular conditions such as:
- Sarcopenia;
- Cachexia;
- Inflammatory bowel disorders;
- Malabsorption syndromes.
Under these conditions, the use of citrulline would have improved the hormonal profile on the one hand and, on the other hand, increased the rate of protein synthesis.
Citrulline and sport
The beneficial properties of citrulline in sports are also in this case to be traced back to the "increase in plasma concentrations of arginine, following the" ingestion of citrulline.
The increased bioavailability of arginine could result in:
- An increase in critical power;
- A generalized improvement in performance;
- A reduction in recovery times;
- The reduction of muscle damage markers following intense physical training.
However, the anabolic potential of this amino acid in relation to muscle mass, and more precisely protein synthesis, remains to be clarified. For further information: Integration of Citrulline in Sports Practice
Dosage and method of use
How to use citrulline
The dose of citrulline most used in the various studies, both athletic and clinical, is that of 3 grams per day, although there are works with higher dosages.
However, the presence of a suggested dose is not sufficient to identify an optimal dose, which can vary from user to user depending on the needs, physical characteristics and physio-pathological conditions.
Side effects
The use of citrulline, even in high doses, is generally well tolerated.
Gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and cramping abdominal pain have been described following the use of disproportionate doses of this supplement.
Contraindications
When should citrulline not be used?
The use of citrulline is contraindicated in subjects hypersensitive to the active ingredient or allergic to the source of extraction.
Pharmacological interactions
What drugs or foods can modify the effect of citrulline?
No notable drug interactions are currently known between citrulline and other active ingredients.
Precautions for use
What do you need to know before taking citrulline?
The use of citrulline supplements for clinical purposes should always be discussed with your physician.
Given the absence of studies concerning the long-term safety profile of this amino acid, the use of citrulline supplements is generally contraindicated during pregnancy and in the subsequent breastfeeding period.