What are
Whey protein is the English name for "whey protein", a powdered protein mix obtained from the liquid - called buttermilk, whey or whey - obtained from the processing of cheese.

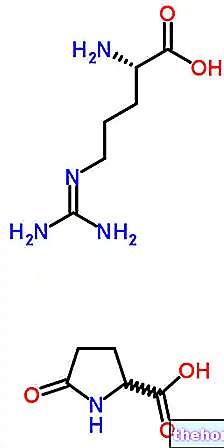
Whey is particularly rich in proteins of the same name, which represent the most precious protein fraction of this food. Their biological value is in fact extremely high, as are the other protein quality indices.
A few lines ago we talked about protein mix because whey proteins are made up of various types of proteins, in particular beta-lactoglobulins (~ 65%), alpha-lactalbumin (~ 25%), serum albumins (~ 8%) and immunoglobulins .
What are they for
Whey proteins find a "wide range of applications, ranging from" the food industry (they are a common additive, especially in confectionery foods, such as pastries, creams, puddings and baked goods) to the zootechnical one. However, it is in the food supplement sector that whey proteins find their best-known application. Compared to other protein sources (eggs, soy, wheat, casein, etc.), in fact, whey boast some peculiar characteristics:
- high content in branched chain amino acids;
- superior biological value due to the excellent presence of essential amino acids;
- high digestibility with rapid increase in postprandial plasma amino acid concentration.
Thanks to these characteristics, Whey proteins:
- provide the substrates necessary for protein synthesis (in which some B vitamins commonly added to whey protein supplements participate);
- suppress protein catabolism;
- promote recovery after strenuous training;
- act as a substrate for gluconeogenesis (production of energy starting from some amino acids, which becomes important in prolonged fasting and physical activity of duration);
- stimulate protein synthesis and promote muscle growth; increase insulin release, decreasing postprandial blood glucose.