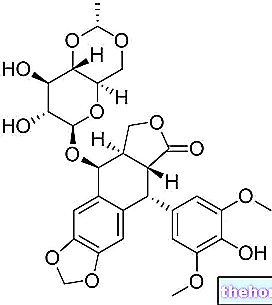
TTX and puffer fish
Puffer fish is a typical delicacy of the Eastern world, in particular of Japan; on the other hand, it is bizarre to consider this dish as a delicacy, given that the fish in question contains the very dangerous TTX or tetradotoxin. Not surprisingly, the consumption of puffer fish has been prohibited by Italian law since 1992.

The TTX toxin was isolated for the first time in 1909 by a Japanese scientist, after which it was necessary to wait until 1964 to definitively discover its mechanism of action, thanks to the scientists Toshio Narahashi and John W. Moore.
TTX and ecstasy
Although it is now well known the absolute danger of TTX, some "lovers" of fish and at the same time contemptuous of the danger, going to Japanese restaurants, like to perceive the numbness of the lips or tongue by eating a small fragment of puffer fish liver containing the deadly toxin. In doing so, many cases of "accidental" death from diaphragm paralysis and respiratory failure were recorded. [adapted from Neuroscience. Exploring the brain, by Mark F. Bear, Barry W. Connors, Michael A. Paradiso]
In any case, the propaganda about the extreme toxicity of the tetradotoxin of puffer fish does not seem to worry these fish lovers excessively, quite the opposite: nevertheless, in fact, the demand for "culinary delicacy" does not tend to diminish. In Japanese restaurants - where this meat is consumed on the agenda - a sort of special license is required, in order to instruct the cooks in the careful and meticulous preparation of fish, rendering it harmless.
TTX is contained in the liver and ovary of puffer fish, while in meat the amount of TTX is almost zero or scarce.
Generality
We have seen that tetrodotoxin is a powerful and dangerous neurotoxin, capable of killing a man even at very low doses; tant "it is true that TTX is considered even more dangerous than cyanide (100 times more toxic than potassium cyanide).
After the ingestion of just 1 milligram of tetradotoxin, a series of chain events is unleashed in the organism that inexorably leads to death: the voltage-dependent sodium channels placed on the surface of the nerve membranes are blocked by the very strong bond established with the tetrodotoxin, which mimics the sodium cation (positively charged). Under normal conditions, the bond between the cation and the channel is quantified in a nanosecond: when TTX replaces sodium, the bond persists for 10 seconds. Obviously excessive time. Consequently, sodium is denied the possibility of entering the canal, so the membrane action is abruptly stopped.
TTX: lethal dose

As we have seen, comparing potassium cyanide to TTX, it has been observed that the latter is 100 times more dangerous and toxic; moreover, tetradotoxin has also been found to be more powerful than the venom of the black widow and some South Asian snakes. .
TTX poisoning
TTX poisoning begins with mild numbness of the tongue and lips after 20 minutes or 3 hours of ingesting the toxic fish. Later, paresis of the face and lower and upper extremities begins, accompanied by dizziness, shortness of breath, tinnitus, irregular heartbeat, and possibly nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
The symptoms of TTX poisoning continue with a progressive worsening of the paralysis, followed by movement disorders and breathing difficulties. The patient, at this stage of intoxication, appears pale, has marked hypotension and difficulty in expressing himself.
In the final stage, the paralysis becomes more and more marked, the affected subject shows convulsions, cardiac arrhythmias and mental imbalances of various degrees.
Death arises after 20 minutes / 8 hours (especially after 4-6 hours) from the "ingestion of poisoned meat: sometimes, the patient remains conscious until a few moments before dying [taken from www.acquaportal.it]
Incidence
From 1974 to 1983, as many as 646 cases of tetrodotoxin poisoning were observed in Japan, including 179 victims. In the habitable areas of the Pacific, on the other hand, there have been very few victims of TTX.
Currently, estimates report around 200 cases of poisoning, with a mortality of around 50%.
The "zombizing" practice carried out in Haiti is curious: some sorcerers exploit the zombie powder (zombie powder, made from puffer fish) in some bizarre voodoo rituals, in order to reduce the adepts to a state of trance.
Therapies
Unfortunately, no truly effective antidote has been devised; however, a possible antivenin in mice has recently been formulated and is still being tested.
After the ingestion of fish containing the TTX toxin, immediate gastric lavage is necessary and indispensable, followed by the intake of molecules capable of binding the toxin (activated charcoal).
When the ingestion of tetradotoxin is accompanied by a marked reduction in blood pressure, it is recommended to take intravenous alpha-adrenergic agonist pharmacological substances in physiological solution.
It is important to monitor the breath and heartbeat of the intoxicated patient: when necessary, practice artificial respiration and cardiac massage. In case of severity, patients are admitted to intensive care for assisted ventilation.
In the medical field, TTX is used to isolate and clone the sodium channel.
Tetradotoxin in brief »
Fish, Molluscs, Crustaceans Anchovies or Anchovies Garfish Alaccia Eel Lobster Herring Lobster Whitebait Bottarga Sea bass (Sea bass) Squid Canocchie Scallops Canestrelli (Sea scallops) Capitone Caviar Mullet Monkfish (Monkfish) Mussels Crustaceans Dates Sea Fruits Fish Flour Fauna Fish stock Prawns Crabs Spider crab (Granceola) Halibut Sea salad Lanzardo Leccia Sea snails Prawns Cod Molluscs Octopus Hake Ombrina Oysters Sea bream Bonito Pangasius Paranza Anchovy paste Fresh seasonal fish Blue fish Puffer fish Swordfish Plaice Octopus (Octopus) Hedgehog of Sea Amberjack Salmon Sardines Sardines Scampi Cuttlefish Mackerel Sole Stockfish Surimi Sushi Telline Tuna Canned tuna Mullet Trout Fish roe Bluefish Clams OTHER FISH ARTICLES Categories Alcoholic Food Meat Cereals and derivatives Sweeteners Sweets Offal Fruit Dried fruit Milk and derivatives Legumes Oils and fats Fish andpeach products Salami Spices Vegetables Health recipes Appetizers Bread, Pizza and Brioche First courses Second courses Vegetables and Salads Sweets and Desserts Ice creams and sorbets Syrups, liqueurs and grappa Basic preparations ---- In the kitchen with leftovers Carnival recipes Christmas Light diet recipes Women's, mom's and dad's day recipes Functional recipes International recipes Easter recipes Celiac recipes Diabetic recipes Holiday recipes Valentine's Day recipes Vegetarian recipes Protein recipes Regional recipes Vegan recipes