Nausea after eating can represent the consequence of large binges, or it can appear in the presence of certain pathologies affecting the gastrointestinal tract, as well as a symptom connected to other particular conditions (poisoning, food intolerances, etc.).
The treatment of nausea after eating depends substantially on the cause that triggered it, although, in some cases, the symptom could also resolve spontaneously.
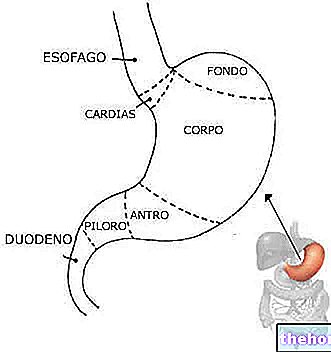
and which can also involve the back of the throat.Nausea after eating, given the particular moment in which it occurs, is generally related to diseases or disorders of the digestive system or nutrition and can occur in individuals of any sex and age (adults, children and the elderly).
d "air during the meal (a condition that mainly occurs when you eat too quickly).
Often and willingly, all the above conditions occur simultaneously with a consequent increase in the risk of onset of the symptom in question.
In other cases, however, nausea after eating could be connected to various types of digestive system diseases, such as, for example:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- Gastritis;
- Peptic ulcer;
- Hiatal hernia;
- Esophagitis;
- Gastroenteritis;
- Gallbladder stones
- Infectious diseases (infectious gastroenteritis).
Nausea after eating can also indicate the presence of food allergies or intolerances; just as it could represent the symptom of food poisoning or poisoning.
Also not to be excluded is the possibility that the symptom may be caused by taking certain types of drugs for which nausea is a known side effect.
In addition, nausea after eating is a symptom considered very common in pregnant women, in particular, during the first trimester of gestation.













.jpg)