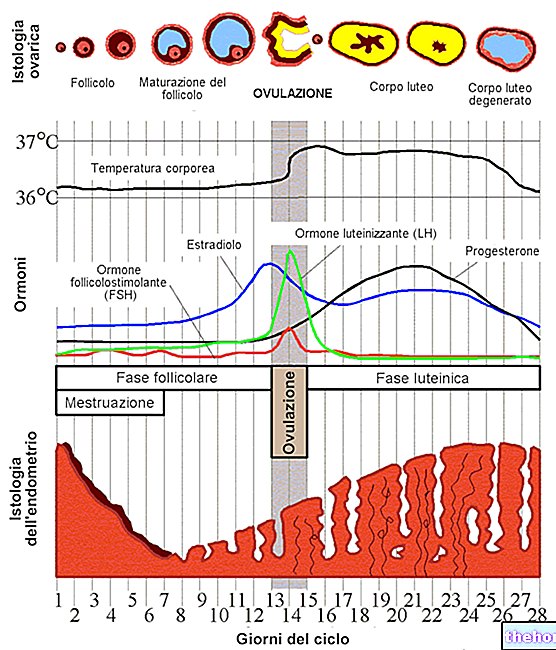
Vomiting is an unpleasant symptom which consists in the rejection of gastric contents outside the body.
The material is expelled in the opposite direction to the norm, ie through the esophagus and mouth.
Sometimes, vomiting is preceded by nausea.
The physiological mechanism that causes vomiting could be simplified into three steps: stimulation of the cerebral emetic center, preparation of the sphincters and muscles, consequent inverse peristalsis.
The causes of vomiting are many; among the most common and least serious we remember:

- Acute and chronic diseases, anatomical compromises and infections of the digestive system.
- Motion sickness (motion sickness), abnormal vestibular nerve stimulation and labyrinthitis. (injury to the inner ear).
- Constipation / gastrointestinal blockage, food intolerances, poisoning (including alcohol and drugs) and poisoning.
- Prolonged fasting (feeling of emptiness in the stomach, hypoglycemia, low blood pressure).
- Emotionality (anxiety, panic, disgust, etc.).
- Pregnancy.
Vomiting does not allow you to eat and drink properly.
If prolonged, it alters the nutritional status of the subject; consequently arise: dehydration, hypotension, hypoglycemia, hypokalaemia, etc.
In particular circumstances, vomiting can have even more serious consequences (esophageal bleeding, etc.).
The published material is intended to allow quick access to general advice, suggestions and remedies that doctors and textbooks usually dispense for the treatment of Vomiting; such indications must in no way substitute the opinion of the attending physician or other health specialists in the sector who are treating the patient.
.
- Exclusion of products that can cause food intolerance (lactose or gluten)
- Reduction of the total volume of meals. Portions and individual bites should be moderate.
- Respect a chewing rhythm and a minimum time within which to consume the meal.
- Prefer digestible foods (from a chemical and physical point of view).
- Go to bed at least one hour after the main meals and prefer the armchairs over the bed (at least during the day).
- If there is a loss of control over food (typical of some eating disorders), vomiting can be spontaneous or self-induced. In both cases it is advisable to rely on a specialized medical center.
- Taking anti-emetic drugs.
- Eating dry and digestible foods.
- Focusing on the vehicle's trajectory by anticipating deviations, focusing on the road, the horizon or a stationary object.
- It should be possible to drive the means of transport.
As there is no cure for labyrinthitis, the resulting vomiting can be fought with antiemetic drugs and bed rest.
- In pregnancy and in all cases of vomiting triggered by emotional or psychological reasons, in addition to following an adequate diet, it may be necessary to adopt one or more of the following options:
- Advanced relaxation techniques and mental training.
- In agreement with a therapist, perform psychotherapy.
Better to avoid:
- Lack of sleep (it is not recommended to rest in a prone position and / or with the head down).
- Heavy work (including housework).
- Sport activity.
- Unpleasant or exhausting family duties.
- Excessive mental commitments.
- Long stays closed, crowded, noisy, hot or polluted.
NB. In case of unconsciousness it is necessary to place the body on its side to prevent choking from vomiting.
Furthermore, it is recommended to avoid:
- Drink large quantities of water, beverages or liquid food.
- Eating large quantities of food, quickly, chewing little, preferring foods that are poorly digested or containing molecules that irritate the stomach.
- Fast.
- Take useless medicines or medicines responsible for the onset of vomiting.
- Smoking, using drugs (even light drugs) and drinking alcohol.
- Move by public transport or in the back seat of the car.
The most suitable foods are:
- Lean crust, crackers, wasa bread, unsalted lean crackers etc.
- Rice and pasta.
- Potatoes, carrots and green beans.
- Hulled legumes.
- Bananas.
The most suitable cooking systems are:
- Affogatura (boiling in water), also vacuum packed.
- Steam powered
- In a pressure cooker
- Vasocooking.
Cooking in a pan over moderate heat and in the oven MA in foil are also allowed.
Functional foods that are hypothetically capable of reducing nausea are:
- Fresh ginger.
- Licorice root or extract.
- Coca-cola (although it is not clear why).
- Ginger ale (it is a ginger-based drink).
- Specific herbs and herbal teas allowed during pregnancy (see below).
Some suggest the use of mint, even though it is one of the foods not recommended for gastroesophageal reflux.
, dietary fiber, raw or overcooked (especially meat).The least recommended products are:
- Fatty meat broth.
- Whole milk and full-fat cheeses.
- Cured meat.
- Oily and / or stewed or fried meats and fish.
- More than two eggs at a time (especially in omelette).
- Fried vegetables.
- Creamy or fatty desserts.
- Sweet and savory snacks.
- All foods that are too salty or rich in chilli and pepper.
- Chocolate.
- Mint.
- Coffee.
- Alcoholic beverages.
NB. Products marked with an asterisk (*) are those that are potentially inconvenient for the pregnant woman.
- antispasmodics for the treatment of vomiting: Meclizine, Trimethobenzamide and Scopolamine.











.jpg)