Premise
When it comes to "genital infections"We immediately refer to venereal diseases, that group of sexually contracted infections in which we are witnessing an" exchange "of pathogens, whether these are

Causes
Genital infections affect a good portion of the sexually active population, both men and women; however, sexual contamination is not the only possible route of transmission, since genital infections can also be an expression of the mixed use of previously infected underwear, towels or sheets. Again, genital infections can be transmitted during childbirth. therefore by maternal-fetal way: the infected mother can pass the infection to the unborn child during its passage through the birth canal.
- The areas most affected by genital infections in WOMEN are represented by: vagina, vulva, cervix, endometrium, pelvis, fallopian tubes, urethra.
- In MAN, on the other hand, the genital areas most involved in infections are the glans penis, the foreskin, the testicles, the epididymides, the urethra, the prostate, the ejaculatory ducts and the seminal vesicles.
Often times, unfortunately, the infection bursts in one site and soon spreads to other areas of the lower genital tract: for example, "orchitis in men" (infection of the testicles) often also involves the epididymis, so we prefer to speak of orcs-epididymitis.Similarly, in women, vaginal infection tends to spread rapidly even in the vulva, for this reason it would probably be more correct to speak of vulvovaginitis rather than vaginitis: it is, in fact, difficult to circumscribe the infection in a single location.
Names of genital infections
All genital infections, both male and female, must not be trivialized, since they can degenerate to compromise - in some cases - the patient's fertility.
Cause table
Genital infections are the expression of a bacterial, viral or fungal insult which, as analyzed, is favored by sexual contact with carrier patients. Pathogens are therefore the protagonists of genital infections; now let's see the microorganisms most involved in the different genital infections:
Mobiluncus spp.
Gardnerella vaginalis
Mycoplasma hominis (typical of vaginitis and pelvic inflammatory disease)
Candida albicans (constitutes 20-30% of all female genital infections)
Trichomonas vaginalis
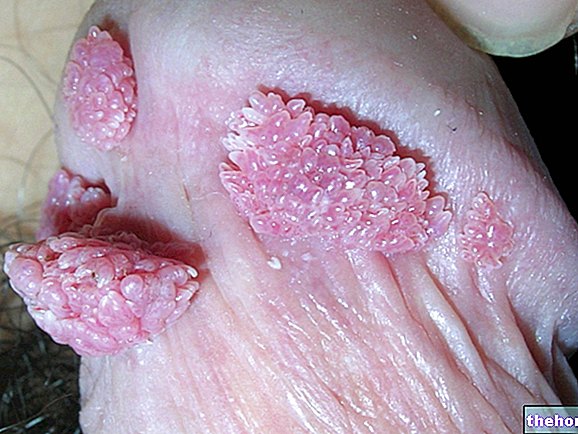
HPV
Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria
Fungi (fungi)
Parasites
Virus
Mycoplasma genitalium and M. hominis
Bacteria
HPV
Herpes genitalis
Virus
Virus
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea)
Chlamydia trachomatis (chlamydia)
Trichomonas vaginalis (trichomoniasis)
Candida albicans
Bacteria
Bacteria
Protozoa
Mushrooms
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Mycoplasma hominis
Bacteria
Bacteria
Streptococci, Staphylococci, Escherichia Coli and gram negative in general
Bacteria
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea)
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus
Gardnerella vaginalis
Candida albicans
Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria
Fungi
Trichomonas vaginalis
Herpes simplex
Sarcoptes scabiei hominis (scabies)
Candida albicans
Protozoa
Virus
Mites
Fungi
Chlamydia trachomatis
Brucella abortus (brucellosis)
Epstein-Barr Virus (mononucleosis)
HAV, HEV, HBV, HDV, HCV (hepatitis)
Bacteria
Bacteria
Virus
Virus
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea)
Chlamydia trachomatis
Candida albicans (rare)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis o Koch's bacillus (tuberculosis)
Bacteria
Bacteria
Fungi
Bacteria
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcal urethritis)
Chlamydia trachomatis
Herpes simplex
Ureaplasma urealyticum
Bacteria
Bacteria
Virus
Bacteria
Chlamydia trachomatis
Escherichi. coli
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria
Neisseria gonorrhea
Streptococci in general
Staphylococci in general
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis)
Trichomonas vaginalis
Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria
Protozoa
Preventing genital infections
Prevention is the ideal premise for avoiding genital infections: first of all, attention to using specific contraceptive methods, including condoms, is certainly the most effective and intelligent option to choose in the event of sexual intercourse with at risk partners. As obvious as it is, it should be stressed that taking the birth control pill does NOT protect against sexually transmitted diseases.
In addition to respecting this simple sexual behavior, even intimate hygiene plays a prestigious role: banned excesses, referring to both infrequent washing and baths repeated over and over again throughout the day. Scarce and occasional washing - especially if carried out with aggressive, excessively perfumed and cheap detergents - increase the risk of pathogenic proliferation, alter the regular genital bacterial flora and the physiological pH of the intimate parts, predisposing the subject to pathogenic attacks. Speaking of excesses, it is recommended to avoid frequent washing, since detergents, however delicate, alter the physiological pH of the female and male genitals, eradicating the lactobacilli that live in symbiosis with man, protecting him from infections.
Intimate hygiene should be perceived almost as a duty by sexual partners, especially following an intercourse.
But that's not all: it seems that even clothing can, in some way, predispose the subject to attacks by microorganisms: many women tend to wear synthetic underwear and particularly tight clothing. Similar attitudes increase the risk of genital infections by altering the physiological genital ecosystem which, inevitably, is made more susceptible to pathogens.
Genital Infections - Symptoms and Treatments "