"Pancreatitis
Complications
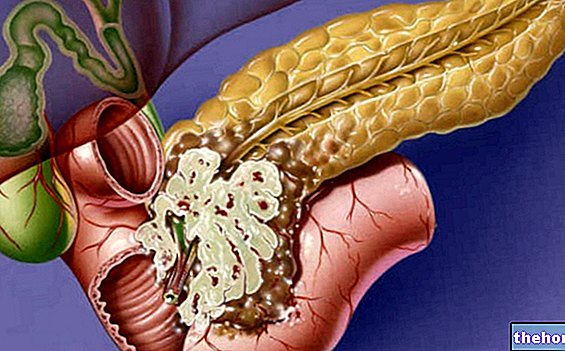
Without treatment, pancreatitis is a rather disabling and life-threatening condition. In acute forms, for example, respiratory problems, renal insufficiency and pancreatic pesudocysts (cavities caused by necrotic processes, which fill with liquids with the risk of rupture and infection) may arise.

Diagnosis
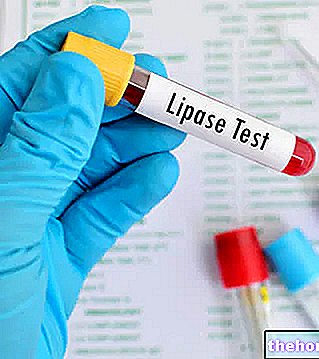
The diagnosis of pancreatitis can make use of blood tests, faeces and instrumental tests. The serum assay of amylases and lipases is very useful for diagnosing pancreatitis, given their characteristic increase in similar circumstances. Often, given the frequent obstructive etiology, the values of Gamma-GT, serum aspartate transferase or AST (SGOT), bilirubin and lactate dehydrogenase are also elevated; sometimes jaundice is present. The rise in blood sugar is often a consequence of pancreatitis, while that of triglyceridemia is more often a contributing cause.
A low concentration of the pancreatic enzymes trypsin and chymotrypsin may be noted in the stool.
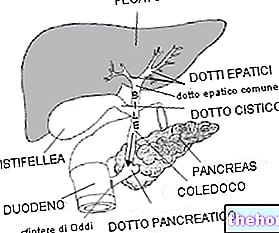
The test for stimulation of the exocrine pancreas with the secretin hormone is useful, especially in chronic forms. For diagnostic purposes, abdominal or endoscopic ultrasound, coumputerized tomography (CT - TAC), magnetic resonance and l "are also used. ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography).
Care and treatment
For further information: Medicines to treat Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, unlike chronic pancreatitis, tends to heal if the cause is removed. Its treatment very often requires hospitalization of the patient; the first therapeutic interventions aim at resolving the inflammatory process, putting the pancreas at rest. For this purpose, oral feeding is suspended for a few days, followed by the slow and gradual reintroduction of food. . At the same time it may be necessary to administer intravenous fluids via drip, and a nasogastric tube to prevent gastric juices from entering the duodenum, stimulating pancreatic activity. The use of pain medications aims to mitigate the pain, often particularly violent, while antibiotic prophylaxis is aimed at preventing any infections of damaged pancreatic tissue.
Once the inflammatory process is under control, treatment moves to the causes that produced the pancreatitis. It may therefore be necessary to remove any stones in the biliary tract, often performed through the aforementioned ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography), which consists in the descent of a tube orally until it reaches the extrahepatic biliary tract. Thanks to the aid of a video camera mounted at the apex and the possibility of sliding very thin surgical instruments inside it, if necessary this technique allows for therapeutic maneuvers such as the removal of stones or the restoration of the patency of occluded canals).
In the treatment of pancreatitis, surgical therapy can also be used, with the removal of the necrotic pancreatic tract (subtotal pancreatectomy) or the drainage of the fluids accumulated within it. The removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) can instead be performed in the case of stones with the risk of new episodes of obstructive pancreatitis.
Very important - especially in the chronic forms, where alcohol is the most common causative agent - is the definitive removal of alcoholic beverages from one's diet. For this purpose, it may be necessary to enter specific psychotherapeutic groups for alcohol addiction.
In chronic pancreatitis with gland insufficiency, pancreatic extracts (pancreatin) are administered at each meal to allow for the normal completion of digestive processes. The diet, in the name of sobriety, should be particularly low in fat, with a preference for fresh fruit and vegetables, whole grains, seeds and lean proteins. In the presence of pancreatitis, smoking cessation is equally important.
More articles on "Pancreatitis: Diagnosis, Treatment and Treatment"
- Pancreatitis
- Pancreatitis - Medicines for the treatment of pancreatitis
- Pancreatitis diet