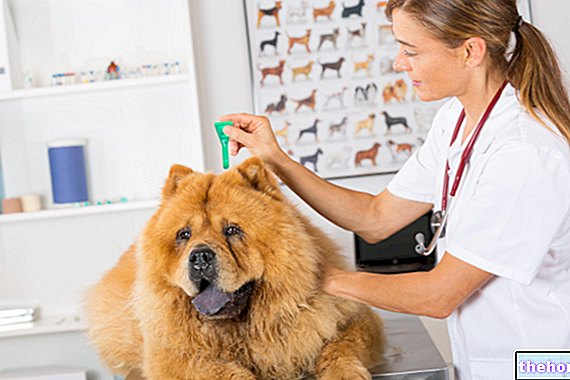
The term "Ringworm" indicates one of the most common superficial mycoses in dogs and cats found all over the world. Ringworm takes the name of dermatophytosis if we refer to its pathogen: dermatophytes. They have a high transmission capacity between animals and from animal to man, becoming one of the most common zoonoses.
caused by a filamentous fungus capable of using the keratin present on the animal's skin as the only source of energy. The fungus, arriving on the animal, invades the hair bulb and obtains the energy necessary for its proliferation in the form of fungal hyphae, called macroconidia; in particular conditions to facilitate its transmission it can assume more resistant forms: the spores or arthroconidia.
The most isolated dermatophytes in dogs and cats are the Microsporum canis (especially in the cat), the Trichophyton mentagrophytes, the Microsporum gypseum and the Microsporum (Ninnizzia) persicolor. The first two deserve particular attention as pathogens of zoonoses, therefore capable of being the cause of the dermatological pathology in the owners of infected dogs or cats.
and make the subject more vulnerable.
The conditions that facilitate the proliferation of the fungus can be:
- a immune system Not still quite qualified, as in very young subjects, or debilitated, in elderly subjects
- the presence of skin lesions or parasites, which alter the barrier system of the skin and can cause itching with consequent self-trauma
- too frequent washing, which alter the sebum present on the skin for protective purposes
- the concomitance of immunosuppressive pathologies or debilitating. In cats, it may be associated with retrovirus infections such as feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) and feline leukemia virus (FeLV).
- treatment with immunosuppressive drugs
- the lifestyle of the animal, being facilitated a transmission in environments of cohabiting cats and dogs
- environmental conditions of temperature and humidity
All breeds of dogs and cats are susceptible to the presence of dermatophytes, but Dalmatian, Poodle, Jack Russel Terrier, Manchester Terrier and Yorkshire Terrier dogs can more easily develop generalized symptoms. For cats it is thought that the Persians and other long-haired breeds help the proliferation of the fungus, even if no real breed predisposition has been found.
For further information: Ringworm in cats peripherals still healthy. The lesions usually affect the front part of the body: legs, snout and ears are the first sites of development, but it is easy to see lesions also in other points due to the transport of the fungus by the animal through licking.
A particular condition of the cat is that of being able to develop asymptomatic forms, to be considered in cases of infection of cohabiting dogs / cats and dermatological lesions of the owner, in which the animal has the role of carrier of the fungus without developing dermatological symptoms.
Ringworm is not a primarily itchy disease: itching can occur due to secondary infections or predisposing factors. While this is the rule, itchy lesions can be found in adult cats with moderate to severe itching.
Often further symptoms of skin progression are observed due to the inflammation created by the fungus. Inflammatory scales and crusts, pustules or papules may be visible, up to moist and exudative lesions caused by bacterial participation.
, registered for the cat in liquid formulation, is the first choice for its safety of use. The therapeutic protocol is given by administering the drug every other week for at least three cycles.Topical treatments require the owner to be willing to perform sponging on alopecic lesions at least twice a week, focusing mainly on the peripheral hair. There are numerous products on the market in liquid form, spray or antifungal sponges, for which the hair clipping can be proposed for greater ease and effectiveness of action.
A treatment becomes effective if carried out for the right amount of time. These antifungal therapies in fact need a time of almost two months and it is important to terminate after receiving the result of two negative cultures. If after 8 weeks the treatment has not yet had an effect, the veterinarian will evaluate the investigation of the case for any concomitant pathologies.
environmental and contaminated objects can be carried out with the use of sodium hypochlorite solutions (household bleach) diluted in water with a ratio of 1:10 or with solutions of enilconazole. The latter exist in fumigant formulations, but are not authorized for domestic use or catteries and kennels.

.jpg)