The result is basically an enlarged prostate, which is responsible for the appearance of urinary symptoms.
In the long run, if neglected, benign prostatic hyperplasia can cause anatomical obstruction of the urethra and create problems with correct urinary outflow, so much so that the subject must increase the pressure necessary to empty the bladder. Other symptoms rather indicative of hyperplasia benign prostatic glands are the urgency and frequency of the day and night urge to urinate, the burning sensation in the penis during and after urination, the weakness of the urinary stream and the sense of incomplete bladder emptying.
.jpg)
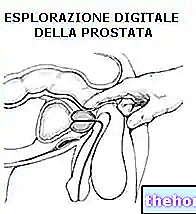
The doctor, after confirming the diagnosis with a visit and some specific clinical tests, can indicate, according to the various situations, a pharmacological or surgical treatment.
that constitute it.
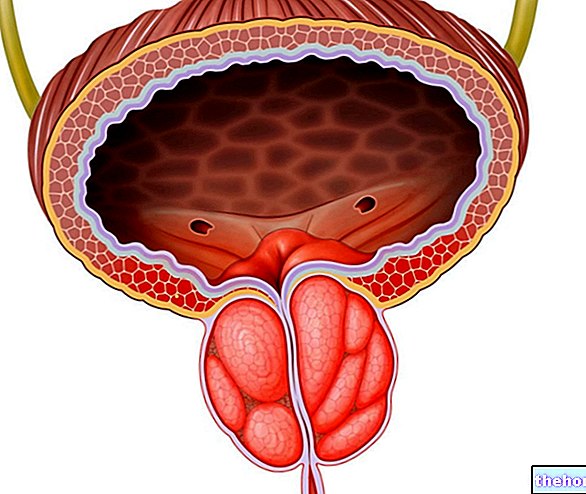
The most important aspect to underline is that prostate enlargement is caused by a physiological, completely benign proliferation. Unlike a tumor, in fact, benign prostatic hypertrophy compresses the surrounding tissues without infiltrating them and originates mainly from the central portion of the gland.
In people suffering from benign prostatic hyperplasia, the prostate can be up to two or three times its normal size. After several years and without treatment, this gland can even grow to the size of a grapefruit.
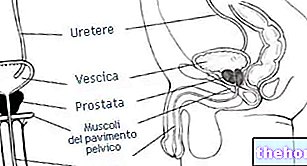
It should be remembered, in fact, that the prostate is placed like a sleeve around the urethra, the channel that carries urine from the bladder to the outside. It is therefore not surprising how the increase in volume of the prostate ends up compressing the urethra. causing problems in the passage of urine, thus causing various annoying symptoms affecting the urinary tract.