Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
Hyperthyoridism causes an increase in oxygen consumption and metabolic heat production. Thyroid hormones are in fact thermogenic and, while their defect is often the basis of a pathological overweight, an excess is correlated to disorders such as hypersweating, tremors, intolerance to heat and excessive thinness.
The clinical picture of hyperthyroidism is quite varied and, in addition to the symptoms described above, it includes numerous disorders, largely related to the increased metabolic activity.The skin of a hyperthyroid patient is hot due to the increased blood flow and peripheral vasodilation, with which the body tries to disperse the excess thermal energy produced.

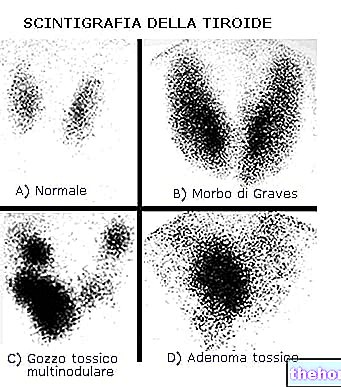
Hyperthyroidism, like hypothyroidism, is often associated with goiter, ie a significant increase in the volume and weight of the thyroid.
An excess of thyroid hormones increases protein breakdown and can cause asthenia (muscle weakness). The scalp also suffers from this condition and the hair, fragile and thin, tends to lose its natural waves becoming straight; frequent alopecia.
Hyperthyroidism affects the activity of the central nervous system, causing psychological disturbances such as nervousness, agitation and insomnia, to the point of causing a real psychosis.
As for the repercussions on the cardiovascular system, hyperthyroidism is associated with an increase in heart rate (tachycardia), and in the force of contraction of the heart. Hypertension is also observed, often associated with hypertrophy of the left ventricle.
Other minor signs of hyperthyroidism include: irregular menstruation, infertility in both males and females, decreased libido, gynecomastia in 5% of males, conjunctivitis, thin but not atrophic epidermis, periorbital edema and extra ocular muscle dysfunction. evident associated with ocular disorders is "exophthalmos, or the protrusion of the eyeballs that gives the patient an" apprehensive and frightened expression.
. The organism produces antibodies called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins or TSI which, by combining with specific TSH receptors, mimic their action, stimulating hormone production, resulting in goiter and the onset of the symptoms described above. After diabetes, hyperthyroidism due to Graves-Basedow's disease is the most common endocrinological disease, mainly affecting women between the ages of 20 and 40.
Hyperthyroidism therapy is closely linked to its root cause. Partial or total removal of the glandular body (thyroidectomy) or the use of marked iodine therapy (capable of selectively destroying abnormal thyroid cells) may be required. Pharmacological treatment is based on the use of thyrostatic drugs, able to block hormone synthesis (substances related to thiourea) or block the peripheral conversion of T4 (inactive form) into T3 (active form).
Hyperthyroidism - Video: Causes, Symptoms, Cures
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to Wellness Destination
- Watch the video on youtube
Other articles on "Hyperthyroidism"
- Hypothyroidism
- Thyroid
- Diseases of the thyroid gland
- Thyroid hormones
- Actions of thyroid hormones: thyroxine and triiodothyronine
- Thyroid hormones T3 - T4 and exercise
- Gozzigeni foods
- Triacana