The thyroid ultrasound is the reference diagnostic test for the morphological study of this gland.
How does it work
Like all ultrasound techniques, it is based on the different ability of the tissues to reflect the ultrasounds emitted by an electric probe; the same device is able to record the intensity of the reflected waves, converting them into electrical signals and reconstructing the anatomical aspect of the thyroid gland in real time (thanks to a special computer program).

The ultrasounds, with a very high frequency and inaudible to the human ear, are emitted by a special probe slid along the anterior region of the neck, previously sprinkled with a small amount of gel and positioned in hyperextension (the patient lies lying down on a bed, face up and looking backwards).
The behavior of ultrasounds therefore depends on the characteristics of the medium passed through and on the frequency with which they are generated.
Preparation, Risks, Contraindications
Thyroid ultrasound is a painless, quick (takes about 10 minutes), safe and completely independent of ionizing radiation or radioactive substances.
No special preparation is required before the examination; it will simply be necessary to remove any jewelry worn around the neck. The investigation is absolutely risk-free and without any contraindications.
After the ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the gel is removed and the patient can safely resume their activities.
When Execute
The diagnostic accuracy of thyroid ultrasound essentially depends on the device used, the skill of the operator and patient-related technical limitations.
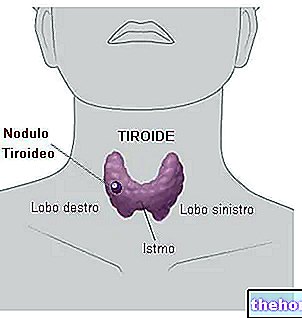
More specifically, ultrasound of the thyroid is particularly useful in defining the volume of the gland (goiter), the presence of inflammatory processes (thyroiditis), the possible presence of nodules and their particular characteristics. By combining the Doppler technique with ultrasound it is also possible to study the vascularization of the thyroid or of a single nodule, obtaining important information about its functionality and metabolic activity.
The functional aspects of the gland can be investigated in more depth through a further diagnostic examination, called thyroid scintigraphy, while to seek confirmation of the suspicion of malignancy it is necessary to evaluate the cell sample aspirated under ultrasound guidance.




.jpg)


















