Generality
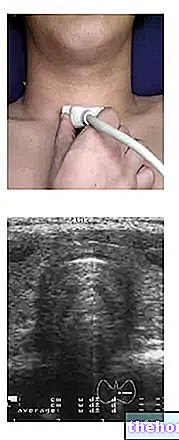
The term goiter, or struma, indicates the increase in volume and weight of the thyroid, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located just below the Adam's apple.

Index Section
Causes and types of goiter
ENDEMIC GOZZO
In the past, goiter was widespread in areas subject to iodine deficiency in water and food; therefore, we spoke of endemic goiter to underline the modest and limited extent of the epidemic. In the absence of an adequate amount of this mineral in fact, the thyroid is unable to synthesize and release two very important hormones containing iodine, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). If hormonal synthesis is insufficient, there is an increase in the TSH or thyroid stimulating hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland to stimulate the production of thyroid hormones; Excessive secretion of TSH for compensatory purposes causes an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland, hence the goiter.
To cope with the alarming spread of endemic goiter, the practice of adding iodine to flour, water or table salt has been introduced in many countries, a choice that has considerably reduced the incidence of the disorder. of the endemic goiter, which some foods - not surprisingly called "goitigens" - can predispose to the disorder if inserted in a "diet already deficient in iodine; these include cabbage, cabbage, turnips and the milk of cows fed with these vegetables.
The endemic goiter is a non-toxic goiter, first widespread and then, due to iodine deficiency protracted over time, multinodular; it can transform into hyperfunctioning toxic goiter (basedowificarsi) if treated with high doses of iodides.
GOZZO SPORADICO
Goiter is due to endogenous causes, for example to the presence of a tumor or other pathologies, or to the "intake of antithyroid drugs. Within a certain population, these are isolated cases, hence the term" sporadic "which distinguishes this type of goiter from the endemic one, defined as such only when present in more than 10% of the general population or in more than two children of school age out of a hundred.
GOZZO CONGENITO
Goiter is caused by genetic defects in thyroid hormone genesis (enzymatic alterations, etc.).
EUTYROID or EUMETABOLIC GOZZO and TOXIC GOZZO
The presence of goiter does not necessarily mean an inability to secrete adequate amounts of thyroid hormones. Despite being conspicuously enlarged, this gland may in fact have a normal, reduced or even increased activity; in the first case we speak of euthyroid goiter, simple goiter or non-toxic goiter, to indicate the maintenance of functionality despite the increase in volume and lack of association with inflammatory or neoplastic processes; in the second case we speak of hypothyroid goiter and in the third case of hyperthyroid goiter or toxic goiter. For what has been said, the "non-toxic" attribute belongs to both eumetabolic and hypothyroid goiter.
When it is caused by hyperthyroidism, goiter is accompanied by an increase in metabolic activity, tachycardia, tremors, sweating and excessive weight loss; the opposite symptoms are typical of hypothyroidism.
On the other hand, not all thyroid diseases cause goiter, such as those due to an insufficient response to pituitary TSH by thyrocytes (thyroid cells).
In addition to a deficiency of iodine in water and food, whether or not combined with the ingestion of particular foods, simple goiter can be linked to the intake of certain drugs (especially thyrostatic drugs, such as thiouracil and potassium percolorate; in the presence of an individual predisposition, also other medicines, such as paraminosalicylic acid, amiodarone, sulfonylureas and phenylbutazone, can favor the onset of goiter) or from genetic defects of thyroid hormoneogenesis.
As anticipated for the endemic one, the eumetabolic goiter is initially uniform or diffuse and evolves over time into a nodular goiter (lumpy appearance).
DIFFUSED GOZZO AND NODULAR GOZZO
The increase in thyroid volume can be uniform and involve the whole gland (diffuse, with a symmetrical and smooth appearance like the colloid goiter of adolescents), or asymmetrical, with hypertrophy and hyperplasia limited to one or more nodules (uninodular or multinodular goiter with lumpy appearance). Most of these bumps have a "benign" origin and as such do not cause cancer; non-toxic multinodular goiter may become hyperfunctioning (toxic plurinodular goiter) spontaneously or if treated with high doses of iodides.
EXOPHALMIC GOZZO, DIFFUSED TOXIC GOZZO or BASEDOWIAN GOZZO
It is due to an autoimmune disease known as Graves' or Basedow's disease, more common in women and associated with hyperthyroidism, ie an exaggerated production of thyroid hormones. The disease manifests itself, among other things, by a diffuse (uniform) toxic goiter.
Goiter - Video: Causes, Symptoms, Cures
Problems with playing the video? Reload the video from youtube.
- Go to the Video Page
- Go to Wellness Destination
- Watch the video on youtube
Continue: Goiter: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment "