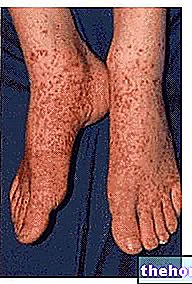
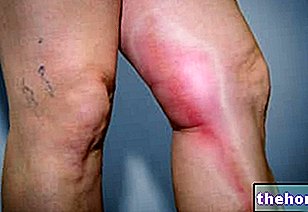
, phlebitis recognizes various causes; among these, the following deserve special mention: damage to the venous walls (which can, for example, result from a trauma or an "infection), prolonged immobility, the phenomenon of varicose veins and congenital disorders of blood coagulation.
Phlebitis mainly affects the veins of the lower limbs and can be of the superficial type (if it affects a vein located near the skin surface) or of the deep type (if it affects a vein located in the most intimate layers of the skin); between superficial phlebitis and deep phlebitis, the second is certainly the most dangerous one.
Phlebitis can be symptomatic or asymptomatic; when it is symptomatic, phlebitis produces, where it occurs, the classic manifestations of inflammatory episodes, namely: pain, redness, swelling, heat and a sense of soreness.
The diagnosis of phlebitis is mostly clinical, that is, based on the patient's report of symptoms, physical examination and medical history.
The treatment of phlebitis is variable and depends on factors such as: the location of the vein involved (whether it is superficial or deep), the anatomical area of interest, the symptoms and the underlying medical condition.
Tags:
sport-and-health antidepressants hydration
Phlebitis mainly affects the veins of the lower limbs and can be of the superficial type (if it affects a vein located near the skin surface) or of the deep type (if it affects a vein located in the most intimate layers of the skin); between superficial phlebitis and deep phlebitis, the second is certainly the most dangerous one.
Phlebitis can be symptomatic or asymptomatic; when it is symptomatic, phlebitis produces, where it occurs, the classic manifestations of inflammatory episodes, namely: pain, redness, swelling, heat and a sense of soreness.
The diagnosis of phlebitis is mostly clinical, that is, based on the patient's report of symptoms, physical examination and medical history.
The treatment of phlebitis is variable and depends on factors such as: the location of the vein involved (whether it is superficial or deep), the anatomical area of interest, the symptoms and the underlying medical condition.
affecting the intimate tunic of a venous vessel.