What is Vasculitis
Vasculitis: key points- Vasculitis is an "inflammation of the blood vessels.
-
Often, the condition is related to an autoimmune reaction, triggered by an "infection, drug, or" other disease. In some cases, the etiology of vasculitis is unknown. The inflammatory process involves damage to the walls of the blood vessels, which extend to the tissues and organs they supply.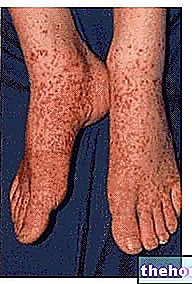
- Vasculitis can affect any type of blood vessel, resulting in a broad spectrum of diseases that can vary greatly in symptoms, severity and duration.
- The diagnosis can be confirmed by a biopsy of the involved tissue or by an "angiography".
- Treatment is aimed at decreasing inflammation of the blood vessels and improving the function of the affected organs.
Diagnosis
Vasculitis is common to a heterogeneous group of diseases, each of which is defined by specific patterns of inflammation that are distinguished by:
- Type, caliber and location of the affected blood vessels;
- Cause and extent of the disease;
- Recognition of particular clinical anomalies;
- Possible involvement of tissues or organs.
Diagnosis of vasculitis is based on history, complete physical examination, and results of laboratory tests.