What is Thrombophlebitis
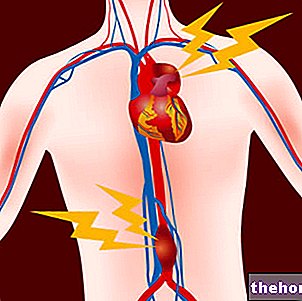
The term thrombophlebitis indicates a generic inflammation of the wall of a vein, associated with the formation of a blood clot inside it (called a thrombus). The thrombus can obstruct the inner lumen of the blood vessel and slow circulation; as a result, the vein affected by thrombophlebitis can become edematous, irritated and hard on palpation.

The disorder is common, with higher incidence rates among women and the elderly. Thrombophlebitis can be managed with a variety of treatments, including surgical approaches and medications, which can help relieve pain and reduce the risk of emboli. The condition, if continued over time, can cause chronic venous insufficiency, with edema, pain, skin pigmentation from stasis and ulcers.
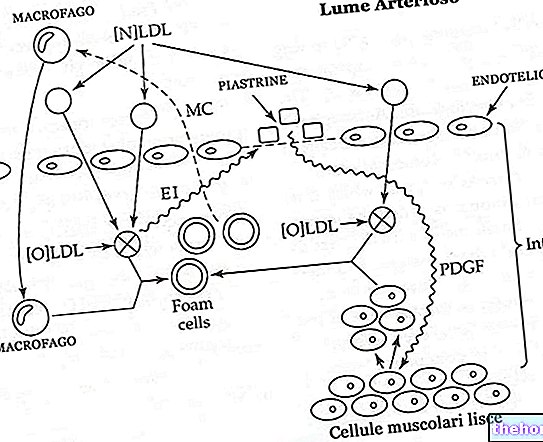
Note. Thrombophlebitis is an inflammatory process associated with thrombosis of the vessel itself. A thrombus arises following the adhesion of platelets with the vessel wall (normally smooth, it may have roughness or plaques that favor its formation). The mass gradually increases its size, projecting itself into the vessel lumen and reducing its diameter. In some cases , the vessel may be completely occluded by the thrombus; at other times, a large piece of thrombus may be detached causing the formation of a dangerous embolus, that is, a blood clot that enters the circulation. An embolus can travel in the blood and be completely cleaved by the plasmin or end up occluding a lower caliber vessel. This second eventuality can determine the block of the circulation in the downstream districts and an "ischemia of the tissue, up to necrosis.
Signs and symptoms
For further information: Symptoms Thrombophlebitis
Signs and symptoms often associated with thrombophlebitis include:
- Pain along the course of the vein;
- Local swelling (edema);
- Swelling of the affected limb;
- Redness (erythema) and inflammation of the skin (not always present).

















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




