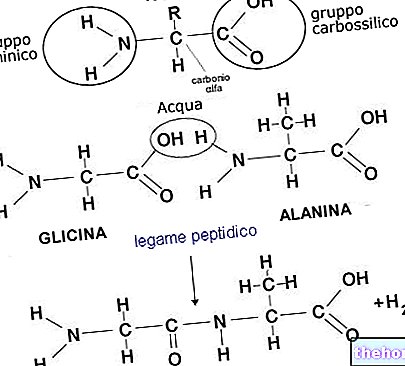
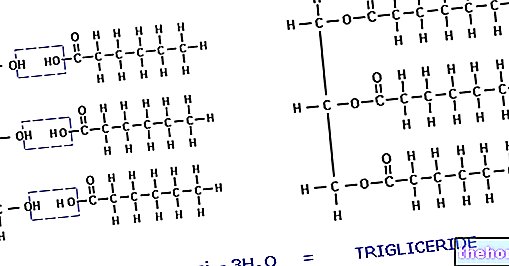
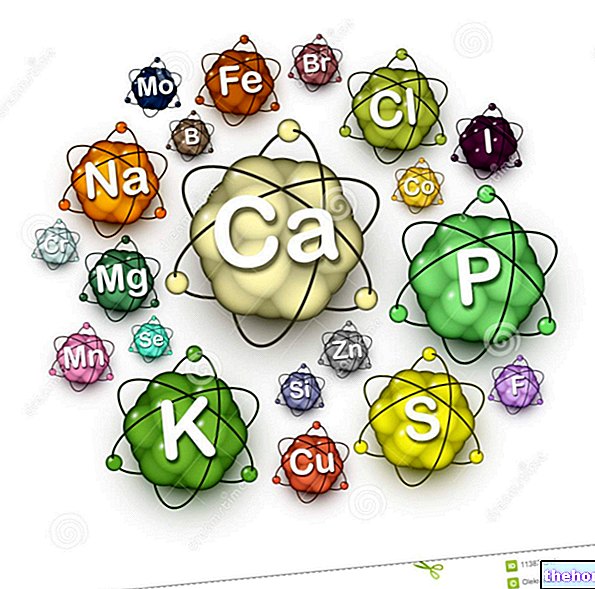
Average Requirement (AR) - average requirement
The level of nutrient intake that is sufficient to meet the needs of 50% of healthy individuals in a specific population group.
Adequate Intake (AI) - Adequate Intake
The level of intake of the nutrient that is assumed is adequate to meet the needs of the population.
Generally it is obtained from the average intakes observed in an apparently healthy population free from manifest deficiencies.
It is used when AR and PRI cannot reasonably be formulated based on the available scientific evidence.
Population Reference Intake (PRI) - recommended intake for the population
The level of nutrient intake sufficient to meet the needs of nearly all (97.5%) healthy individuals in a specific population group.
Tolerable maximum level of intake (UL) and nutritional goal for the population (SDT): values on a daily basis.
Note
na: not defined.
For the age groups, reference is made to the chronological age; for example for 4-6 years s "means the period between the completion of the fourth and seventh year of life. The 6-12 month interval corresponds to the second semester of life.
In the group of infants the UL is definable only for Ca. For P, K, Fe, Mn and Cr, scientific evidence does not allow the definition of UL.
For Mg, the UL value refers to the Mg taken in pharmacological or supplement form, in addition to what is already present in the diet.
For Fe, do not exceed the dose of 60 mg / day from supplements.
Note
na: not defined.
For the age groups, reference is made to the chronological age; for example for 4-6 years s "means the period between the completion of the fourth and seventh year of life. The 6-12 month interval corresponds to the second semester of life.
For Na, K, I, Mn, Mo and F, scientific evidence does not allow to define the AR for any of the interest groups; in the group of infants the RA is only definable for Fe and Zn.
For calcium, in postmenopausal women who are not on estrogen therapy, the RA is 1000 mg.
For Fe, in the 11-14 age group the second RA values refer to adolescents who are menstruating; in females 39-59 years old, the second RA values refer to postmenopausal women.
Note:
For the age groups, reference is made to the chronological age; for example for 4-6 years s "means the period between the completion of the fourth and seventh year of life. The 6-12 month interval corresponds to the second semester of life.
For calcium, in postmenopausal women who are not on estrogen therapy, the PRI is 1200 mg.
For Fe, in the 11-14 age group the second PRI values refer to adolescents who are menstruating; in females aged 39-59, the second PRI values refer to postmenopausal women.
Maximum tolerable level of intake (UL): values on a daily basis.
Note:
na: not defined.
For the age groups, reference is made to the chronological age; for example for 4-6 years s "means the period between the completion of the fourth and seventh year of life. The 6-12 month interval corresponds to the second semester of life.
For none of the vitamins, UL for infants are available.
For the vit. C, thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, biotin, vitamin B12 and vitamin K, scientific evidence does not allow to define UL for any of the interest groups.
For niacin, UL is expressed as nicotinamide (NA) or nicotinic acid (AcN) and refers to the forms found in supplements and fortified foods. UL does not apply to individuals on drug treatment under medical supervision.
For folate, the UL value is indicated for synthetic folic acid.
Vit. A is expressed in μg of retinol equivalents (1 RE = 1 μg of retinol = 6 μg of beta-carotene = 12 μg of other provitamin carotenoids).
Vit. D is expressed as cholecalciferol (1 μg colicalceferol = 40 IU vit. D).
Vit. E is expressed in alpha-tocopherol equivalents (1 α-TE = 1 mg RRR-tocopherol = 1.5 IU = 2 mg β-tocopherol = 3 mg γ-tocotrienol = 10 mg γ-tocopherol).
For folate, the reference intake levels for women of childbearing age (planning or not ruling out pregnancy) and pregnant do not include supplements indicated for the prevention of neural tube defects.
Vit. A is expressed in μg of retinol equivalents (1 RE = 1 μg of retinol = 6 μg of beta-carotene = 12 μg of other provitamin carotenoids).
Vit. D is expressed as cholecalciferol (1 μg of cholecalciferol = 40 IU vit. D). The RA considers both food intake and endogenous synthesis in the skin.