). The most characteristic symptom of this inflammation is represented by the bleeding of the same, which also occurs following minor trauma, such as energetic brushing or chewing of hard foods. Furthermore, an inflamed gum loses its natural hard-elastic consistency and the pinkish shades that characterize it, leaving room for abnormal redness and swelling.
Periodontitis: early symptoms (not to be underestimated)
- Bad breath
- Generally, there is no pain
- Slight bleeding from the gums on brushing (or for other modest stimuli such as chewing hard foods).
- Strange taste in the mouth and change in color (redness), texture (softening) or shape (swelling) of the gums.
Periodontitis: late symptoms
- Severe bleeding
- Marked halitosis
- Gingival recessions with exposure of the roots
- Appearance of spaces between the teeth
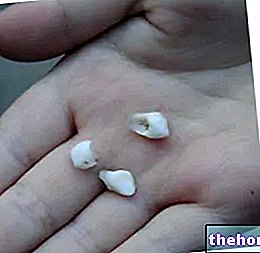
- Excessive dental mobility
- Minor discomfort up to widespread aching of the teeth.
Gingivitis, like periodontitis, is primarily due to dental plaque, that sort of sticky patina that is distributed on the surface of the teeth at the end of a meal. Behind this opalescent material, very small food residues and entire bacterial colonies are hidden. The more they are left free to proliferate, the more these bacteria adhere tenaciously to the surface of the tooth, recalling minerals and other substances, present in the saliva, which act as a real "protective shield".
This sort of armor is called tartar and its hardness is such that not even normal oral hygiene interventions (brushing, mouthwash, dental floss) can scratch it; the only solution, in these cases, is to undergo a professional scaling operation in the dentist's office. An annoying visit, which many would gladly do without, but very important for the health of our teeth.

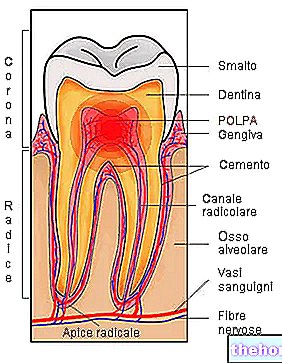
A neglected gingivitis, in fact, leads to a retraction of the normal gingival sulcus, to form - with the complicity of the bacterial plaque that generated it - the so-called periodontal pockets. As a consequence of the inflammation, in fact, the gums retract and become they form these "pockets", whose name is a whole program; pocket, in fact, makes the idea of protection, of a relatively safe and sheltered place from saliva with its immune cells and from drugs. Unfortunately, it is not our teeth that benefit from this, but some plaque bacteria; so, in the absence of interventions, the anaerobic germs multiply inexorably until the inflammatory process extends to the periodontium and to the bones that form the basis of the teeth. The toxins produced during their metabolism, in fact, attack the cells of the periodontal tissues, including osteoblasts ( cells used for the reproduction of the bone that supports the tooth).
Did you know that ...
- Oral hygiene is also very important for the overall health of the body. According to recent studies, periodontitis, in addition to the classic problems with the teeth, increases the risk of suffering cardiovascular diseases and, in the pregnant woman, of giving birth prematurely; it is also more serious in the diabetic patient, suffering from Crohn's disease or suffering from other pathologies that undermine the immune defenses and / or the connective tissues of the gums.
- Periodontitis recognizes numerous synonyms, such as pyorrhea, periodontal disease, periodontosis and periodontal disease.
- Periodontitis affects approximately three quarters of the adult population at varying degrees of severity.
Unfortunately, all this often happens asymptomatically, so much so that periodontitis can progress and worsen almost without realizing it. Unfortunately, the later it is diagnosed and the more difficult the disease is to treat; the costs and risks of the interventions rise to the point, in the most serious cases, of the irreversibility of the process. In the most advanced stage, due to the loss of its natural support, the tooth falls out.





















-nelle-carni-di-maiale.jpg)




