The cause is essentially the lack or deficiency of the intestinal lactase enzyme.
There are different forms of lactose intolerance, which can be distinguished mainly on the basis of etiology (genetic or acquired). Some ethnic groups are statistically more affected by this condition and there are quite important risk factors.
The therapy mainly consists of an exclusion diet, replacing milk and derivatives with delactosed or fermented products and therefore naturally lactose-free. It is also necessary to eliminate the occult latose, contained in ingredients and additives.
Recently, a food supplement has been proposed that can improve the digestibility of lactose (based on lactase).However, its efficacy is not repeatable on all subjects, but the results that can be obtained improve with the technological advancement of synthesis.
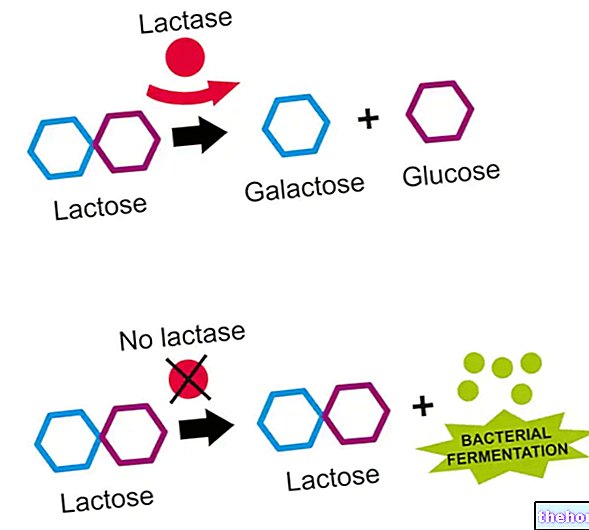
responsible for the digestion of lactose, that is the sugar contained in milk and its derivatives, must physiologically should be split into two simpler units or monosaccharides.
These enzymes, present in the "brush border" of intestinal cells and called lactase (beta-galactosidase), are responsible for splitting lactose into the two sugars that make it up: galactose and glucose.
Galactose is essential for the formation of nervous structures in the child, glucose is the primary energy substrate of the organism.
In some rare cases, lactose intolerance may be due not so much to the lack of lactase, as to the deficiency of the proteolytic enzymes necessary for the digestion of milk proteins.
Evolutionary lactose intolerance
Developmental lactose intolerance occurs during development can occur in premature babies and usually improves over a short period of time.
Congenital lactose intolerance
Congenital lactose intolerance is an extremely rare genetic disorder in which little or no lactase is produced from birth.
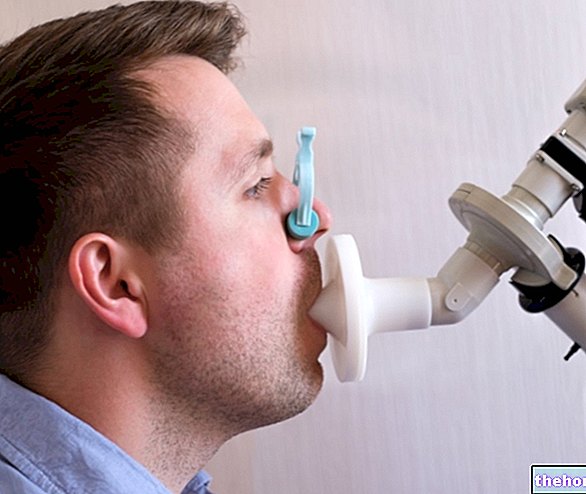
.This test evaluates the concentration of hydrogen in the exhaled air after a lactose load.
Since the fermentation of undigested sugar produces hydrogen which is readily reabsorbed by the intestinal walls and eliminated by breathing, in case of lactose intolerance a peak of hydrogen concentration is observed in the exhaled air.
Another less used test is that of stool acidity.
These tests are basically used for the differential diagnosis from: irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease.
To learn more: Breath test or breath test in which lactose is, for the most part (70-75%), already broken down into glucose and galactose.
Alternatively, you can "settle" for vegetable milks such as soy milk, rice milk, oat milk, etc.
Even yogurt and the like, such as buttermilk or kefir, or skyr thanks to the fermentation of lactose operated by the enzymes they contain, are generally well tolerated.
As far as cheeses are concerned, very aged ones such as parmesan and parmesan of many months are generally well tolerated.
Finally, those who suffer from lactose intolerances can benefit from the consumption of probiotics ("special" yoghurt, freeze-dried lactic ferments, etc.), but above all from exogenous lactase-based supplements.
For further information: Drugs to Treat Lactose IntoleranceOther articles on "Lactose Intolerance"
- Medicines to Treat Lactose Intolerance
- Lactose in food
- Lactose-free milk
- Lactase