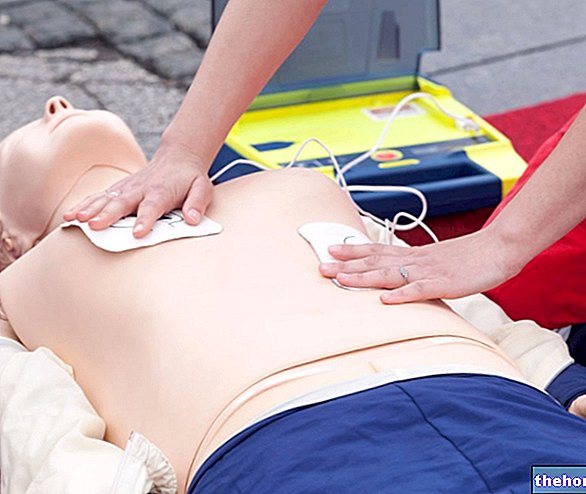
In some cases, sudden cardiac death can be avoided by promptly intervening with specific first aid maneuvers. Unfortunately, however, despite the timely rescue, the death of the individual cannot always be avoided.
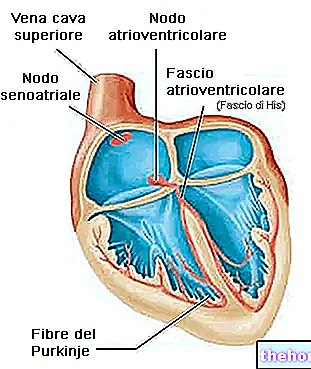
"are considered as synonyms. Nevertheless, from a pathophysiological point of view, it could be said that sudden cardiac death is immediately preceded by" cardiac arrest, ie the cessation of the heart's function which - acting as a pump - guarantees blood circulation throughout the body.Cardiac arrest is immediately followed by circulatory arrest and a drop in blood pressure with consequent loss of consciousness after just 10-15 seconds. After a few moments, the lack of perfusion of the respiratory centers leads to respiratory arrest and already after 4 minutes from cardiac arrest - due to the lack of blood supply, therefore, of oxygen - the brain cells suffer, begin to die and they experience irreversible neuronal damage.
For further information: Cardiac Arrest (the heart contracts quickly, irregularly and ineffectively); while in 10-15% of cases the MIC occurs due to asystole (absence of cardiac systole). More rarely, on the other hand, sudden cardiac death occurs due to electro-mechanical dissociation, that is a condition in which there is electrical activity but the mechanical pumping action that allows blood circulation and the transport of oxygen to organs and tissues.