Introduction
Molluscum contagiosum is an infectious disease of viral etiology that affects the skin and, in some circumstances, the mucous membranes. Although it is a benign pathology, molluscum contagiosum must always be kept under control: for this purpose, a differential diagnosis with pathologies characterized by similar lesions is necessary, also useful for managing a "possible - even if unlikely - malignant transformation of the lesion. .

As we will analyze in the course of the article, molluscum contagiosum must be treated with targeted medical aids, the same used for the treatment of warts. In some patients, especially those suffering from AIDS, the disease is particularly difficult to eradicate: in similar situations, surgery or cauterization of the lesions are conceivable.
Diagnosis
In general, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is rather simple, and is based on direct medical observation of the papular lesions.
When the diagnosis is uncertain, the suspicion of molluscum contagiosum can be confirmed by means of a tissue biopsy, a minimally invasive test that allows the lesion to be examined under an electron microscope, thus tracing the triggering cause.
The serological antibody test is not particularly reliable for the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum.
The differential diagnosis must be made with:
- Basal cell carcinoma (or basal cell carcinoma): Probably the most common form of skin cancer.
- Keratoacanthoma: generally benign neoplasm, typical of the skin of the face and neck, characterized by the formation of papular lesions similar to raised nodules, superimposable to those of the molluscum contagiosum.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis: irritative phenomenon of the skin, characterized by the formation of serous bubbles and redness, sometimes indistinguishable from the lesions of the molluscum contagiosum.
- Viral skin infections: Herpes simplex infections, chicken pox and warts.
- Lichen planus: chronic inflammatory erythematous lesion, immunological in nature, involving skin and mucous membranes. This disease is also characterized by the formation of papular lesions similar to that of the contagious molluscum.
- Milia: small yellowish bumps or cysts that grow on the skin surface.
- Nevi: skin spots, well circumscribed and evident, often in relief.
- Fibrous papules of the face: common neoformation that presents itself as a solitary skin lesion, with a size equal to or less than 5 mm.
Medicines and treatments
Although molluscum contagiosum tends to regress spontaneously, most dermatologists still recommend treating the disease, to avoid the spread of the virus and speed up healing times. We remind you, in fact, that the spontaneous resolution of papular lesions can also require very long waiting times: some patients recover definitively after a couple of months, while for others it may even take a few years.
The treatment aimed at eliminating molluscum contagiosum is comparable to that for the treatment of warts.
Molluscum contagiosum can be treated with specific drugs or removed using alternative surgical / therapeutic strategies.
AIDS patients also affected by molluscum contagiosum are generally subjected to more aggressive treatments, since the lesions struggle to regress both spontaneously and with the application of drugs.
PHARMACOLOGICAL THERAPY
The application of drugs directly on the lesion is a discrete resolutive practice, aimed at shortening the waiting time for healing. The drugs most used in therapy are:
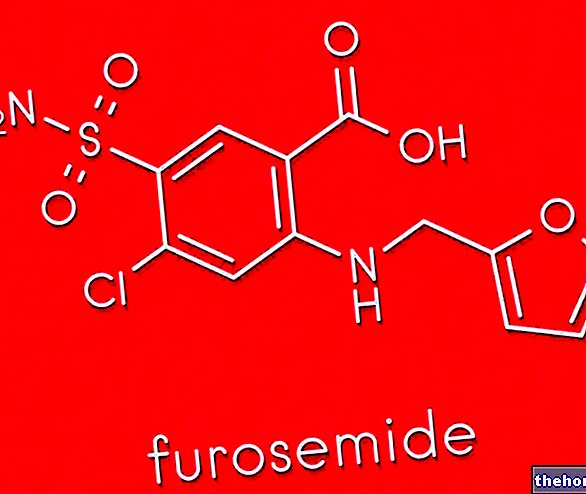
- Salicylic acid: keratolytic drug
- Potassium hydrochloride (astringent agent)
- Antiviral / immunosuppressive drugs (eg Imiquimod)
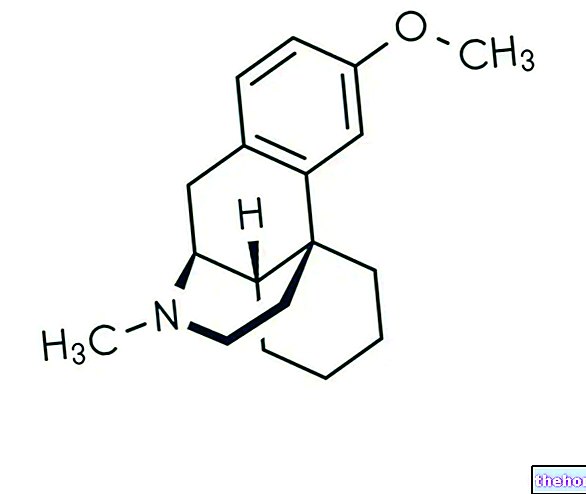
- Tretinonin or retinoic acid: the drug exerts keratolytic properties, promoting cell turnover. DO NOT undergo the sun during retinoid treatment. DO NOT take the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding: the active ingredient is a teratogen.
MEDICAL TREATMENTS
Medicines do not always resolve papular lesions caused by molluscum contagiosum in a short time: for particularly aggressive forms, specific medical interventions are recommended.
The most used methods for molluscum contagiosum are:
- Scraping of the lesion (after superficial anesthesia of the area, with local anesthetics)
- Cryotherapy (cold therapy): uses liquid nitrogen to "burn" the papular lesions of the molluscum contagiosum. Cryotherapy can cause pain, swelling and hypersensitivity in the point where it is performed. Its effectiveness for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum is comparable to that exerted by salicylic acid (topical application).
- Laser therapy
- Bleaching with specific chemical agents (e.g. benzoyl peroxide)
Remember that the surgical removal of molluscum contagiosum lesions can leave indelible scars on the skin.
Molluscum contagiosum infections can recur, even after completing a specific treatment cycle. To minimize the risk of relapse, it is recommended to start treatment for molluscum contagiosum when the lesions are still in the first stage, therefore few in number and small in size.
Other articles on "Molluscum Contagiosum: Diagnosis and Treatment"
- Contagious mollusk
- Molluscum Contagiosum - Drugs and Treatment
- Molluscum Contagiosum Remedies

-cause-sintomi-e-cura.jpg)