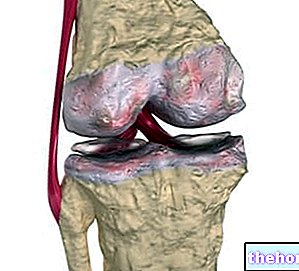
Neck pain that radiates down the arm (brachialgia) is the characteristic symptom of cervical disc herniation, the intensity of which depends on the severity of the pathological condition.
Persistent neck pain, headache, arm weakness and difficulty in moving the upper limb are all signs of a cervical hernia in progress. In such situations, the patient should undergo a medical consultation as soon as possible: clinical evaluation is the starting point for a correct diagnosis and adequate therapy.
, or with the collection of general data and information regarding the patient: in this case, the doctor will try to understand the intensity of the pain, its location, the general state of health of the patient and the causes responsible for neck pain.
The clinical investigation is performed through precise maneuvers, useful for highlighting cervical and radicular pain. For example, cervical hernia becomes more painful by lengthening the neck, while the extension of an arm behind the head slightly alleviates the pain.
Imaging tests are generally the very first diagnostic tests to confirm or disprove a suspicion of cervical hernia:
- Computed tomography (CT): diagnostic technique that uses ionizing radiation to obtain detailed images of the cervical area;
- MRI of the neck: can show an "abnormal protrusion of the disc and a" possible compromise of the nerves and spinal cord. Furthermore, the MRI highlights the ligaments and the degenerative bone components, showing at the same time any disc pathologies of the rachis;
- X-ray of the neck, useful for having a "general idea of major cervical anomalies;
- Myelography: radiological test performed on the spinal cord. The diagnostic examination uses a contrast medium to detect any pathologies or trauma affecting the spinal cord (including cervical localization). The procedure is rather invasive and is followed by puncture in the cervical tract, with CSF sampling and subsequent injection of medium Immediately after the procedure, numerous X-ray projections are made.
- Discography: rather invasive diagnostic test which involves the injection of a contrast medium in the cervical area to precisely identify the origin of the pain. The test is generally performed only when cervical pain is so intense that surgery is required. The discography is always accompanied by a CT scan, which is useful for obtaining more information;
- Electromyography: diagnostic test useful for identifying the muscles involved in the disease.
The investigations necessary for the diagnostic assessment are exclusively of medical competence: the specialist in fact evaluates the need or the priority of a specific test by carefully analyzing the clinical picture that the patient presents.
painkillers and anti-inflammatories that accelerate pain relief.Cervical Hernia Drugs
The drugs most commonly used in therapy to relieve neck pain are:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), useful for relieving pain, at the same time exert an anti-inflammatory action. The active ingredients most used for this purpose are: Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Diclofenac and Acetylsalicylic acid.
- Muscle relaxants, useful for calming muscle spasms caused by cervical hernia. The most used drugs are: Diazepam and Ciclobenzaprina
- Corticosteroid drugs (eg Prednisone, Methylprednisolone and Hydrocodone), exert a powerful anti-inflammatory activity.
- Epidural injection with pain / analgesic drugs (for very painful cervical hernia)
Sometimes, the use of a collar can be useful to relieve neck pain after a violent trauma to the cervical spine: the collar is a support device suitable for reducing cervical movement, preventing further damage.
After having achieved a moderate improvement in pain and related symptoms, it is advisable to undertake a specific rehabilitation process, aimed at maximizing the general health of the back (and specifically of the cervical tract), also very useful and above all to prevent any, possible, future damage.
using the aid of direct current produced by a generator.
After a discectomy surgery, the patient must observe a convalescence period of 30-40 days: during this time, the subject must completely abstain from heavy work, must not drive, must not assume incorrect postures and must respect rest. .
The patient operated on for cervical hernia will have to undergo regular routine checks during the postoperative period, to ensure that the operation is perfectly successful.
Other articles on "Cervical Hernia: Diagnosis and Therapy"
- Cervical hernia
- Remedies for Cervical Hernia