Acute low back pain recognizes various causes; in most cases, an injury to the muscles or ligaments belonging to the back is due; more rarely, it is the result of a vertebral fracture, a vertebral tumor, disc herniation, vertebral stenosis, sciatica, cruralgia, pregnancy, spondylodiscitis, etc.
Very often, the presence of acute low back pain is associated with other symptoms, such as stiffness, difficulty moving and tingling.
As a rule, a physical examination and medical history are sufficient for the diagnosis of acute low back pain and the recognition of its triggering cause.
Acute low back pain requires resorting to causal therapy; only through the management of the triggering factor, in fact, it is possible to achieve healing.
Acute Low Back Pain and Chronic Low Back Pain: the differences
Acute low back pain contrasts with chronic low back pain.
By "chronic low back pain", doctors mean any pain in the lumbar area of the back, which appeared gradually and lasted for at least 12 weeks.
The pain that characterizes chronic low back pain is less intense than the pain felt in the presence of acute low back pain; however, as reported above, "on the contrary, it is decidedly more lasting over time.
Meaning of Acute Low Back Pain
The term "acute low back pain" recalls all the main characteristics of the condition to which it refers; in medicine, in fact, "loin" is the word that refers to the lumbar area of the back, "algia" is the term used to indicate any painful state and, finally, "acute" is the adjective used to describe the onset conditions abrupt and sudden.
; the back includes:
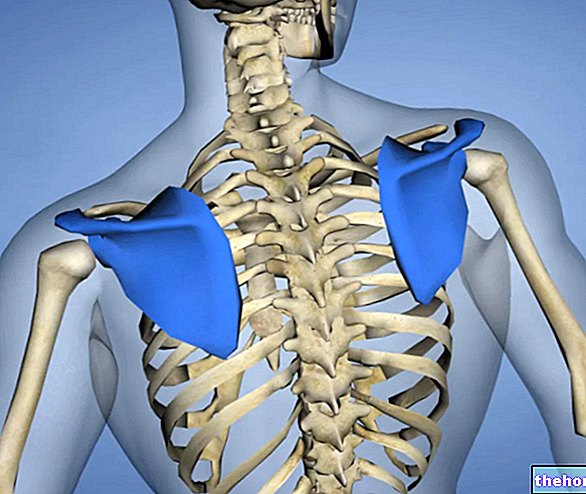
- Bone. The bones of the back are the shoulder blades and vertebrae that make up the spine. It is important to point out that between each vertebra there is a fibrocartilage structure, called the intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushioning pad;
- Joints and ligaments. It is the joints and ligaments that join the vertebrae together and, at the same time, ensure a certain mobility to these bones;
- Muscles. The back muscles are essential for the movement of the shoulders, upper limbs, rib cage and spine;
- The spinal cord and spinal nerves. The spinal cord is contained within the vertebrae column; from it originate, subsequently distributing themselves in various parts of the human body, the spinal nerves.
Acute low back pain recognizes various causes.

In most cases, it is due to an injury to the muscles and / or ligaments of the back (contracture, strain or tear), following excessive physical exertion; less commonly, it is related to:
- Vertebral fractures. Typically, vertebral fractures are the result of accidental falls on the back or the effects of osteoporosis;
- Vertebral tumors (ie involving a vertebra). Vertebral tumors are examples of bone tumors;
- Disc herniation. It is the medical term that indicates the release, from an intervertebral disc, of the gelatinous substance contained inside and called the nucleus pulposus;
- Sciatica (or sciatica). It is the inflammation of the sciatic nerve, which generally originates from the compression or irritation of the nerve roots in question.
When sciatica is combined with back pain in the lumbar region, it also takes the name of lumbosciatalgia; - Cruralgia. It is the inflammation of the crural nerve, which usually originates from the compression or irritation of the aforementioned nerve roots;
Cruralgia combined with back pain along the lumbar spine is also called low back pain; - Spinal stenosis along the lumbar spine. By spinal stenosis, doctors mean the pathological narrowing of a portion of the vertebral canal (or spinal canal), that is the canal present inside the spinal column and destined to house the spinal cord;
- Abnormalities of the spine, such as scoliosis or hyperkyphosis
- Arthritis affecting the spine. Arthritis is the medical term that describes inflammation of one or more joints. There are various forms of arthritis, the most common being osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis;
- Spinal infections. These infections can involve the vertebrae (spondylitis), the intervertebral discs (discitis) or both (spondylodiscitis);
- Kidney stones or kidney infections
- State of pregnancy;
- Diseases of the female genital system, such as endometriosis, ovarian cancer, ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids;
- Sacroiliitis. It is inflammation of the sacroiliac joint (or sacroiliac joint). The sacroiliac joint is the equal joint element, which connects the sacrum to the iliac bone;
- Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. This situation represents a "medical emergency, so those who suffer from it need immediate treatment.
Did you know that ...
The lumbar area is the part of the back most prone to muscle or ligament injuries; this happens because it is the part of the back that supports most of the weight of the body and the loads that an individual may have to lift.
Who is Most at Risk for Acute Low Back Pain?
Anyone can suffer from acute low back pain, especially acute low back pain resulting from muscle or ligament problems in the back; however, statistics regarding the frequency of acute low back pain indicate that this painful condition affecting the lower back is more common among:
- Those who practice sports;

- Those who practice a job that involves repeated lifting of loads;
- Overly sedentary people;
- Individuals involved in automobile accidents;
- Seniors.
Did you know that ...
In the United States, acute low back pain and chronic low back pain are the second most common reason people request a doctor's appointment; before them, there is only influence.
;Characteristics of pain
Pain related to acute low back pain can be stabbing, burning, or dull; moreover, it can be continuous or alternate phases of great intensity with phases of apparent remission.
Complications
Any complications that may arise from acute low back pain depend on the underlying causes of the painful condition.
In the most common cases of acute low back pain (therefore when the cause of the pain is a muscle or tendon injury), the possible complications consist of: an "important inability to carry out movements with the back, such that even the simplest activities are impossible , and in a state of bad mood / low mood, consequent to the incapacity just mentioned and described.
When to see a doctor?
In the presence of acute low back pain, it is good to contact a doctor if:
- The pain is very strong and debilitating;
- Pain does not subside despite rest (could be indicative of a more serious condition than a muscle or ligament injury)
- The patient has a fever (this could be a sign of an "infection in progress);
- The patient presents with lameness and / or loss of control of the anal or bladder sphincter (this could indicate a neurological cause, such as sciatica);
- The patient is subject to weight loss for no reason (this could indicate the presence of a neoplasm).
Physical examination and anamnesis
For those who complain of a form of acute low back pain, the physical examination consists of an accurate check of the back, during which the doctor asks the patient to indicate the exact location of the pain and to describe the movements that accentuate this sensation; instead, it involves a series of questions aimed at clarifying the possible event that triggered the painful condition, the patient's general state of health and the patient's past medical history.
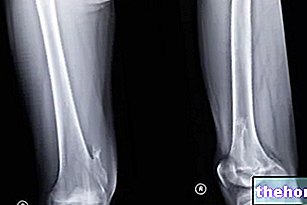
Instrumental tests: what do they allow to identify?
Tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance or CT of the spine are useful for the diagnosis of acute low back pain due to: vertebral tumors, scoliosis, hyperkyphosis, disc herniation, spondylitis, discitis, spondylodiscitis, spinal stenosis, arthritis, etc.
on the most painful area, repeated 4 to 5 times a day, for a period of time between 15 and 20 minutes per pack;Did you know that ...
In bed, the ideal positions for the back are:
- Face up, with a pillow under the knees;
- On your side, with your knees bent towards your chest and your chin pointing down.
WHAT TO DO IF THE PAIN PERSISTS?
If the pain persists despite rest and the above remedies, your doctor may recommend:
- Therapies, such as laser therapy, ultrasound or tecar therapy;
- A cycle of physiotherapy sessions, which includes manipulations, stretching exercises and muscle strengthening.
WHAT TO DO AFTER RECOVERY HAPPENED?
After recovery from acute low back pain due to a muscle or ligament injury, the return to physical activity, even the most trivial one (such as lifting light objects off the ground), must be gradual and take place in an extremely cautious manner.
The risk that those who do not follow the indication to a gradual recovery run is to get injured again, further prolonging the healing time.
Therapy in less common situations
When the cause of acute low back pain is a condition other than a muscle or ligament injury, possible therapeutic approaches include surgery, antibiotic therapy, postural gymnastics, and a specific physiotherapy program.
there are numerous guides that teach how to lift a weight without burdening the spine.