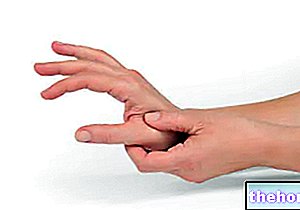
The cause of the epitrocleitis is the functional overload of the aforementioned muscles; in fact, the exasperated and excessive stress of these muscles (functional overload), through a very precise gesture, produces a stress on the connected tendons, such that the latter s "inflame and become painful.
Particularly widespread in those who practice sports such as golf, tennis or baseball, epithrocleitis is responsible for: pain on the inner side of the elbow, joint stiffness in the elbow, weakness in the hand and wrist (only in some cases ), and numbness and tingling along the fingers.
Generally, the diagnosis of epithrocleitis is clinical, that is, based on the description of symptoms, on the physical examination and on the anamnesis.
As a rule, the treatment of epithrocleitis involves a conservative treatment, based on: rest of the suffering limb, ice packs, use of compressive bandages, use of an elbow brace, intake of anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy.
Brief review of what "is a Tendon
A tendon is a band of fibrous connective tissue, with a certain flexibility and high in collagen, which joins a skeletal muscle to a bone.
which connect part of the anterior muscles of the forearm to the medial epicondyle of the humerus.Epitrocleitis is a "disease" of the musculoskeletal system; more precisely, it is an example of tendonitis, ie inflammation of one or more tendons.
Epithrocleitis is also known as "golfer's elbow" and "medial epicondylitis".
Epitrocleitis is a very similar condition, albeit on the opposite side of the elbow, to lateral epicondylitis (or tennis elbow).
Tendinitis belongs to the large clinical group of tendinopathies, that is, diseases / sufferings of the tendons; Tendinosis also belongs to the group of tendinopathy, ie chronic affections of the tendons sustained by a degeneration of the normal tendon structure.
To understand: a brief anatomical review
- The humerus is the equal bone of the human body that constitutes the skeleton of the arm, that is of the anatomical section between the shoulder and the elbow;
- The humerus is a long bone, therefore 3 portions can be distinguished on it: the proximal epiphysis, the diaphysis and the distal epiphysis;
- Through the proximal epiphysis (which is the portion closest to the center of the human body), the humerus articulates with the scapula, to form the shoulder joint; through the distal epiphysis (which is the portion furthest from the center of the human body), on the other hand, is articulated with the ulna and radius (forearm bones), to form the elbow joint.
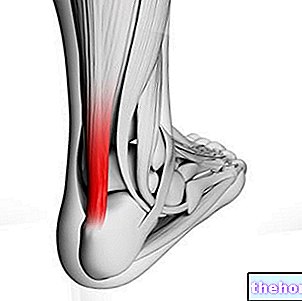
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE OF THE HUMERUS
Imagining that the upper limb is extended along the side and with the palm of the hand facing the observer, the medial epicondyle of the humerus is the prominence, perceptible to the touch, present on the inner side of the last part of the distal end of the bone constituting the skeleton of the arm.
The medial epicondyle of the humerus is important from the anatomical point of view, because it is the anchoring site of the tendon complex connected to the initial head of 5 of the 8 anterior muscles of the forearm.
FOREARM ANTERIOR MUSCLES

The anterior muscles of the forearm are in total 8; these 8 muscles are arranged in 3 different depth planes:
- On the most superficial plane, there are 4 muscles, which are: the ulnar flexor of the carpus, the long palmar, the radial flexor of the carpus and the pronator teres;
- On the intermediate plane, there is only one muscle: the superficial flexor of the fingers;
- On the deeper plane, there are 3 muscles: the deep flexor of the fingers, the long flexor of the thumb and the square pronator.
For the understanding of this article on epithrocleitis, only the anterior muscles of the forearm connected to the medial epicondyle of the humerus are of interest, that is: all the muscles of the superficial plane (ulnar flexor of the carpus, long palmar, radial flexor of the carpus and pronator teres) and the only muscle of the intermediate plane (superficial flexor of the fingers).
Origin of the name
The term "epitrocleitis" derives from "epitrochlea", which is another name, coined by anatomists, to indicate the "medial epicondyle of the humerus".
involved in epithrocleitis during movement of pitching;Risk Factors of Epithrocleitis?
Factors such as:
- The repetition, for over two hours and with an improper technique, of movements at risk;
- The use, in risky sports practices, of inadequate equipment;
- L "over 40 years of age;
- Obesity;
- Cigarette smoke.
The execution technique of a potentially risky gesture is very important: if correct, in fact, it involves less stress on the anterior muscles of the forearm.
borne by the latter and this translates into a worsening of the symptoms (especially the painful one).When to see a doctor?
In case of epithrocleitis, it is advisable to contact your doctor or consult an expert in diseases of the musculoskeletal system, when the symptoms (especially pain and a sense of soreness) persist despite the rest.
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, epithrocleitis can develop into a more severe tendinopathy, characterized by a lesion or degeneration of the tendon structure.
The occurrence of the aforementioned complication involves chronic and debilitating symptoms, and requires specific medical intervention.
The chronic symptoms and the debilitating effects of an epithrocleitis resulting in complications can strongly affect the patient's mood, as the latter has difficulty, due to pain, in performing the simplest movements with the affected upper limb.
, ultrasound and / or magnetic resonance imaging.
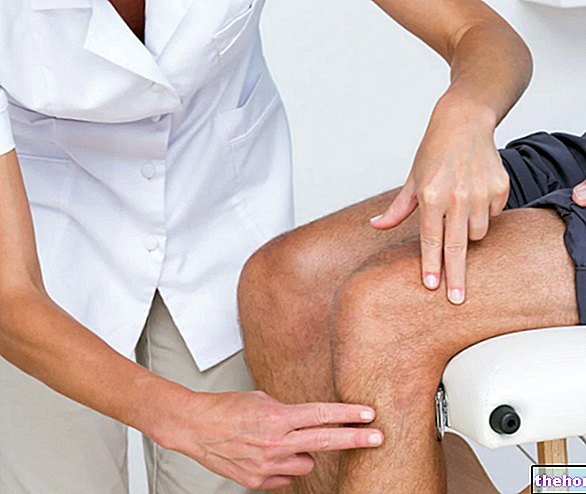
Physical examination

The physical examination consists in the medical observation, also through particular maneuvers and palpation, of the symptoms and signs that the patient complains or exhibits.
For those who complain of the typical disorders of epithrocleitis, the physical examination includes a palpatory examination of the elbow and the execution, with the painful upper limb, of all those movements which, in the presence of inflammation, would evoke pain.
Anamnesis
The anamnesis is the critical study of the symptoms noted during the physical examination and of the facts of medical interest collected through specific questions (concerning not only the symptoms, but also the general state of health, habits, daily activity, diseases recurring in the family, etc.).
In the presence of a condition such as epithrocleitis, the anamnesis allows to identify the factors that, in the given patient, induced the inflammatory process.
, especially at the beginning of an "inflammation.Generally, the indications for its use are: 4-5 compresses a day on the painful area (in the case of epithrocleitis, it is the inner side of the elbow), for 15-20 minutes each (shorter or longer applications are ineffective) ;

- The application of a compression bandage around the elbow. The compression bandage relieves pain and speeds up healing;
- The use of an elbow brace. The elbow brace has the purpose of preserving the suffering upper limb from those movements that could further stress the tendons;
- The intake of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) or paracetamol. The use of these drugs is indicated to calm inflammation and painful symptoms.
Among the NSAIDs, the most commonly used by those suffering from epithrocleitis is ibuprofen; - Local injection of corticosteroids. Corticosteroids represent an "alternative to NSAIDs and paracetamol, when the latter are ineffective and symptoms persist."
The use of corticosteroids in the therapeutic management of epithrocleitis is rare, due to the possible side effects related to the use of the drugs in question.
Remember that corticosteroids must be taken with a medical prescription; - Physiotherapy exercises.Physiotherapy for those suffering from epithrocleitis involves stretching exercises and strengthening the muscles of the suffering upper limb.
To know exactly what these exercises consist of, it is good to contact an expert in the field, with experience in problems with tendons.
Surgery: when can it be useful?
Typically, epithrocleitis does not require surgery.
However, if the symptoms persist for more than 6 months in spite of the conservative treatment described above or if the condition has evolved into a more severe tendinopathy, surgery becomes a viable therapeutic option.
Did you know that ...
Less than 10% of patients with epithrocleitis require surgery to resolve the condition.
vary from person to person, depending on the severity of the inflammation, however, in general, most patients with epithrocleitis heal within 3-4 weeks.
Return to activities after the Healing: how should it happen?
After recovery, the resumption of activities carried out before the onset of epithrocleitis must take place gradually; failure to comply with this indication is strongly associated with relapses.