In Italy, permanent gluten intolerance is known as celiac disease or celiac disease, while in the English language it is labeled with many other names, such as: c (o) eliac sprue, c (o) eliac disease, nontropical sprue, endemic sprue And gluten enteropathy.
The term "celiac disease" or "c (o) eliac" comes from the Greek "koiliakos κοιλιακός ‚", which means" abdominal "; this term was introduced in 1800 to translate an" ancient Greek description of the so-called "Areteo of Cappadocia" disease.
If it is true that it involves the intervention of the immune system (like allergies), it is also true that celiac disease does it in a totally different way from allergic forms. Gluten intolerance causes a localized complication in the mucous membrane of the intestine and, only later, it leaves some traces on the parameters of the blood type. However, even in the most important cases, the implication of specific antibodies for allergies (IgE) is missing and there is no risk of anaphylaxis.
More than a disease, gluten intolerance is preferably defined as a paraphysiological condition, since, in the absence of exposure to the specific agent (gluten), the organism remains calmly in homeostasis as if it were healthy. pathological of extremely variable severity and symptomatology.
, called gliadin and glutenin, which combine only in the presence of water.Gliadin is one prolamine present in some cereals (botanically: family Poaceae or Gramineae) belonging to the Tribe of Triticeae; to be clear, the major exponents of this group are: hard and soft wheat, small spelled, medium and spelled, kamut etc. The seeds of some plants of the Tribe also contain gliadin Hordeae, such as barley and rye, as well as of the Tribe Aveneae, such as "oats. The latter", however, is tolerated by some celiac subjects.
Going further into the specifics of gliadin, the elements that stimulate intolerance are three peptides. Precisely on these, the enzyme tissue transglutaminase it brings about a structural change that triggers the reaction of the immune system. The defense mechanism, unnecessarily alerted, carries out a cross-reaction and inflames the target tissue (which we remember to be the mucosa of the small intestine).
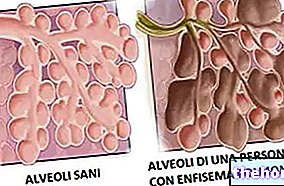
The excessive and useless reaction of the immune system causes edema and shortening of the intestinal villi that line the mucosa (phenomenon called villous atrophy). Since these are structures responsible for the absorption of food nutrients, their annihilation reduces the entry of many nutritional substances, including the so-called essential ones.
Gluten intolerance can easily determine some vitamin deficiencies, due to the reduced absorption capacity of the small intestine.
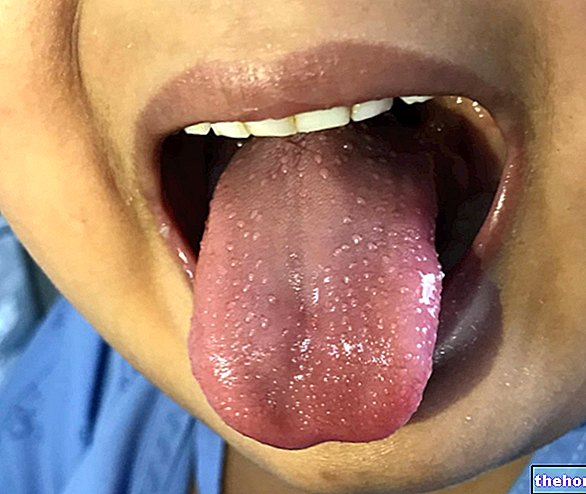
are: pain and discomfort of the digestive tract, chronic constipation or diarrhea (sometimes alternating, thus simulating an irritable bowel syndrome), growth failure in children, anemia (apparently unjustified and unresponsive to martial food supplementation) and fatigue .
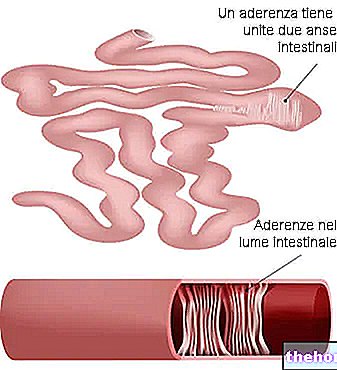
In some less frequent cases, the typical symptoms of celiac disease may be absent or marginal; on the other hand, atypical manifestations prevail, referring to other organs / districts of the organism (a peculiarity that often makes diagnosis very difficult). It is possible to deepen the alternative manifestations of celiac disease by reading: Celiac disease: The Atypical Symptoms.
Sometimes, it is also possible that the exact opposite happens: a series of "typical" symptoms associated with the consumption of gluten-containing foods, however, in the absence of the diagnostic criteria for intolerance. It must be remembered that, according to some, these eventualities largely depend on: psychosomatic (autosuggestion) and other reasons completely independent of gluten itself. On the other hand, it seems that the diagnosis of this discomfort is constantly increasing, which requires not to underestimate it.
For more information, see the Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity article.
There are various types, more or less invasive and more or less precise. Among these, the safest is the intestinal biopsy: even if quite invasive, it has the advantage of allowing an assessment of the severity of the functional and histological impairment. Follow the dosages of certain blood parameters, such as the detection of antibodies: antiendomysium, anti gliadin IgA, anti gliadin IgG and antitransglutaminase.
If initially the diagnosis of gluten intolerance was made almost exclusively on people who suffered from gastrointestinal disorders, thanks to increasingly effective screening methods, today the cases of asymptomatic celiac disease or with atypical symptoms are rapidly increasing. Globally, gluten intolerance affects about one in 100-170 people; however, the results vary by region of the world, from very poor like 1: 300 to very frequent like 1:40.
For more information on the diagnosis of gluten intolerance, I suggest reading the article Exams for the diagnosis of Celiac disease.
or diet for celiac disease; wanting to broaden the topic, please refer to the articles: Drugs to cure Celiac disease, Celiac disease: nutrition, advice, therapy and Gluten-free foods.