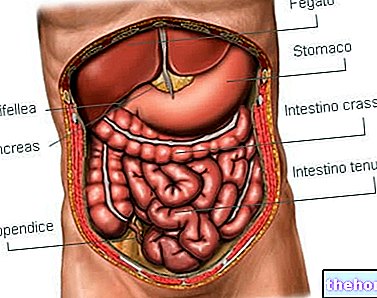
By reaching the intestine alive, probiotics counteract the proliferation of harmful bacteria (biological antagonism), optimize the functionality of the colon and contribute to the assimilation of indigestible food components in our diet, in addition to the synthesis of essential substances, such as vitamin K.
The characteristics of a food or probiotic supplement are: compatibility with the intestine, resistance to gastric pH, harmlessness and healthiness.
Learn more about the General Characteristics of Probiotics ;LIKELY
- Traveler's diarrhea;
- Helicobacter pylori;
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis);
- Colon cancer prevention;
- Diverticular disease and irritable bowel syndrome;
- Food allergy;
- High cholesterol
- Chronic constipation;
- Bacterial vaginitis and Candida infections;
- Dental caries and other affections of the oral cavity;
- Urinary tract infections.
Please note
However, the effectiveness of probiotics may vary in relation to the type of bacteria used and the individual response.
Some strains, for example, may be indicated in the presence of certain pathologies and prove to be useless or even harmful in other situations.For this reason it is a good idea to consult your doctor before taking foods enriched with probiotics, especially in the presence of gastrointestinal disorders. Furthermore, it must be considered that commercial probiotics (sold in the supermarket) are intended for the healthy population, while the freeze-dried ones marketed in pharmacies have a much higher microbial concentration (they are therefore considered a real therapeutic aid). See also the article on the possible side effects of Probiotics.
, especially in fermented milks (yogurt and kefir); there is no shortage of plant derivatives such as:
- The miso;
- The tempeh;
- The tofu;
- The kombucha;
- The sauerkraut;
- The sour gherkins.
Although these foods are still useful for our well-being (milk and milk derivatives are excellent sources of calcium and phosphorus; those of soy contain phytosterols and omega 3 etc.), the quantity of probiotics able to overcome the digestive action is totally insufficient to obtain the same beneficial effects associated with the use of specific supplements.
For this reason, products fortified with probiotics have been studied and marketed, especially yoghurt, the result of internal research by the manufacturers and often containing bacterial strains that differ slightly from one product to another, also as regards the beneficial effects (some regularize the intestinal function, others above all stimulate the immune defenses).
Before resorting to supplements or foods fortified with probiotics, it is however good to follow some useful rules to normalize your bacterial flora and consequently improve intestinal functions and general well-being. These benefits are achievable by following a high-fiber diet, which:
- Avoid excesses (especially alcohol, sugars and proteins);
- Provide the right amounts of dairy products (especially yogurt and low-fat cheeses).
Finally, it should be remembered that the "hyperproliferation of pathogens to the detriment of probiotic strains is also favored by a series of disadvantages such as:
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Drug abuse;
- Various additives present in food;
- Irregular and hectic pace of life.
Probiotics: when is it better to take them?
When using probiotics, it is necessary to ensure that the acid barrier of the stomach (the body's natural defense against pathogens) does not kill the microorganisms, which we remember are taken orally.
Most gastric juices are excreted at meals, so probiotics should be taken on an empty stomach. Avoiding this inconvenience increases the chances that the bacteria reach the large intestine by strengthening the physiological bacterial flora.
Read the in-depth Probiotics: which ones to choose and how to use them