of the organism. Its main task is to metabolize glucose to make it usable energy.
Lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer with subunits belonging to two different types which, combining with each other in various ways, give rise to five different isoenzymes: LDH1 and LDH2 are elevated in the heart and erythrocytes, while LDH 4 and LDH 5 are elevated in the liver. and in the muscle;
Tags:
anatomy cooking-food lose weight

Lactate dehydrogenase is found in numerous tissues, but is mainly concentrated in the skeletal muscles, liver, heart, kidneys, pancreas and lungs.
When the cells are damaged or destroyed, the LDH enzyme is released in the liquid fraction of the blood (serum or plasma), as well as increasing its concentration in other biological liquids (eg liquor) in the presence of some pathologies. LDH represents , therefore, a general indicator of tissue and cellular damage.
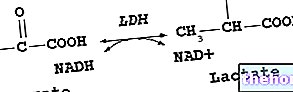
) is a cytoplasmic enzyme with a wide distribution in the tissues, where it catalyzes the interconversion of lactate to pyruvate.Lactate dehydrogenase is a tetramer with subunits belonging to two different types which, combining with each other in various ways, give rise to five different isoenzymes: LDH1 and LDH2 are elevated in the heart and erythrocytes, while LDH 4 and LDH 5 are elevated in the liver. and in the muscle;
- LDH1 is prevalent in the myocardium, red blood cells, kidney and germ cells;
- LDH2 is prevalent in the myocardium and red blood cells, as well as being concentrated in white blood cells and kidneys (where it is present in lower concentrations than LDH1);
- LDH3 is prevalent in the lungs and other tissues;
- LDH4 is found in skeletal muscle, in the liver (where it is present in lower concentrations than LDH5), in lymph nodes and in white blood cells;
- LDH5 is characteristic in the liver and skeletal muscle.
This tissue specificity makes the lactate dehydrogenase assay of great clinical interest to assess the site of hypothetical tissue damage.