«Introduction to the Conconi Test
Threshold heart rate and training rhythms

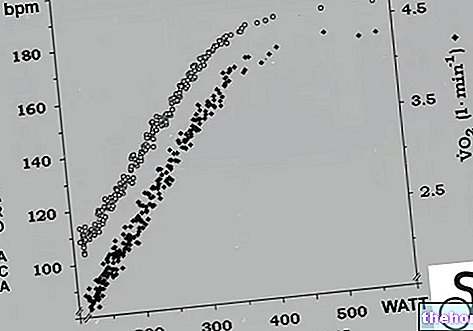
In addition to providing an estimate of athletic performance, the Conconi test allows you to obtain useful information for planning workouts. Thanks to simple mathematical steps that take into account the threshold heart rate it is in fact possible to establish the various training rhythms. Particularly:
- Slow pace: Training HR = heart rate at threshold x 0.8
- Average pace: Training HR between: threshold heart rate x 0.9 and threshold heart rate x 0.85
- Fast pace: Training HR between: threshold heart rate x 0.97 and threshold heart rate x 1.03
This information is indicative and must be adapted according to the discipline practiced and the physical condition of the athlete (for example, when the efforts of previous workouts have not been well recovered, the heart rate struggles to increase and the subject feels exhausted already at lower frequencies. to the pre-established limits).
However, these data provide a very useful indication since with a simple heart rate monitor the various training parameters can be monitored. All this makes the Conconi test one of the best tools that the athlete has at his disposal to obtain a precise functional evaluation and to set a correct training methodology that helps him to reach the set goals.
Conconi and Pal test (lactacid anaerobic power)
The "classic" Conconi test also provides us with some important information on the subject's alactacid anaerobic power1 such as:
- difference between maximum power and power at the anaerobic threshold (ΔP)
- time spent outside the threshold (Δt)
- difference between Fcmax and deflection HR (ΔFC).
The higher the ΔFC, ΔP and Δt are, the better the lactic acid anaerobic performance of the athlete will be.
However, Professor Conconi and his team have developed a variant of the traditional test to measure the athlete's lactacid anaerobic power (PAL) with greater precision.
after performing a classic Conconi Test, the anaerobic threshold exercise intensity is reached in slow progression (at least 5 min). At this point, a maximum variation of:
- 200m running (outdoor)
- 20-30 sec (indoor cycling)
The power delivered in this fraction depends on the anaerobic lactacid metabolism
Conconi test for PAL, some experimental data:
Marathon runners
5000-10000m
400-800m
Sprinters
V threshold
17.8 ± 1.6
17.8 ± 2.0
17.1 ± 2.3
13.7 ± 1.1
Vaer max
18.8 ± 1.6
19.0 ± 2.0
18.4 ± 2.5
15.1 ± 1.0
Vmax
23.1 ± 1.7
25.2 ± 2.0
28.1 ± 1.6
29.2 ± 0.6
Vmax-V threshold
5.3 ± 0.8
7.4 ± 0.8
11.0 ± 1.4
15.5 ± 1.3
Vanaerobics
4.1 ± 0.9
6.2 ± 0.7
9.7 ± 1.8
14.0 ± 1.3
Note how sprinters have a lower threshold speed than marathon runners (13.7 km / h vs 17.8 km / h) and a higher anaerobic speed (14.0 km / h vs 4.1km / h)
1: maximum amount of energy produced in the unit of time through the anaerobic lactacid mechanism
The anaerobic threshold
The VO2max METS IP maximum oxygen consumption
Lactic acid