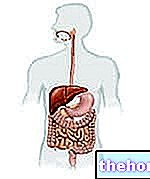
Under normal conditions, candida acts as a saprophyte and lives on the intestinal mucosa without causing problems. However, in certain situations, it can transform from saprophytic to pathogenic, replicating itself excessively and causing real infections (candidiasis).
In addition to intestinal candida, this yeast can also cause infections in the oral cavity (thrush), at the urogenital level (urogenital candidiasis), at the skin and nails (candidiasis of the skin and nails), at the level of the respiratory system ( respiratory candidiasis) and systemically.
Fortunately, intestinal candida does not seem to be a particularly widespread disease; however, given its possible complications, it should not be underestimated in any way.
, which affects the intestine causing very annoying and sometimes even serious symptoms.
Although in most cases the infection is caused by the species C. albicans, the possibility that intestinal candidiasis is also caused by other species belonging to the genus cannot be excluded Candida.
Since the aforementioned yeasts are part of the intestinal bacterial flora of many healthy individuals, intestinal candida can affect any person, both female and male. However, patients with immune system deficiency and patients undergoing certain drug therapies are more prone to the onset of the disorder.