Lactate threshold: definition and test to measure it
By lactacid threshold we mean the moment of physical performance, or the graphic point of a test, in which the anaerobic lactacid metabolism intervenes massively in support of the aerobic one; this condition determines a production of lactate higher than the muscular and systemic disposal capacity (> 3.9 mmol / l).
The lactate threshold is also better defined as the anaerobic threshold.
The lactate threshold correlates with the ability to sustain prolonged exercise; the effort exerted above or below the threshold includes an essential difference in metabolic commitment. Below the lactacid threshold, the muscles involved in the execution of the athletic gesture maintain a constant aerobic activation and a persistent lactacid MA BLANDO anaerobic commitment.
To clarify the trend of lactic acid during an incremental effort, it is essential to have one or two graphs that show the cardiac activity and the concentration of lactate in the blood. These values can be obtained by carrying out:
- Blood sampling during exercise
- Heart rate detection during activity (even better by performing a Conconi test)

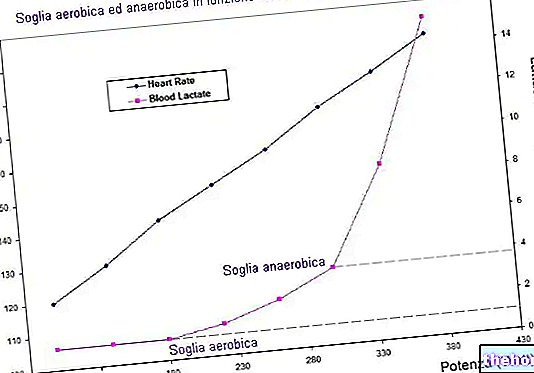
Image of a Conconi test in which it is possible to notice the classic deflection of the straight line that relates heart rate and exercise intensity. The lactacid threshold is identified at the point of deflection.
Unfortunately, in many subjects the trend of heart rate as a function of exercise intensity does not allow to identify a point of deflection; for this reason, many exercise physiologists prefer to measure the amount of lactate in the blood at predetermined time intervals. during an incremental test similar to that envisaged by the Conconi test (see image below).

Why is it important to determine the lactate threshold?
Detecting the lactacid threshold is of fundamental importance both in the athlete and in the subject who practices sports therapy (against hypertension, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, etc.).
- In the "endurance athlete (long-distance races) the lactate threshold represents the maximum limit beyond which it is NOT possible to increase the effort WITHOUT lactate accumulating and negatively affecting muscle contraction; running, swimming, pedaling, rowing, paddling in lactacid threshold allows you to fully train your aerobic metabolism by raising this capacity and bringing it as close as possible to the maximum consumption of oxygen or aerobic power (BP: parameter measurable by measuring VO2max - consumption of ml O2 / minute). This physiological modification determines a direct increase in performance to which, however, a second limiting factor is correlated, aerobic capacity; to be clear, the lactacid threshold effort involves the energetic combustion of a mixture mainly composed of muscle glycogen, which is contained in the myofibrils in a LIMITED quantity. The "AUTONOMY" performance in the lactacid threshold depends on the consistency of the glycogen stocks and the disposal potential of the lactic acid produced (almost 4 mmol / l), and is defined as AEROBIC CAPACITY. In addition, raising the lactic acid threshold also increases the aerobic threshold (SAE), which represents the ideal intensity level (about 2mmol / l of lactic acid) in competitions that reach two hours in duration (very long cross-country competitions) and which involves the combustion of a mixture containing a percentage fatty acids higher than the lactacid threshold; carrying out activities in SAE does not require a particular ability to dispose of lactate and the duration of the effort depends above all on the importance of muscle glycogen stores, hydration and hydrosaline homeostasis. This ability is better defined AEROBIC RESISTANCE. As for the importance of the lactic threshold in middle distance, it seems that it plays a less important role than the long and very long one; in fact, although it is established that the aerobic metabolism comes into play even in the last moments of a relatively short race such as the 400m floors, the development of a higher lactic acid threshold MUST leave room for the search for the maximum LACTIC POWER. In any case, the more the middle distance approaches the times and distances of the bottom, the greater the importance of the lactic threshold.
- In the subject who practices sports therapy or simply physical activity, determining the lactic acid threshold is very important but also VERY COMPLEX. While it is routine for an athlete to perform an incremental test, some complications may arise for the average person:
- NOT SUITABLE "for the practice of very high intensity exercises (cardiac, joint, respiratory compromises, etc.)
- Insufficient remission or motivation
- Insufficient training level
As easy as it may seem, carrying out an incremental test does not always lead to blatant results like those shown in the graphs of elite athletes. Often, the training level of a sedentary subject is so low as to involve the lactacid metabolism even at very low intensity, making it impossible to identify the lactic acid and SAE threshold points.
To make the idea better, it is possible to define that:
- if for an elite athlete, the lactacid threshold is around 85% of the VO2max (almost comparable to the maximum heart rate), for a sedentary the accumulation of lactic acid> 3.9 mmol / l can occur at a level of exercise equal to 50-55% of VO2max.
Carrying out an incremental test (such as the Conconi test) on a sedentary subject, in addition to being risky for excessive heart effort, in most cases would provide confusing and insignificant values. In a similar situation it is much more correct to proceed with the " TRADITIONALLY GRADUAL start-up to exercise, until reaching a good physical shape. This could be identified in ability to carry out prolonged physical activity for 45-60 "at at least 60-70% of maximum heart rate (HRmax); such a process could last up to a couple of years.
Contraindications in training below and / or above the lactate threshold
Aware of the fact that training must be established on the basis of specific objectives, we remind you that training in the lactacid threshold determines an enhancement of the aerobic metabolism with a relative increase in race speed thanks to some anatomical, functional and enzymatic modifications.
In this regard, we remind you that, if it is true that for an endurance athlete training too much below the lactacid threshold determines, not only a stall of the same, but even a lowering of the deflection value (VD - synonym of lactacid threshold), it is equally true that, as anticipated, for a middle-distance runner (especially a short one) to commit too much in raising the lactacid threshold could prove to be an unsuccessful choice.
We conclude by recalling that the training in lactacid threshold is established in relation to the heart beat and is easily manageable with intensities ranging between 3% below and 3% above the RV, applicable to repetition tables, rhythm variations or prolonged distances.