Watch the video
- Watch the video on youtube

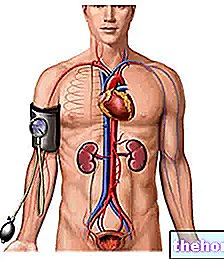
Also called hypotension, could be defined as a condition exactly opposite to hypertension or high blood pressure - a serious pathology characterized by resting blood pressure values above 140/90 mmHg and associated with a significant increase in cardiovascular risk.
Although less common than the more serious and worrying hypertension, low blood pressure is a fairly common disorder, which is frequently associated with generalized fatigue, dizziness, fainting, confusion and blurred vision. Low blood pressure can be caused by various factors, including: genetics, constant physical activity, certain diseases, certain medications, and pregnancy.
Generally, cases of hypotension sustained by pathological states, pharmacological assumptions or pregnancy deserve the attention of the doctor, as they are symptomatic and potentially dangerous.
Treatment of low blood pressure depends on the underlying causes; as a rule, symptom-free "hypotension does not require any specific therapy.
Note: genetic predisposition and constant physical activity are responsible for mild blood pressure drops, with no consequences and even benefits, in some cases.
that the blood exerts against the walls of the blood vessels, following the pumping action carried out by the heart.
Its value depends on various factors, including:
- The contraction force of the heart
- Systolic output, which is the amount of blood leaving the heart with each ventricular contraction
- The heart rate, i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute
- Peripheral resistances, that is the resistances opposed to the circulation of the blood by the state of constriction of the small arterial vessels (arterioles)
- The elasticity of the aorta and the great arteries (the so-called vascular compliance)
- The volume, i.e. the total volume of blood circulating in the body.
Measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and in a resting state, blood pressure is usually defined as systolic or "maximum" (it is the blood pressure when the heart contracts) and diastolic or "minimum" ( is the blood pressure when the heart is in the relaxation phase).
In a healthy individual, resting blood pressure can have systolic values between 90 and 129 mmHg and diastolic pressure values between 60 and 84 mmHg.
According to the medical-scientific community, optimal resting blood pressure is 120 mmHg (p. Systolic) out of 80 (p. Diastolic) mmHg - also written 120/80 mmHg. Recently it is being evaluated whether this value can be further reconsidered at 110/70 mmHg.