Definition
Frequent urination, identified by the medical term pollakiuria, consists of an increase in the daily episodes of expulsion of urine.
Generally, the volume emptied with each voiding act is rather small, while when frequent urination is accompanied by the elimination of large quantities of urine *, the term polyuria is preferred. In the latter case, the condition may be linked to the simple consumption of liquids in abundance, even when they are obtained from plant foods (which we remember to be indicatively composed of 90% of water).

* the bladder of an adult has an average capacity of about 250-500 ml.
Causes
There are numerous causes potentially capable of causing frequent urination, let's see them in detail together with the other symptoms that characterize them:
- FREQUENT URINATION ACCOMPANIED WITH INTENSE THIRST AND POLYURY: in both men and women it is one of the characteristic symptoms of diabetes mellitus and insipid diabetes.
- FREQUENT URINATION ASSOCIATED WITH BURNS AND / OR LEAKS FROM THE GLAND OR VAGINA: urinary tract infections or inflammation and / or sexually transmitted diseases. Often accompanied by stranguria, that is, painful urination, mild fever, cloudy urine, sometimes with traces of blood and malodorous.
- FREQUENT URINATION ASSOCIATED WITH MORNING NAUSEA AND INCREASED SENSITIVITY OF THE BREAST: in women, it could be a sign of pregnancy due to hormonal factors and the "increased uterine volume that" pushes "against the bladder.
- FREQUENT URINATION ASSOCIATED WITH SMALL LEAKS: in women, after menopause, hormonal changes involve some unfavorable changes in the bladder, urethra and all the structures involved in the elimination of urine. The result, in some cases, is a very unpleasant disorder, called urinary incontinence.
- PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY: excessive growth of the prostate, quite common after the age of 50-60, tends to narrow the prostatic urethra more and more, resulting in frequent urination accompanied by decreased intensity of the urinary jet, stranguria, post-voiding drip and sensation of not having completely emptied the bladder.
- PROSTATE CANCER: in the initial stages the symptoms are comparable to that of prostatic hypertrophy; for this reason, after the age of 50 it is good practice to undergo periodic screening, even in the absence of symptoms.
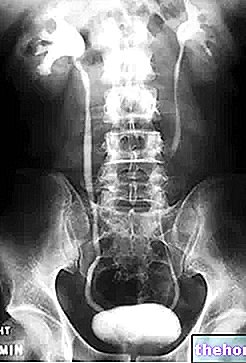
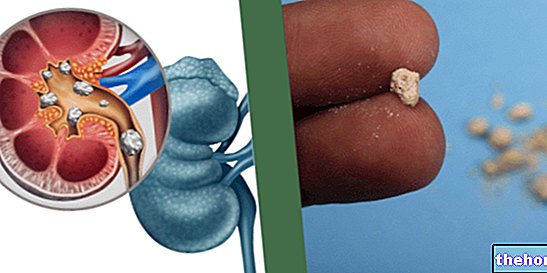
- CALCULATIONS OF THE URINARY TRACT: they can be accompanied by hematuria and pain and burning during urination, but are not always associated with colic pain in the side.
- heart failure CONGESTIA: nocturnal reabsorption of edema can cause nocturia (urinary emission, bothersome and frequent, especially during the night).
- Stroke or OTHER NEUROLOGICAL DISEASES: Damage to the nerves that control the bladder can cause frequent urination. For stroke symptoms click here.
- FREQUENT URINATION AND HYPERTENSION: it could be attributable to certain drugs prescribed for the purpose of controlling blood pressure;
- EMOTIONAL FACTORS (states of psychic excitement) AND NERVOUS DISEASES (tabe, stringomelia, etc.) can cause frequent urination.
- OTHER CAUSES OF FREQUENT URINATION:
- bladder diverticula;
- bladder neoplasms (frequent symptoms are the presence of blood in the urine and the formation of clots, the burning sensation in the bladder when the abdomen is compressed, difficulty and pain in urinating, the greater ease of contracting infections);
- neoplasms from neighboring organs (uterus, rectum, sigmoid, prostate) that infiltrate the detrusor wall (the bladder muscle that allows urine to contract and empty).





.jpg)


















